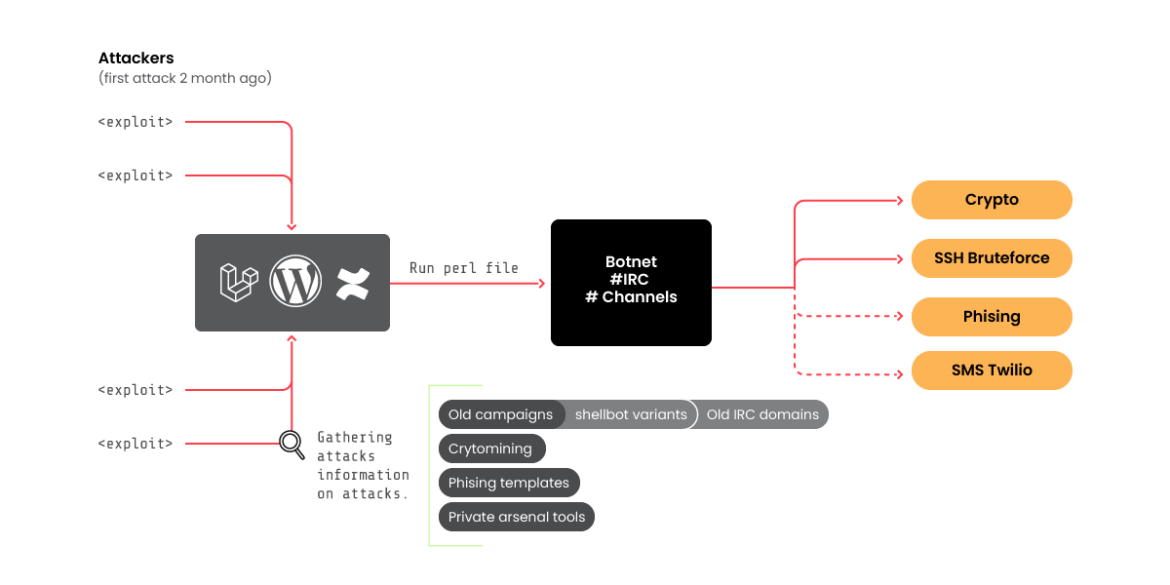
The Sysdig Menace Analysis Crew (Sysdig TRT) not too long ago found a long-running botnet operated by a Romanian menace actor group, which we’re calling RUBYCARP. Proof means that this menace actor has been lively for at the very least 10 years. Its major methodology of operation leverages a botnet deployed utilizing quite a lot of public exploits and brute power assaults. This group communicates by way of private and non-private IRC networks, develops cyber weapons and focusing on information, and makes use of its botnet for monetary achieve by way of cryptomining and phishing. This report explores how RUBYCARP operates and its motivations.
RUBYCARP, like many menace actors, is focused on payloads that allow monetary achieve. This consists of cryptomining, DDoS, and Phishing. We have now seen it deploy various completely different instruments to monetize its compromised property. For instance, via its Phishing operations, RUBYCARP has been seen focusing on bank cards. As we now have seen with different menace actors, it has a diversified set of illicit revenue streams.
Attribution
RUBYCARP, the identify we now have given this group, is a financially-motivated menace actor group that’s more than likely Romanian. RUBYCARP could also be associated to the Outlaw superior persistent menace (APT), because it does share lots of the similar techniques, methods, and procedures (TTPs). Nevertheless, since these shared TTPs are frequent throughout many botnet operators, we can not definitively make this conclusion. RUBYCARP leverages Shellbot usually throughout its operations, which might additionally trigger attribution confusion since this software is a standard alternative amongst menace actors.
Within the murky world of cybercriminal menace intelligence, there’s usually a variety of crossover in each instruments and focusing on. Within the current advisory from CISA, the Androxgh0st menace actor’s alternative to take advantage of Laravel is mentioned. That is one other instance of cybercriminal overlap, with RUBYCARP notably focusing on the identical framework vulnerabilities. Many of those menace actors are preventing it out over the identical goal house, making it tough to attribute assaults.
What’s RUBYCARP?
For months, Sysdig TRT’s has been monitoring RUBYCARP via the focusing on and exploitation of Laravel functions susceptible to CVE-2021-3129. This led to proof of SSH Brute forcing as one other approach the group gained entry to its targets. Not too long ago, we additionally found proof of the menace actor focusing on WordPress websites utilizing dumps of usernames and passwords. RUBYCARP continues so as to add new exploitation methods to its arsenal with a view to construct its botnets.
As soon as entry is obtained, a backdoor is put in primarily based on the favored Perl Shellbot. The sufferer’s server is then related to an IRC server performing as command and management, and joins the bigger botnet. Throughout RUBYCARP’s reconnaissance part, we discovered 39 variants of the Perl file (shellbot), however solely eight have been in VirusTotal. Because of this just a few campaigns have been beforehand detected. The modifications of the information are:
- A nickname is used to hitch the IRC server
- The channel the place the sufferer joins is usually marked by both a platform identify (e.g., apache) or a member identify (e.g., juice)
- Typically auth is added
- The IRC server
Campaigns
After connecting to the IRC server, we found the precise variety of compromised hosts at over 600. Then again, by not correctly configuring the connection to the server, RUBYCARP has a detection system to kick out surprising/undesirable customers of the server and ban their IP to forestall new connections. It tries to maintain the community hidden as a lot as attainable.
