What’s encryption?
Encryption is the strategy by which data is transformed into secret code that hides the data’s true that means. The science of encrypting and decrypting data known as cryptography.
Encryption has lengthy been used to guard delicate data. Traditionally, it was utilized by militaries and governments. In trendy instances, encryption is used to shield information each at relaxation and in movement. At-rest information is the kind saved on computer systems and storage units. In-motion information refers to information in transit between units and over networks.
Encryption is utilized in a wide range of circumstances. Each time somebody carries out a transaction on an ATM or buys one thing on-line with a smartphone, encryption protects the transmitted information. Companies additionally depend on encryption to guard delicate data from publicity within the occasion of a information breach or unauthorized people buying the info. Such publicity can have in depth monetary implications and severely injury a company’s status.
Why is encryption vital?
Encryption performs an important position in securing several types of IT belongings and personally identifiable data (PII). To this finish, encryption serves 4 important capabilities:
- Confidentiality. Encodes the info to stop it from being understood whether it is intercepted.
- Authentication. Verifies the origin of the info that has been encrypted.
- Integrity. Validates that the info has not been altered because it was encrypted.
- Nonrepudiation. Prevents senders from denying they despatched the encrypted information.
What are the advantages of encryption?
The first goal of encryption is to guard the confidentiality of digital information saved on pc methods or transmitted over the web or different pc networks. It’s used to safeguard a variety of knowledge, from PII to delicate company belongings to authorities and navy secrets and techniques. By encrypting their information, organizations cut back the chance of exposing delicate data, serving to to keep away from expensive penalties, prolonged lawsuits, decreased income and tarnished reputations.
Many organizations use encryption not solely to guard their information, but in addition to fulfill compliance rules that require delicate information to be encrypted. Encryption ensures that unauthorized third events or menace actors can’t perceive the info within the occasion they achieve entry to it. For instance, the Cost Card Trade Information Safety Customary requires retailers to encrypt buyer fee card information each at relaxation and when transmitted throughout public networks.
What are the disadvantages of encryption?
Though encryption retains unauthorized people from having the ability to perceive delicate information, encryption can even forestall the info’s house owners from having the ability to entry their very own data. If the encryption keys get misplaced or destroyed, the info house owners is perhaps completely locked out of that information. Cybercriminals may also go after the encryption keys, moderately than the info itself. As soon as they’ve acquired the keys, they’ll simply decipher the info.
Key administration is among the greatest challenges of constructing an enterprise encryption technique as a result of the keys to decrypt the ciphertext need to dwell someplace within the setting, and attackers usually have a good suggestion of the place to look.
There are many finest practices for encryption key administration, however they add additional layers of complexity to the backup and restoration processes. If a serious catastrophe ought to strike, retrieving the keys and including them to a brand new backup server may improve the time that it takes to get began with the restoration operation.
Having a key administration system in place is not sufficient. Directors should additionally give you a complete plan for safeguarding the important thing administration system. Usually, this implies backing it up individually from every part else and storing these backups in a means that makes it simple to retrieve the keys within the occasion of a large-scale catastrophe.
One other problem with encryption is the truth that cybercriminals can even use it for their very own functions, which has led to an rising variety of ransomware assaults. On this situation, the criminals achieve entry to the delicate information, encrypt it with their very own algorithms after which maintain the info hostage till the sufferer group comes up with the ransom, which could be fairly steep.
How does encryption work?
An encryption system is made up of three main parts: information, encryption engine and key supervisor. In software architectures, the three parts normally run or are hosted in separate locations to scale back the chance {that a} single element is compromised and results in your complete system being compromised. On a self-contained machine, equivalent to a laptop computer, all three parts run on the identical system.
When an encryption system is in place, the info is all the time in considered one of two states: unencrypted or encrypted. Unencrypted information is also called plaintext, and encrypted information known as ciphertext. Encryption algorithms, or ciphers, are used to encode and decode the info. An encryption algorithm is a mathematical methodology for encoding information in response to a selected algorithm and logic.
Through the encryption course of, the encryption engine makes use of an encryption algorithm to encode the info. A lot of algorithms can be found, differing in complexity and ranges of safety. The engine additionally makes use of an encryption key along side the algorithm to make sure that the ciphertext that’s output is exclusive. An encryption secret’s a randomly generated string of bits which can be particular to the algorithm.
