Australian organisations and their IT groups could also be “missing the point” of synthetic intelligence in the event that they focus solely on utilizing generative AI to spice up productiveness and speed up present plans, in response to a number one skilled within the know-how.
Martin D. Adams, an moral AI entrepreneur and enterprise advisor, advised audiences at Sydney’s SXSW Pageant in October that some AI purposes touted by consulting companies like McKinsey & Firm, Accenture, and Deloitte might really be dangerous for organisations and miss the true worth of AI.
“Their view as I understand it is to help push the idea of AI as helping us achieve business cases that are already approved, to do things we’re already doing, but to do them faster and cheaper,” Adams mentioned.
Calling this productiveness framing of AI’s potential the “mad view of AI” and “short-sighted,” he mentioned that, whereas there was nothing improper with sooner and cheaper, doing so with out contemplating the broader enterprise and societal context may even see enterprises threat relationships with clients and communities.
Generative AI’s attract could cause companies to overlook its true function
Adams defined that generative AI collapses the hole between an concept and its execution, eliminating a lot of the time, value, and energy historically required for creation.
“Generative AI plays into the mad view of AI really seductively, and dangerously seductively, if we’re not careful,” he warned.
Generative AI’s enchantment can lead companies into new ventures, however Adams warned that this isn’t all the time helpful in a digital or AI-driven age. For instance, within the advertising business, AI is supercharging the AdTech and social media race for content material views, typically with the push of a button.
SEE: Organisatinos are dealing with obstacles getting AI into manufacturing
“You’ve got people getting promotions on the basis of numbers of views skyrocketing,” Adams famous. “Meanwhile, brand equity and loyalties are all absolutely disappearing because we’ve mechanised production, and it’s really, really dangerous. It’s not actually helping our relationships.”
The most important drawback enterprises in any business are more likely to have is what Adams calls the “informed company bias.” This can be a drawback the place, due to their place, corporations suppose they’re extra knowledgeable than they’re and find yourself being much less knowledgeable than they have to be.
“They under-invest in the systems, and the mindsets, and the people, and the technology to understand market trends, consumer preferences, and the knowledge to adapt and respond to those,” he defined.
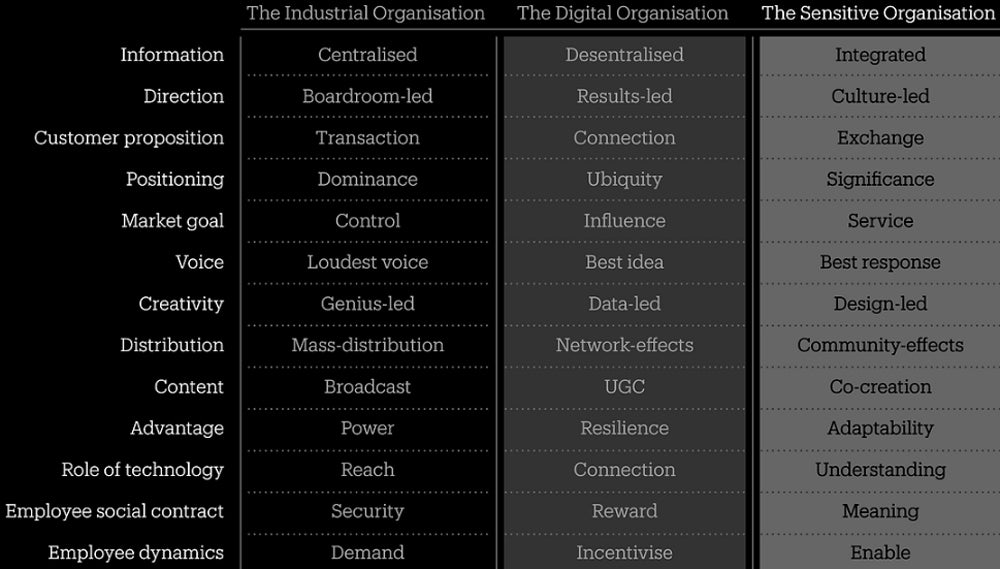
Organisations and IT can use AI to turn into ‘sensitive’
In distinction, the best organisations — which Adams calls “sensitive organisations” — are as a substitute utilizing generative AI in tandem with completely different applied sciences, together with slender AI, utilized AI, and analytics. They’re doing this to achieve a extra holistic identification of unmet wants of communities and clients.
“They [sensitive organisations] understand people the way those people would describe themselves; with all their full dimensionality and complexity and everything else, rather than seeing them as purely sort of commercial entities,” he mentioned.
PREMIUM: The way to use AI in enterprise
Adams added that AI has the potential to supply organisations this sensitivity, reasonably than stagnation. “In business and life, the opposite of sensitive is not strong, resilient, and robust. It’s actually death. It’s actually to be cut off from the reality of what is going on out there,” he mentioned.
The way to flip your enterprise right into a delicate organisation
Adams defined that delicate organisations typically use AI to course of, combine, and reply to data in ways in which improve capabilities and competitiveness, reasonably than merely boosting productiveness.
Taking in data
Adams mentioned AI applied sciences now enable organisations to tug in data from the surface world at scale, depth, and pace. This enables them to raised perceive actual demand, pursuits, and communities, reasonably than merely specializing in markets as customers.
He cited the instance of banking establishment UBS, which used AI and content material evaluation to find that their high-net-worth shoppers have been consuming a major quantity of content material associated to isolation, loneliness, and psychological well being struggles. This gave them insights into the unmet wants of this neighborhood.
Integrating data
Delicate organisations are likely to combine the knowledge and insights gathered by means of AI into the broader organisation. This will enable them to alter the form and performance of the corporate by means of stakeholders throughout the enterprise, so it will possibly adapt to the surroundings.
Adams mentioned L’Oreal’s NYX model, for instance, was in a position to make use of AI and content material evaluation to determine naturally occurring communities and pursuits round “goth romance, goth horror, and goth comedy.” They then used this data to design a brand new product line aligned with these neighborhood pursuits.
Responding to data
Adams mentioned delicate organisations use built-in data to develop a robust “sense and response” functionality, the place they’re extra open, receptive, and responsive to alter. For instance, he mentioned delicate organisations are unlikely to make use of AI merely to provide extra of the identical at a sooner fee. As a substitute, they’re more likely to leverage it to redefine the issues they face and create extra exact drawback statements.
IT leaders ought to deal with psychological security
Adams advisable organisations use slender AI “upstream,” not as a manufacturing know-how, however as a software to grasp demand, curiosity, neighborhood, and unmet wants. Then, generative AI can be utilized to unfold that data all through organisations, and reply sensitively to the surroundings.
He additionally urged IT leaders to not neglect the groups and staff they are going to be working with to deploy AI.
“If you’re a leader of any type, and you’re talking about AI as being in there to create these efficiencies, to automate processes, you’ve got to be aware this might be very, very scary for people in your organisation; AI is a system, but you’re also bringing it into a system,” he cautioned.
Creating psychological security inside groups will really help AI’s function within the organisation, he mentioned.
“Emphasize the fact AI can unlock things we wouldn’t be able to do but for the existence of AI, and it can enable them to do their best work,” Adams urged. “Having this view is not some diplomatic thing and doesn’t get in the way of adoption; it actually greases the wheels for adoption to create psychological safety.”