The final lively area of this botnet is chat[.]juicessh[.]professional, and we have been capable of get hold of the knowledge under:
- It was created on Monday, Could 1, 2023 at 04:30:05 UTC
- 624 nicks [2 ops, 0 halfops, 0 voices, 622 normal]
- VICTIMS by channel in the mean time of writing:
- #juscan1, 176 victims
- #cfs, 11 victims
- #php3, 34 victims
- #sb, 33 victims
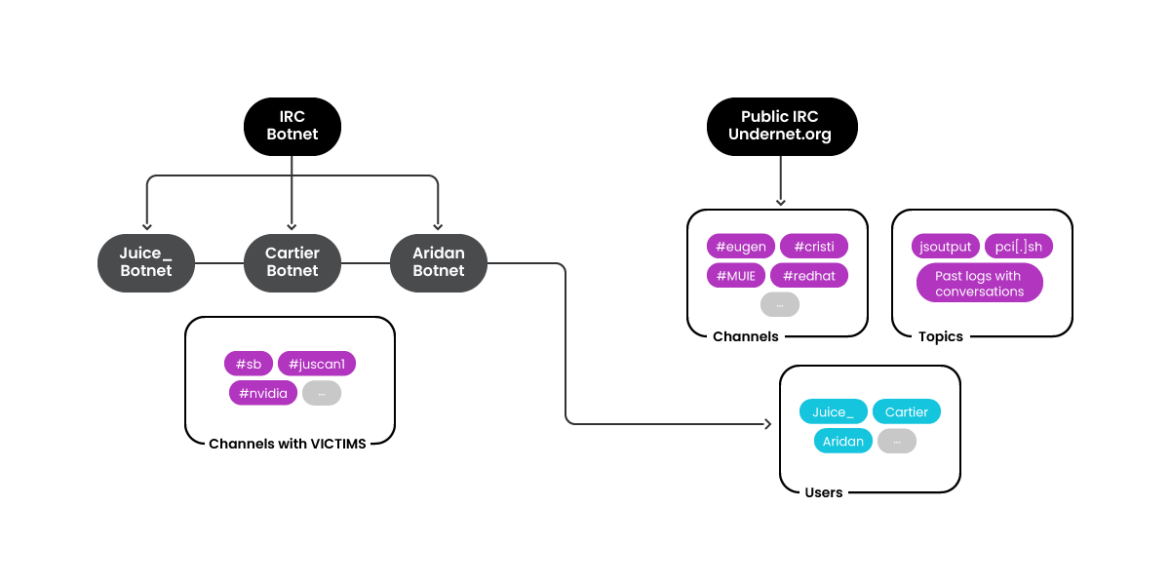
Primarily based on naming schemes and connection configuration, the obvious group could be composed of customers like “juice,” “cartier,” or “aridan,” however there could possibly be extra, the place every one could be devoted to a function, cryptomining, personalized instruments, and many others. Throughout our investigation, we decided that its IRC server of alternative for private and non-private internet hosting is undernet.org. The lively non-public IRC networks are chat[.]juicessh[.]professional and sshd[.]run.
The infrastructure we found for RUBYCARP is comprised of a big variety of malicious IPs and domains, rotated often and infrequently changed and emptied of its malicious content material as quickly as any potential analysis exercise was detected. A full infrastructure listing is out there right here.
How does RUBYCARP Function?
RUBYCARP makes use of a number of IRC networks for basic communications, but additionally to handle its botnets and coordinate cryptomining campaigns. An overview of its group when managing botnets could be as follows:
In one of many logs we acquired, RUBYCARP tends to share the instruments it’s utilizing, which embody lots of the instruments we now have been capable of gather via our honeypot, comparable to:
- Banner
- Masscan
- X (kernel module)
- brute

Communications
Personal IRC
For managing its botnet, RUBYCARP makes use of a set of personal IRC servers and appears to rotate them often. “Juice.baselinux.net,” “chat.juicessh.pro,” and others are the newest lively ones on the time of writing. Every RUBYCARP marketing campaign will get its personal IRC channel and the bots inside every channel are then named in response to a predefined scheme. We have been capable of map the noticed servers and their respective channels, though, sadly, not all of them are nonetheless lively or accessible.