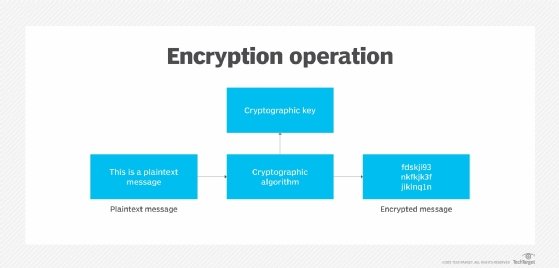
After the info is transformed from plaintext to ciphertext, it may be decoded solely via the usage of the right key. This key is perhaps the identical one used for encoding the info or a special one, relying on the kind of algorithm — symmetric or uneven. If it is a totally different key, it is usually referred to as a decryption key.
When encrypted information is intercepted by an unauthorized entity, the intruder has to guess which cipher was used to encrypt the info and what secret’s required to decrypt the info. The time and problem of guessing this data is what makes encryption such a worthwhile safety instrument. The extra in depth the encryption algorithm and key, the harder it turns into to decrypt the info.
What are the 2 kinds of encryption?
When establishing a system for encrypting information, a safety workforce should decide which encryption algorithm to make use of to encode the info. Earlier than doing that, nonetheless, the workforce ought to first resolve on the kind of algorithm. The 2 commonest varieties are symmetric and uneven:
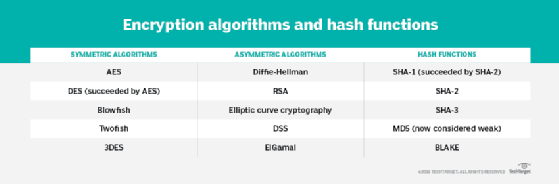
- Symmetric ciphers. Additionally known as secret key cyphers, these algorithms use a single key for each encrypting and decrypting information. The secret’s typically known as a shared secret as a result of the sender or computing system doing the encryption should share the key key with all entities approved to decrypt the message. Symmetric key encryption is normally a lot sooner than uneven encryption. Probably the most broadly used symmetric key cipher is the Superior Encryption Customary (AES), which was designed to guard government-classified data.
- Uneven ciphers. Also called public key encryption, these kinds of algorithms use two totally different — however logically linked — keys for encrypting and decrypting information. Uneven cryptography usually makes use of prime numbers to create keys since it’s computationally tough to issue giant prime numbers and reverse-engineer the encryption. The Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) encryption algorithm is at the moment essentially the most broadly used public key algorithm. With RSA, the general public or the personal key can be utilized to encrypt a message; whichever key will not be used for encryption turns into the decryption key.
Right this moment, many cryptographic processes use a symmetric algorithm to encrypt information and an uneven algorithm to securely change the key key.
Encryption key administration and wrapping
Encryption is an efficient approach to safe information, however the cryptographic keys have to be fastidiously managed to make sure information stays protected but accessible when wanted. Entry to encryption keys needs to be monitored and restricted to these people who completely want to make use of them.
Organizations ought to have methods in place for managing encryption keys all through their lifecycle and defending them from theft, loss or misuse. This course of ought to start with an audit that determines how the group at the moment configures, controls, screens and manages entry to its keys.
Key administration software program can assist centralize key administration, in addition to shield keys from unauthorized entry, substitution or modification.
Key wrapping is a sort of safety function present in some key administration software program suites that basically encrypts a company’s encryption keys, both individually or in bulk. The method of decrypting keys which have been wrapped known as unwrapping. Key wrapping and unwrapping actions are normally carried out with symmetric encryption.
Encryption algorithms
A wide range of symmetric and uneven ciphers can be found for encrypting information. The algorithms range of their complexity and the precise strategy they take to defending information. The next ciphers are a number of the extra frequent algorithms which have been used over time:
- AES. A symmetric block cipher chosen by the U.S. authorities to guard categorised data. It’s carried out in software program and {hardware} all through the world to encrypt delicate information. The Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Know-how (NIST) began growth of AES in 1997 when it introduced the necessity for a successor algorithm for the Information Encryption Customary (DES), which was beginning to grow to be weak to brute-force assaults.
- DES. An outdated symmetric key methodology of knowledge encryption. DES works through the use of the identical key to encrypt and decrypt a message so each the sender and the receiver should know and use the identical personal key. DES has been outdated by the safer AES algorithm.
- Diffie-Hellman key change. A symmetric algorithm that makes use of numbers raised to particular powers to supply decryption keys on the premise of parts which can be by no means immediately transmitted, making the duty of a would-be code breaker mathematically overwhelming. The Diffie-Hellman key change can be referred to as the exponential key change.
