Safety researchers found two beforehand unseen backdoors dubbed LunarWeb and LunarMail that had been used to compromise a European authorities’s diplomatic establishments overseas.
The items of malware have been used to breach the Ministry of Overseas Affairs of a European nation with diplomatic missions within the Center East and have been lively since not less than 2020.
Researchers at cybersecurity firm ESET imagine that the backdoors could also be linked to the Russian state-sponsored hacker group Turla, though attribution has medium confidence at this level.
Lunar assault chain
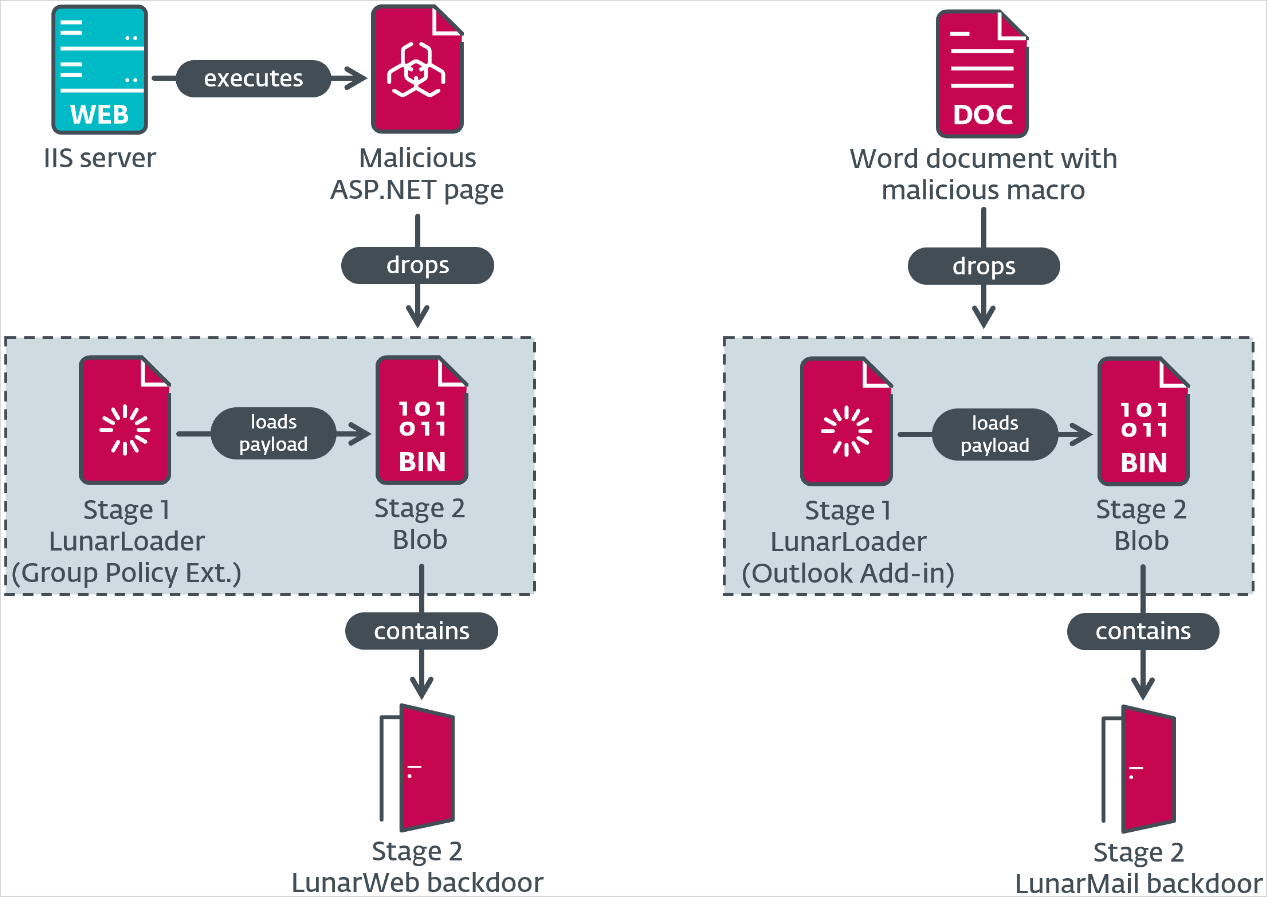
In its report, ESET says that the assault begins with spear-phishing emails that carry Phrase recordsdata with malicious macro code to put in the LunarMail backdoor onto the goal system.
The VBA macro additionally establishes persistence on the contaminated host by creating an Outlook add-in, making certain it’s activated at any time when the e-mail shopper is launched.
Supply: ESET
ESET analysts have additionally seen proof pointing to the potential abuse of a misconfigured open-source community monitoring software Zabbix to drop the LunarWeb payload.
Particularly, a element mimicking a Zabbix agent log is deployed on a server, and when accessed with a particular password by way of an HTTP request, it decrypts and executes the loader and backdoor parts.