Public IRC
Members
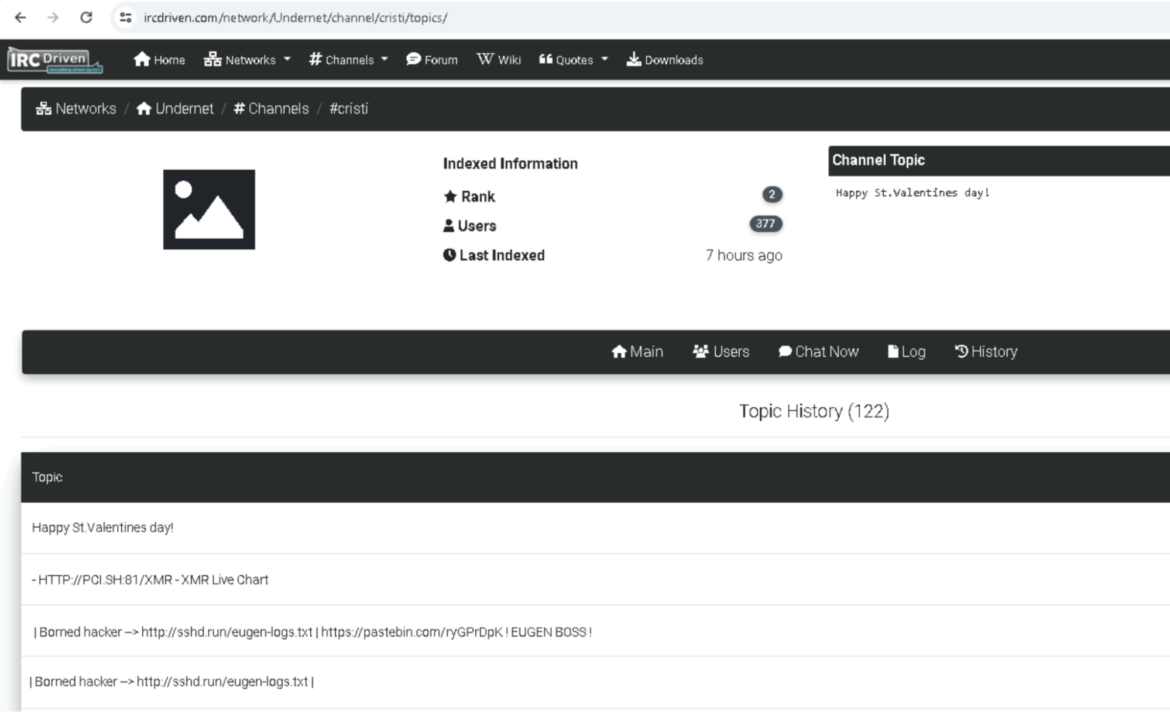
Members of RUBYCARP primarily talk via an Undernet IRC channel known as #Cristi. Public logs for the channel present a consumer (and admin) “_juice” interacting with different members of the group in Romanian; we are able to additionally see that the channel subject is expounded to earlier or present campaigns, out there under.
Whereas we monitored the chats, each actors, juice and Eugen, who personal the channel #Eugen from which we collected a lot of the mining setup proof, have been current in channel #Cristi.
Throughout the consumer base of the channel #Cristi, which on the time of writing contained 280 customers, we recognized a number of acquainted names of actors who attacked our honeypot. For instance, “Catalin” attacked our honeypot on Jan. 8, 2024 from IP 80[.]83[.]124[.]150. The next picture is of the web site hosted there on the time of the assault. Discover the attribution to “Catalin” on the backside.
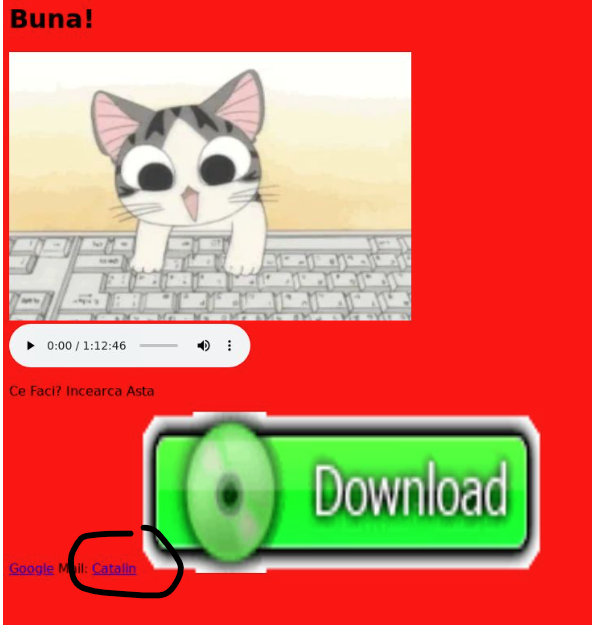
One other one is “aridan,” who we noticed in earlier assaults with the area “aridan.men.”
Probably the most recurring IRC admins we discovered throughout the Shellbot configuration information are “juice,” “MUIE,” and “Smecher,” who additionally every have their very own respective channels for malicious operations. “juice” has been probably the most prolific in establishing new malicious Shellbot configurations, new servers, and new sufferer channels. Under is the WHOIS screenshot for the #Cristi channel members we’ve recognized:
juice_, admin
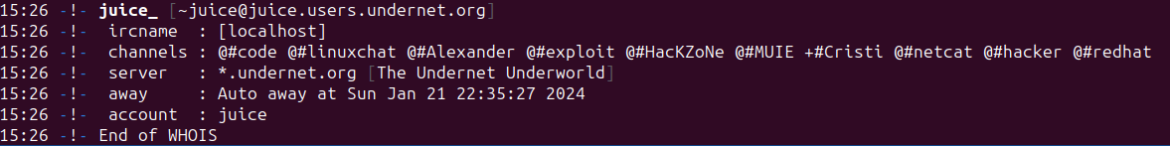
Smecher, admin
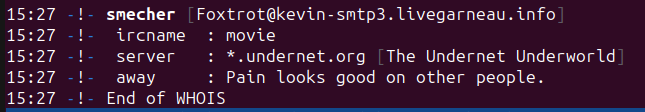
MUIE, admin
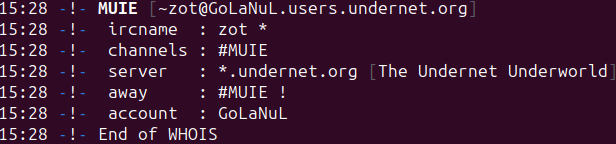
Aridan, member
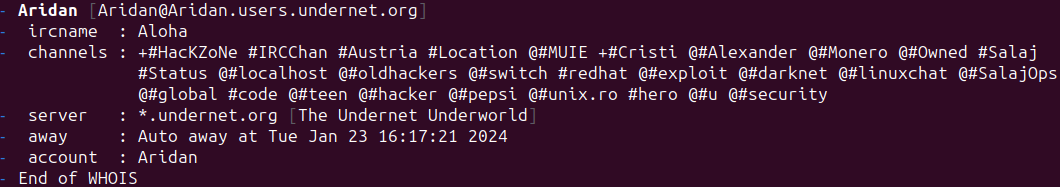
Catalin, member
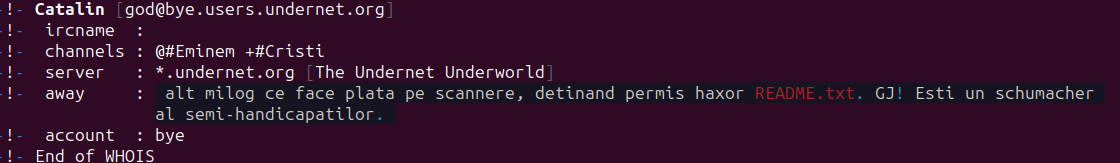
Canine, developer
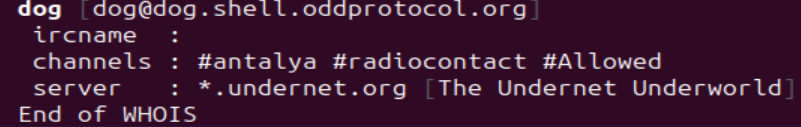
We recognized a customized script that’s plausibly circulated among the many group members on the best way to arrange the juice mining operation. It then lists the #redhat channel hosted on undernet for help. This channel has no official relation to RedHat the enterprise or software program, and is probably going only a nod to redhat vigilante hacking.