- Elliptical curve cryptography (ECC). An uneven cipher that makes use of algebraic capabilities to generate safety between key pairs. The ensuing cryptographic algorithms could be sooner and extra environment friendly and might produce comparable ranges of safety with shorter cryptographic keys. This makes ECC algorithms a sensible choice for web of issues (IoT) units and different merchandise with restricted computing assets.
- Quantum key distribution (QKD). Accessible as each a symmetric cipher and semisymmetric cypher. The QKD algorithm is a technique for encrypting information with the help of quantum mechanics. The encryption keys are generated through the use of a pair of entangled photons which can be then transmitted individually from the info. Quantum entanglement permits the sender and receiver to know whether or not the encryption key has been intercepted or modified earlier than the transmission even arrives. It is because, within the quantum realm, the act of observing the transmitted data modifications it. As soon as it has been decided that the encryption is safe and has not been intercepted, permission is given to transmit the encrypted message over a public web channel.
- RSA. Uneven cypher that was first publicly described in 1977 by Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir and Leonard Adleman of the Massachusetts Institute of Know-how. British mathematician Clifford Cocks created a public key algorithm in 1973, however the U.Okay.’s Authorities Communications Headquarters stored it categorised till 1997. Many protocols, equivalent to Safe Shell (SSH), OpenPGP, Safe/Multipurpose Web Mail Extensions, and Safe Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Safety (TLS) — depend on RSA for encryption and digital signature capabilities.
- Twofish. A symmetric key block cipher with a block dimension of 128 bits and variable-length key of dimension 128, 192 or 256 bits. Optimized for 32-bit central processing models, the algorithm is open supply and accessible without spending a dime. Twofish stands out from different encryption algorithms by its use of the S-box, a pre-computed, key-dependent substitution field. The S-box obscures the connection between the important thing and the ciphertext, though it nonetheless relies on the cipher key to decrypt the info.
The safety offered by encryption is immediately tied to the kind of cipher used to encrypt the info, in addition to to the power of the decryption keys used to transform the ciphertext to plaintext. In the US, cryptographic algorithms accredited beneath NIST’s Federal Info Processing Requirements needs to be used each time cryptographic companies are required.
Implementing encryption
Organizations take a wide range of approaches to encrypting information. The strategies they use rely upon their environments, the kind of information, the degrees of safety they’re attempting to realize and different variables. Listed here are a number of the methods that they use when implementing encryptions:
- Deliver your individual encryption (BYOE) is a cloud computing safety mannequin that permits cloud service prospects to make use of their very own encryption software program and handle their very own encryption keys. BYOE can be known as convey your individual key. BYOE works by enabling prospects to deploy a virtualized occasion of their very own encryption software program alongside the enterprise software they’re internet hosting within the cloud.
- Cloud storage encryption is a service supplied by cloud storage suppliers whereby information or textual content is reworked utilizing encryption algorithms and is then positioned in cloud storage. Cloud encryption is sort of equivalent to in-house encryption with one vital distinction: The cloud buyer should take time to study in regards to the supplier’s insurance policies and procedures for encryption and encryption key administration to match encryption with the extent of sensitivity of the info being saved.
- Column-level encryption is an strategy to database encryption during which the data in each cell in a selected column has the identical password for entry, studying and writing functions.
- Deniable encryption is a sort of cryptography that permits encrypted information to be decrypted in two or extra methods, relying on which decryption secret’s used. Deniable encryption is typically used for misinformation functions when the sender anticipates, and even encourages, interception of a communication.
- Encryption as a service is a subscription mannequin that permits cloud service prospects to make the most of the safety that encryption provides. This strategy supplies prospects who lack the assets to handle encryption themselves with a approach to handle regulatory compliance issues and shield information in a multi-tenant setting. Cloud encryption choices usually embody full-disk encryption (FDE), database encryption or file encryption.
- Finish-to-end encryption (E2EE) ensures information being despatched between two events can’t be considered by an attacker that intercepts the communication channel. Use of an encrypted communication circuit, as offered by TLS between net consumer and net server software program, will not be all the time sufficient to make sure E2EE; usually, the content material being transmitted is encrypted by consumer software program earlier than being handed to an online consumer and decrypted solely by the recipient. Messaging apps that present E2EE embody Meta’s WhatsApp and Sign. Fb Messenger customers may get E2EE messaging with the Secret Conversations possibility.