LunarWeb persists on the breached system utilizing a number of methods that embody creating Group Coverage extensions, changing system DLLs, and deploying as a part of official software program.
Each payloads are decrypted by a malware loader that the researchers known as ‘LunarLoader’ from an encrypted blob utilizing the RC4 and AES-256 ciphers. The loader makes use of the DNS area title for decryption and ensures that it runs solely throughout the focused setting.
As soon as the Lunar backdoors are working on the host, the attackers might ship instructions immediately by way of the command and management (C2) server and use stolen credentials and compromised area controllers for lateral motion on the community.
Supply: ESET
LunarWeb and LunarMail
The 2 Lunar backdoors are designed for extended and covert surveillance, knowledge theft, and sustaining management over compromised programs, resembling high-value targets like authorities and diplomatic establishments.
LunarWeb is deployed on servers, mimicking official site visitors by spoofing HTTP headers from Home windows and ESET product updates.
It receives instructions for execution that are hidden in .JPG and .GIF picture recordsdata utilizing the steganopraphy method.
The instructions LunarWeb helps embody executing shell and PowerShell instructions, gathering system info, working Lua code, zipping recordsdata, and exfiltrating knowledge in AES-256 encrypted kind.
ESET researchers say that they noticed an assault the place the risk actor dropped LunarWeb at three diplomatic establishments of the focused European Ministry of Overseas Affairs simply minutes aside.
The attacker might have been in a position to transfer this shortly as a result of that they had beforehand gained entry to the area controller of the ministry and leveraged it to maneuver to machines from different establishments on the community.
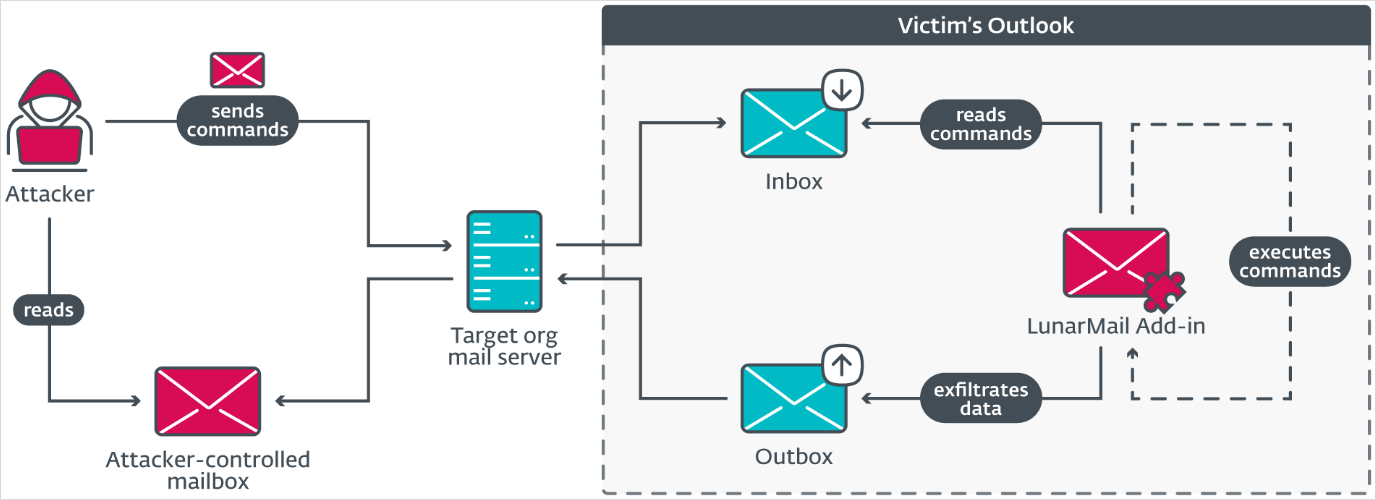
LunarMail is deployed on person workstations with Microsoft Outlook put in.
It makes use of an email-based communication system (Outlook MAPI) for knowledge change with particular Outlook profiles linked to the C2 to evade detection in environments the place HTTPS site visitors could also be extra intently monitored.
Instructions despatched from the C2 are embedded in e-mail attachments, sometimes hidden in .PNG photos, which the backdoor parses to extract the hidden directions.
LunarMail can create processes, take screenshots, write recordsdata, and run Lua code. Lua script execution permits it to not directly run shell and PowerShell instructions if wanted.
Supply: ESET
Primarily based on similarities in noticed ways, methods, and procedures (TTPs) between the Lunar toolset and and previous actions, ESET attributes the backdoors to the Russian hacking group Turla with medium confidence.
Nonetheless, the researchers observed “varying degrees of sophistication in the compromises,” which means that the instruments had been developed and operated by a number of people.
Regardless of the intrusions being of a newer date, ESET discovered artifacts indicating that the backdoors have been utilized in operations and evaded detection since not less than 2020.
The cybersecurity firm is offering an inventory of indicators of compromise (IoCs) for recordsdata, file paths, community, and registry keys noticed in compromised environments. An entire listing is accessible right here.