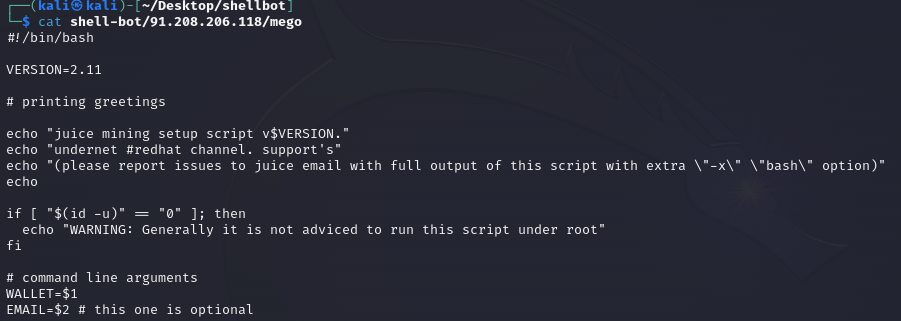
The redhat channel makes use of the undernet IRC community. Particularly, this group makes use of the Romanian server bucharest.ro.eu.undernet[.]org, the place the username @juice_ is current.
The channel #Cristi is used to arrange mining operations and retains observe of the members using the customized malicious instruments we encountered, usually signed by “Juice” and “Cartier” (aka “dog” and “Kartier”) group members.
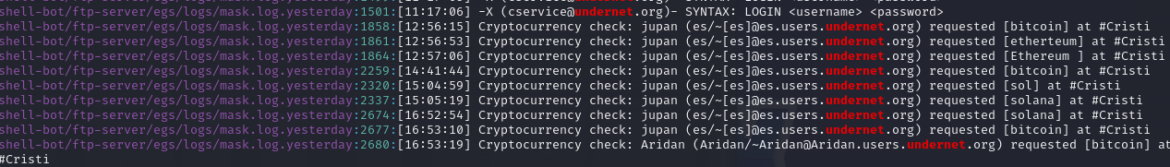
Throughout the channel #Cristi logs we have been capable of scrape, we discovered a reference to an exterior hyperlink http://physics.uctm.edu/funis/eugen. To our shock, it contained fairly an intensive report of logs taken from the non-public channel #Eugen, which we had not seen earlier than.
By investigating what we had discovered, we shortly found that the 2 individuals concerned in a lot of the interactions inside these logs have been consumer “Kartier” (signed as “dog”) and “Eugen.” Each members have been current, at completely different instances, within the channel #Cristi. “Eugen” appears to be a moniker for a Romanian particular person who additionally conducts malicious operations alongside the opposite members, because the logs containing their very own miner setups attest.


The primary area the place these logs are presently saved belongs to a reliable Bulgarian College, the College of Chemical Expertise and Metallurgy. The subdomain physics.uctm[.]edu seems to be compromised by RUBYCARP and comprises detailed directions and knowledge on the instruments used and the miner configuration.
We’ve recognized the consumer “dog” as the primary malicious software developer of the group, signing their instruments with “Cartier” and “Kartier.” We have now additionally discovered direct proof of software developer, “Cartier,” throughout the channel #Cristi, as proven under.