- FDE is encryption on the {hardware} stage. FDE works by mechanically encrypting information on a storage drive right into a kind that can’t be understood by anybody who would not have the important thing to undo the conversion. With out the right authentication key, even when the drive is eliminated and positioned in one other machine, the info stays inaccessible. FDE could be put in on a computing machine on the time of producing, or it may be added in a while by putting in particular software program.
- Area-level encryption is the flexibility to encrypt information in particular fields on a webpage. Examples of fields that may be encrypted are bank card numbers, Social Safety numbers, checking account numbers, health-related data, wages and monetary information. As soon as a discipline is chosen, all the info in that discipline is mechanically encrypted.
- Homomorphic encryption is the conversion of knowledge into ciphertext that may be analyzed and labored with as if it have been nonetheless in its authentic kind. The homomorphic encryption strategy permits advanced mathematical operations to be carried out on encrypted information with out compromising the encryption.
- HTTPS permits web site encryption by operating HTTP over the TLS protocol. To allow an online server to encrypt all content material that it sends, a public key certificates have to be put in.
- Hyperlink-level encryption encrypts information when it leaves the host; decrypts it on the subsequent hyperlink, which can be a bunch or a relay level; after which reencrypts it earlier than sending it to the following hyperlink. Every hyperlink could use a special key or perhaps a totally different algorithm for information encryption, and the method is repeated till the info reaches the recipient.
- Community-level encryption applies cryptoservices on the community transport layer — above the info hyperlink stage however under the appliance stage. Community encryption is carried out via IP Safety, a set of open Web Engineering Job Pressure requirements that, when utilized in conjunction, create a framework for personal communication over IP networks.
- Quantum cryptography relies on the quantum mechanical properties of particles to guard information. Particularly, the Heisenberg uncertainty precept posits that the 2 figuring out properties of a particle — its location and its momentum — can’t be measured with out altering the values of these properties. Consequently, quantum-encoded information can’t be copied as a result of any try to entry the encoded information modifications the info. Likewise, any try to repeat or entry the info causes a change within the information, thus notifying the approved events to the encryption that an assault has occurred.
Cryptographic hash capabilities
Hash capabilities present one other kind of encryption. Hashing is the transformation of a string of characters right into a fixed-length worth or key that represents the unique string. When information is protected by a cryptographic hash operate, even the slightest change to the message could be detected as a result of it makes a giant change to the ensuing hash.
Hash capabilities are thought of to be a sort of one-way encryption as a result of keys aren’t shared and the data required to reverse the encryption doesn’t exist within the output. To be efficient, a hash operate ought to have the next traits:
- Computationally environment friendly. Simple to calculate.
- Deterministic. Reliably produces the identical consequence.
- Preimage-resistant. Output that doesn’t reveal something about enter.
- Collision-resistant. Extraordinarily unlikely that two situations produce the identical consequence.
Standard hashing algorithms embody Safe Hash Algorithms and Message Digest Algorithm 5.
How one can break encryption
For any cipher, essentially the most fundamental methodology of assault is brute pressure — attempting every doable decryption key till the best one is discovered. The size of the important thing determines the variety of doable keys, therefore the feasibility of one of these assault. Encryption power is immediately tied to key dimension, however as the important thing dimension will increase, so too do the assets required to carry out the computation.
Various strategies of breaking encryptions embody side-channel assaults, which do not assault the precise cipher. As a substitute, they measure or exploit the oblique results of its implementation, equivalent to an error in execution or system design.
Attackers may try to interrupt a focused cipher via cryptanalysis, the method of searching for a weak spot within the cipher that may be exploited with a complexity lower than a brute-force assault. The problem of efficiently attacking a cipher is less complicated if the cipher itself is already flawed.
For instance, there have been suspicions that interference from the Nationwide Safety Company (NSA) weakened the DES algorithm. Following revelations from former NSA analyst and contractor Edward Snowden, many consider the NSA has tried to subvert different cryptography requirements and weaken encryption merchandise.
Encryption backdoors
An encryption backdoor is a approach to get round a system’s authentication or encryption. Governments and legislation enforcement officers world wide, notably within the 5 Eyes (FVEY) intelligence alliance, proceed to push for encryption backdoors, which they declare are essential within the pursuits of nationwide security and safety as criminals and terrorists more and more talk by way of encrypted on-line companies.
In response to the FVEY governments, the widening hole between the flexibility of legislation enforcement to lawfully entry information and their capability to accumulate and use the content material of that information is “a pressing international concern” that requires “urgent, sustained attention and informed discussion.”
Opponents of encryption backdoors have mentioned repeatedly that government-mandated weaknesses in encryption methods put the privateness and safety of everybody in danger as a result of the identical backdoors could be exploited by hackers.