Canine’s software experience is mirrored in the way in which it instructs different members of the group the best way to arrange and run the customized malicious instruments. These malicious instruments have been present in virtually the entire campaigns we have been focused in. This listing consists of:

Right here, consumer “Eugen” exhibits operating miners, bash, and ld-linux-x8:
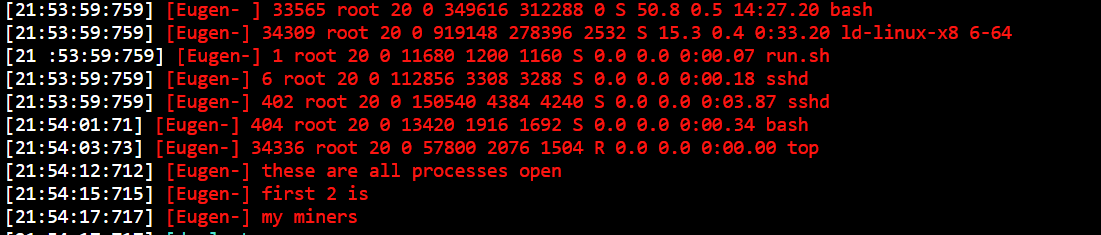
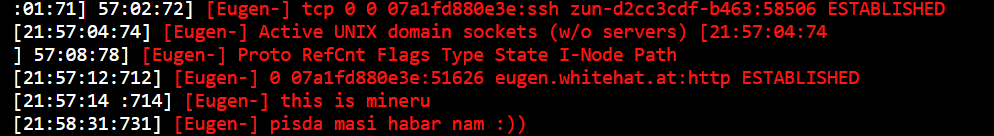
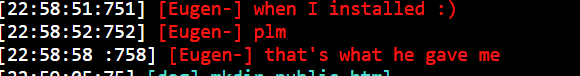
There may be additionally a reference to malicious ELF “plm,” noticed a number of instances in assaults in opposition to our honeypot and likewise reported in previous campaigns:
Under, there’s an excerpt of how consumer “dog” is trying to present entry to consumer “Eugen” to a malicious area containing a setup script for its infrastructure.
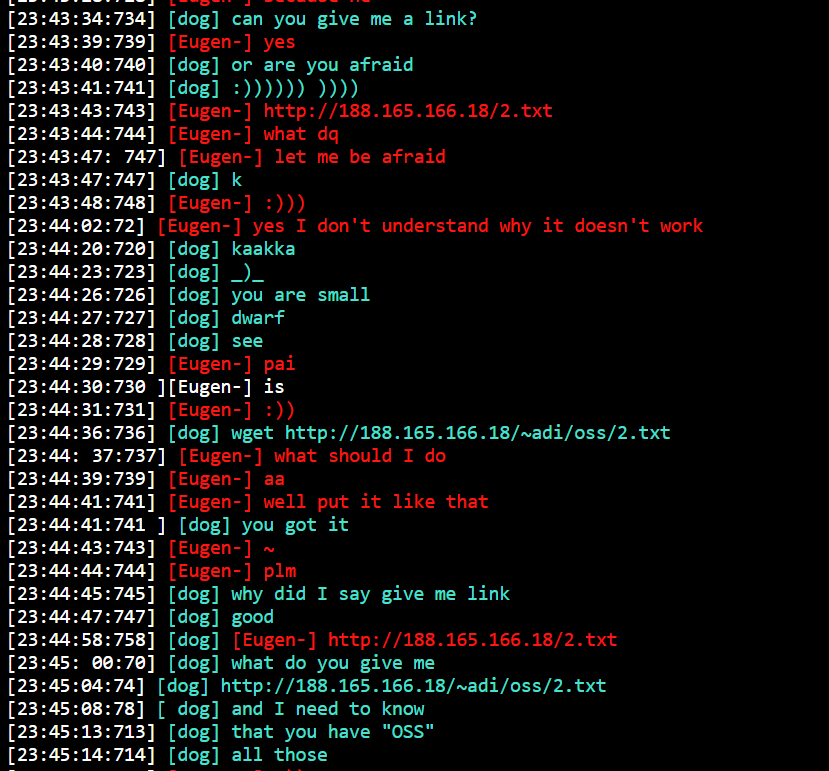
The IP above corresponds to a malicious indicator on VirusTotal, recognized as malware.
There are additionally references to RUBYCARP’s mostly used software, Mass Scanner (masscan), a software omnipresent inside its pre-exploitation actions and utilized to search out new potential victims.
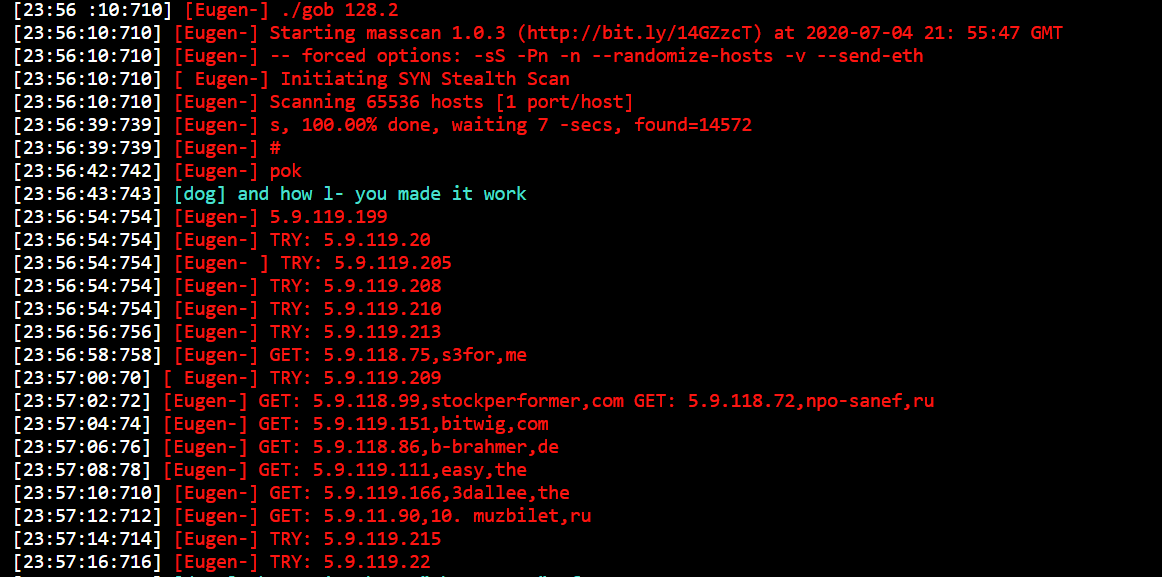
RUBYCARP’s Motivations
Cryptomining
RUBYCARP makes use of its personal swimming pools for mining which can be hosted on the identical domains the place it has created the IRC server to regulate the bots. These customized mining swimming pools enable it to keep away from detection from IP-based blocklists, and the utilization of frequent and random ports offers one other layer of stealth from easy detection methods. We’ve additionally found that it has not centered on a single cryptocurrency or mining software however, as a substitute, has a number of miners and wallets with exercise. All the next IoCs are associated to the “juice” menace actor.
Mining Swimming pools:
- juicessh[.]house:443
- juicessh[.]house:4430
- juicessh[.]house:5332
- 91[.]208.206.118:443
- 194[.]163.141.243:4430
- sshd[.]baselinux[.]internet
- run[.]psybnc[.]org:443
Recognized miners
Cryptocurrencies
- Monero
- Ethereum
- Ravencoin
The Ravencoin pockets has been notably prolific. From a pockets checker, its complete quantity in USD could be over $22,800 obtained. The pockets has a lot of transactions related to it and has been lively since February 2022, and the final out there transaction was mined on March 12, 2024.
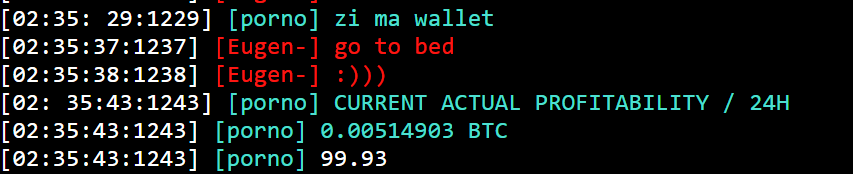
There are additionally a number of exchanges of pockets data among the many members, in an try to indicate how a lot they’ve gained from these malicious campaigns. Within the excerpt under, consumer “porno” claimed to have gained 0.00514903 BTC, round $360 USD, inside 24 hours.
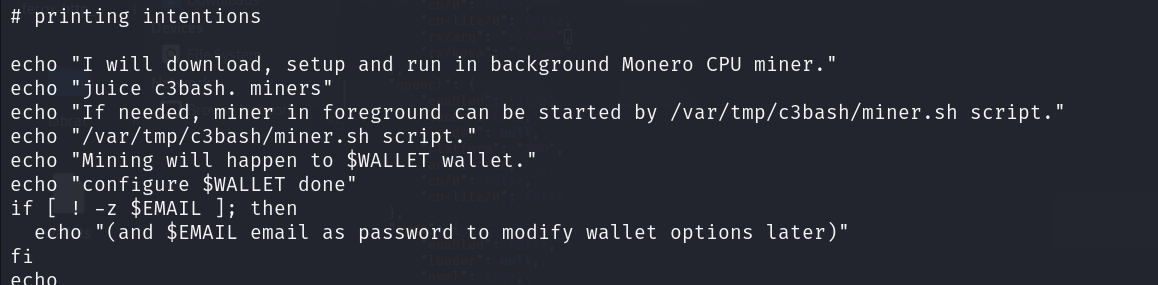
C3Bash
On high of the already identified miners we noticed above, we additionally encountered a customized command-line miner arrange known as merely “miner,” which we named “C3Bash” because of the self-labeling we discovered. The script in query is signed by “Juice” and it permits a possible consumer to arrange its pockets deal with with a command line argument, in addition to any miner of alternative.
As soon as the consumer has arrange its configurations, the script takes care of downloading, putting in, and operating the miners within the background, additionally alerting the consumer if the script will get killed by an antivirus or just eliminated. It additionally suggests what the CPU utilization must be in comparison with the host, most likely to keep away from detection. On a sufferer system, this may increasingly outcome within the operating of a number of miners on the similar time, successfully lowering each the time it takes for the attacker to execute the malicious payload and the possibilities of it being detected, because the execution will now depend on a single script.
The script in the mean time helps miners XMRig/Monero, and the script itself was hosted on a now-dead area “download[.]c3bash[.]org.”
Phishing
We discovered proof that RUBYCARP additionally executes phishing operations to steal financially helpful property, comparable to bank card numbers. Primarily based on logs, it seems that it’s utilizing this to fund its infrastructure however it’s affordable to suppose RUBYCARP additionally makes use of these for different functions, or probably to promote.
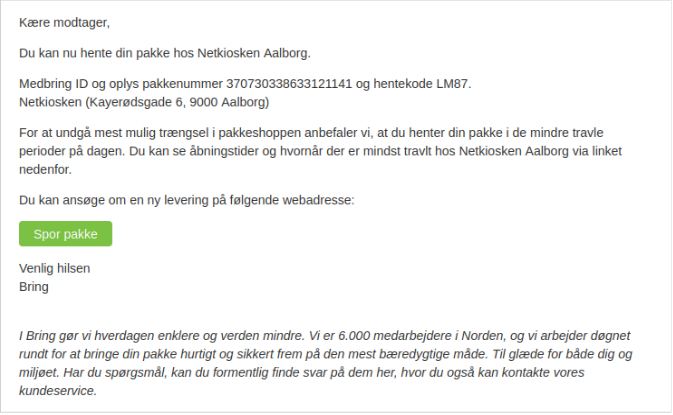
In one of many assaults we obtained in opposition to our honeypot in December 2023, we recognized a phishing template (letter.html) focusing on Danish customers and impersonating the Danish logistics firm “Bring.”