Legislation enforcement businesses, such because the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), have criticized expertise firms that provide E2EE, arguing that such encryption prevents legislation enforcement from accessing information and communications even with a warrant. The FBI has referred to this situation as “going dark,” whereas the U.S. Division of Justice has proclaimed the necessity for “responsible encryption” that may be unlocked by expertise firms beneath a court docket order.
Australia, one of many FVEY members, handed laws that enables Australian Border Pressure (ABF) officers to look and seize digital units with none kind of warrant. Though vacationers coming into the nation aren’t required to present their passcodes or provide help to entry their units, the ABF has the best to confiscate these units.
Threats to IoT, cellular units
By 2019, cybersecurity threats more and more included these on IoT and cellular computing units. In response to Kaspersky’s Securelist, 97.91% of password brute-force makes an attempt focused Telnet within the first half of 2023. Telnet is an unencrypted textual content protocol broadly used on IoT units. Securelist additionally reported that Kaspersky merchandise blocked 438,962 malicious set up packages on cellular units. Of those packages, 21,674 have been associated to cellular banking Trojans, and 1,855 have been cellular ransomware Trojans.
In the meantime, NIST has inspired the creation of cryptographic algorithms appropriate to be used in constrained environments, together with cellular and IoT units. In a primary spherical of judging in April 2019, NIST selected 56 light-weight cryptographic algorithms candidates to be thought of for standardization. Since then, NIST has performed a second spherical after which a remaining spherical. From the ten finalists, the NIST Light-weight Cryptography Staff chosen the Ascon household for standardizing light-weight cryptography functions.
Historical past of encryption
The phrase encryption comes from the Greek phrase kryptos, that means hidden or secret. Using encryption is almost as outdated because the artwork of communication itself. As early as 1900 B.C., an Egyptian scribe used nonstandard hieroglyphs to cover the that means of an inscription.
In a time when most individuals could not learn, merely writing a message was usually sufficient, however encryption schemes quickly developed to transform messages into unreadable teams of figures to guard the message’s secrecy whereas it was carried from one place to a different. The contents of a message have been reordered (transposition) or changed (substitution) with different characters, symbols, numbers or photos to be able to conceal its that means.
In 700 B.C., Spartans wrote delicate messages on strips of leather-based wrapped round sticks. When the tape was unwound, the characters turned meaningless, however with a stick of precisely the identical diameter, the recipient may recreate (decipher) the message.
Later, Romans used what’s generally known as the Caesar shift cipher, a monoalphabetic cipher during which every letter is shifted by an agreed quantity. So, for instance, if the agreed quantity is three, then the message “Be at the gates at six” turns into “eh dw wkh jdwhv dw vla.” At first look, this may increasingly look tough to decipher, however juxtaposing the beginning of the alphabet till the letters make sense would not take lengthy. Additionally, the vowels and different generally used letters, like t and s, could be rapidly deduced utilizing frequency evaluation, and that data, in flip, can be utilized to decipher the remainder of the message.
The Center Ages noticed the emergence of polyalphabetic substitution, which makes use of a number of substitution alphabets to restrict the usage of frequency evaluation to crack a cipher. This methodology of encrypting messages remained widespread, regardless of many implementations that didn’t adequately conceal when the substitution modified — also called key development. Presumably essentially the most well-known implementation of a polyalphabetic substitution cipher is the Enigma electromechanical rotor cipher machine utilized by Germans throughout World Conflict II.
It was not till the mid-Seventies that encryption took a serious leap ahead. Till this level, all encryption schemes used the identical secret for encrypting and decrypting a message: a symmetric key.
Encryption was virtually solely used solely by governments and huge enterprises till the late Seventies when the Diffie-Hellman key change and RSA algorithms have been first revealed and the primary PCs have been launched.
In 1976, Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman’s paper, “New Instructions in Cryptography,” solved one of many elementary issues of cryptography: tips on how to securely distribute the encryption key to those that want it. This breakthrough was adopted shortly afterward by RSA, an implementation of public key cryptography utilizing uneven algorithms, which ushered in a brand new period of encryption. By the mid-Nineties, each public key and personal key encryption have been being routinely deployed in net browsers and servers to guard delicate information.
See tips on how to use a public key and personal key in digital signatures and tips on how to use centralized encryption strategies in large-scale IT environments. Discover our complete information to information safety. Find out how encryption is carried out in {hardware} via the usage of {hardware} safety modules.