We additionally found a PHP script, named “ini.inc,” used to ship these phishing emails. An electronic mail.txt file was discovered that contained two potential compromised electronic mail accounts from which the attackers would ship emails: “test@lufaros[.]com” and “maria@cenacop[.]com.” On the time of this writing, the area “lufaros[.]com” is marked as Malicious on VirusTotal.
Analyzing the shellbot code exhibits that it has particular instructions to ship emails, and it’s seemingly that that is the template used within the campaigns:
sendraw($IRC_cur_socket, "PRIVMSG $printl :!u sendmail <subject> <sender> <recipient> <message>");
We recognized 36 textual content information containing lots of of Danish electronic mail addresses, a few of which have been current in each previous and up to date information leaks. It’s affordable to suppose that the e-mail addresses could have been the goal of the phishing template proven above.
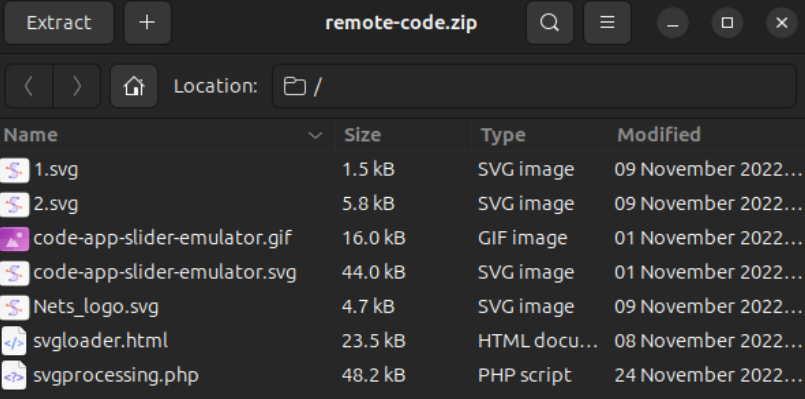
Throughout the similar information, we additionally recognized a Zip file named “remote_code.zip.” As soon as extracted, the archive comprises a brand picture of the European financial institution Nets. Throughout the similar folder, there are additionally SVG information containing an “ID Check” verification picture and a Visa brand. Extra pictures have been additionally discovered containing a cell phone format, as proven under, successfully emulating a Nets dwelling banking utility. These could be used to construct a convincing phishing touchdown web page.
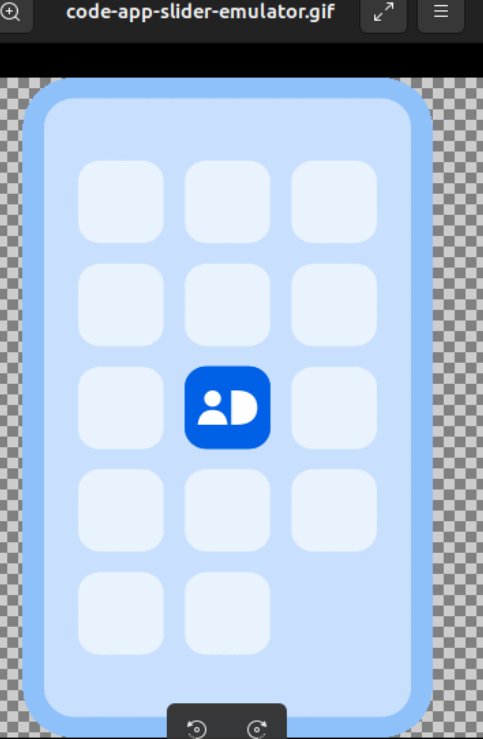 |
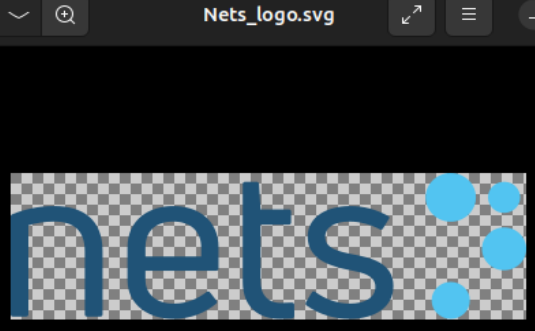 |
Lastly, we additionally discovered direct proof of a brand new area buy. In an excerpt under, it’s attainable to see how the consumer “dog”/”cartier” is getting ready to buy a brand new potential area with stolen bank card information.
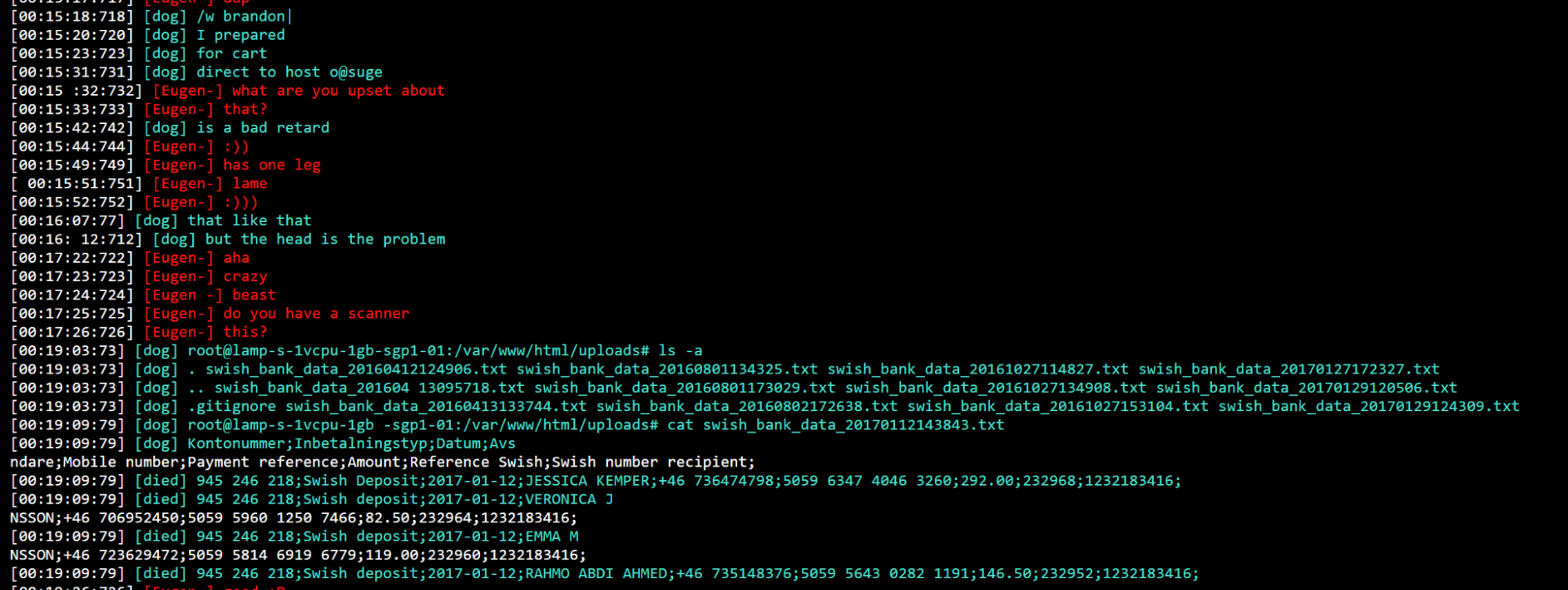
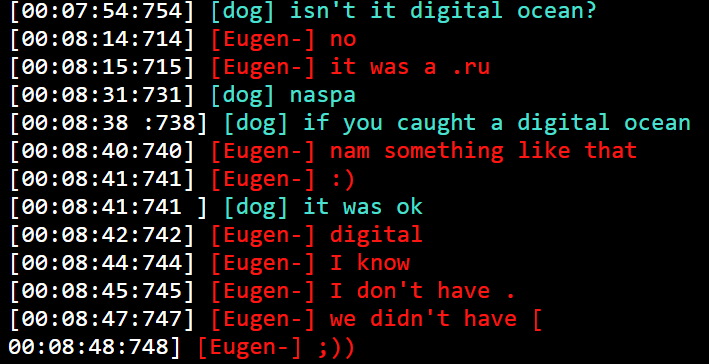
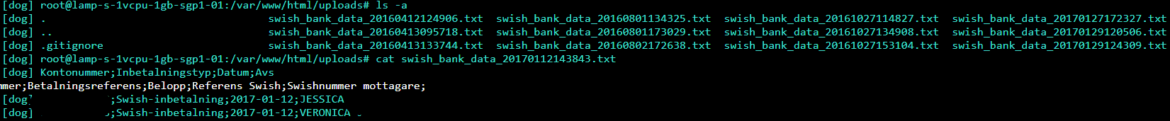
The screenshot above exhibits a dialog the place consumer “dog” lists information which we consider it has stolen. The filenames appear a transparent reference to Swedish financial institution Swish, and the timestamp within the filenames suggests they could have been stolen in 2016. “Dog” additionally offered bank card data for use, presumably, by different members. These have been printed in clear textual content throughout the channel, and have been redacted as they contained cost data.
Given the proof above, it’s believable that the attackers could depend on phishing templates to gather cost data. It’s protected to imagine the phishing targets European entities, comparable to Swish Financial institution, Nets Financial institution, and Deliver Logistics, amongst others.
Conclusion
RUBYCARP is a gaggle of Romanian menace actors who’ve been lively for nearly a decade. Attribution is at all times tough, however they’re more than likely Romanian and will have some crossover with the “Outlaw APT” group and others who leverage the Perl Shellbot. These menace actors are additionally concerned within the improvement and sale of cyber weapons, which isn’t quite common. They’ve a big arsenal of instruments they’ve constructed up over time which supplies them fairly a variety of flexibility when conducting their operations.
Communications between menace actors hasn’t modified very a lot over time, with IRC nonetheless being highly regarded. There may be additionally a neighborhood facet to RUBYCARP which is fascinating, as they assist mentor people who find themselves new to the scene. This does present some monetary advantages to the group since it may well then promote them the toolset that it has made.
Whereas RUBYCARP targets identified vulnerabilities and conducts brute power assaults, what makes it extra harmful is its post-exploitation instruments and the breadth of its capabilities (i.e., Phishing). Defending in opposition to this group requires diligent vulnerability administration, a strong safety posture, and runtime menace detection.