The primary UEFI bootkit particularly focusing on Linux programs has been found, marking a shift in stealthy and hard-to-remove bootkit threats that beforehand targeted on Home windows.
Named ‘Bootkitty,’ the Linux malware is a proof-of-concept that works solely on some Ubuntu variations and configurations moderately than a completely fledged menace deployed in precise assaults.
Bootkits are malware designed to infect a pc’s boot course of, loading earlier than the working system and permitting it to achieve management over a system at a really low stage.
The benefit of this follow is that bootkits can evade safety instruments working on the working system stage and modify system elements or inject malicious code with out risking detection.
ESET researchers who found Bootkitty warn that its existence is a big evolution within the UEFI bootkit threats house regardless of the present real-world implications.
A Linux bootkit within the making
ESET found Bootkitty after analyzing a suspicious file (bootkit.efi) uploaded to VirusTotal in November 2024.
Upon evaluation, ESET confirmed that this was the primary case of a Linux UEFI bootkit to bypass kernel signature verification and preload malicious elements in the course of the system boot course of.
Bootkitty depends on a self-signed certificates, so it will not execute on programs with Safe Boot enabled and solely targets sure Ubuntu distributions.
Moreover, hardcoded offsets and simplistic byte-pattern matching make it solely usable on particular GRUB and kernel variations, so it is unsuitable for widespread deployment.
ESET additionally notes that the malware accommodates many unused features and handles kernel-version compatibility poorly, usually resulting in system crashes.

Supply: ESET
The malware’s buggy nature and the truth that ESET’s telemetry exhibits no indicators of Bootkitty on dwell programs led the researchers to conclude that it’s in early-stage growth.
Bootkitty’s capabilities
Throughout boot, Bootkitty hooks UEFI safety authentication protocols (EFI_SECURITY2_ARCH_PROTOCOL and EFI_SECURITY_ARCH_PROTOCOL) to bypass Safe Boot’s integrity verification checks, making certain the bootkit masses no matter safety insurance policies.
Subsequent, it hooks varied GRUB features like ‘start_image’ and ‘grub_verifiers_open’ to control the bootloader’s integrity checks for binaries, together with the Linux kernel, turning off signature verification.
Bootkitty then intercepts the Linux kernel’s decompression course of and hooks the ‘module_sig_check’ operate. This forces it to at all times return success throughout kernel module checks, permitting the malware to load malicious modules.
Additionally, it replaces the primary atmosphere variable with ‘LD_PRELOAD=/decide/injector.so’ in order that the malicious library is injected into processes upon system launch.
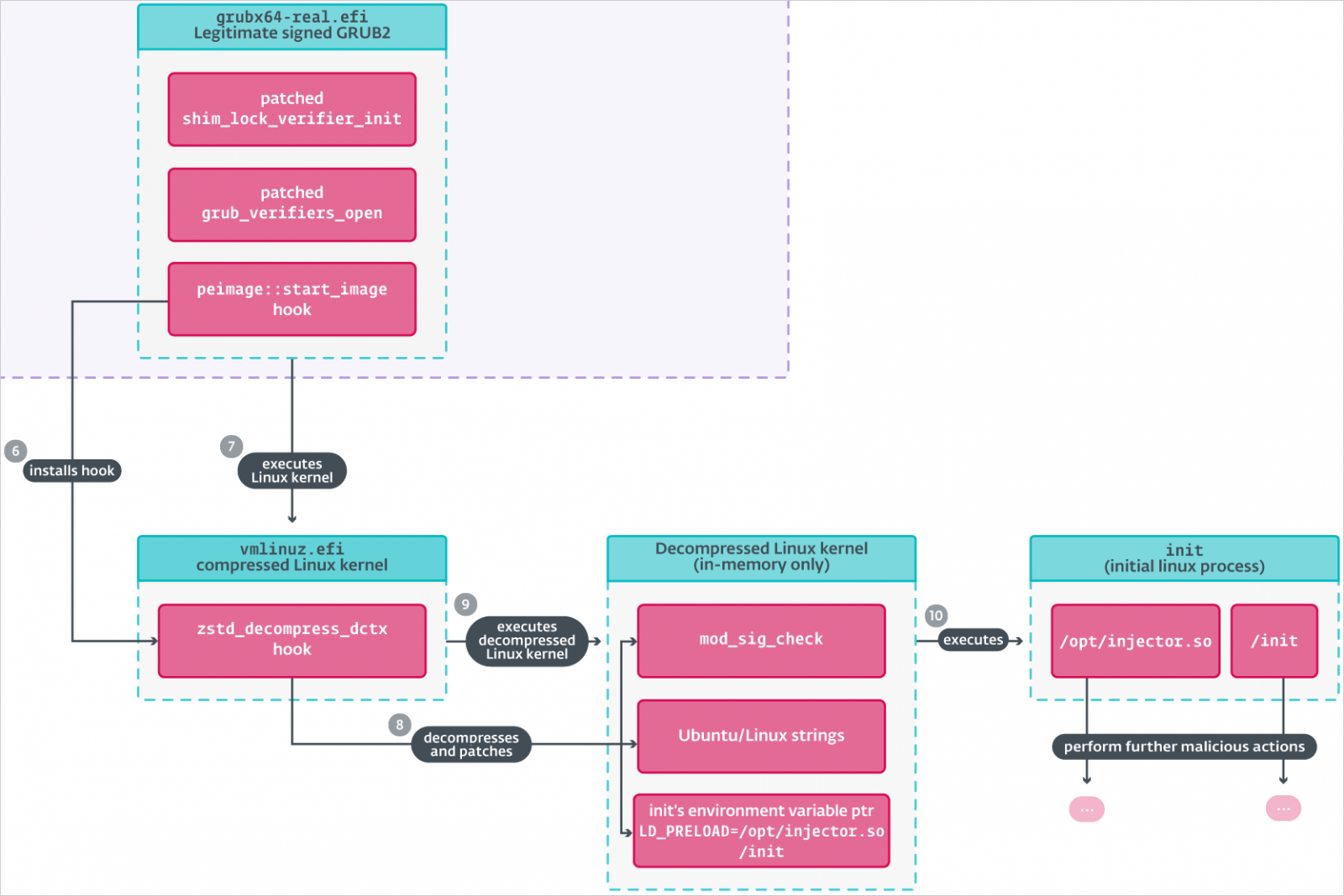
Supply: ESET
This entire course of leaves behind a number of artifacts, some meant and others not, explains ESET, which is one other indication of Bootkitty’s lack of refinement.
The researchers additionally famous that the identical consumer who uploaded Bootkitty onto VT additionally uploaded an unsigned kernel module named ‘BCDropper,’ however obtainable proof weakly hyperlinks the 2.
BCDropper drops an ELF file named ‘BCObserver,’ a kernel module with rootkit performance that hides recordsdata, processes, and opens ports on the contaminated system.
The invention of the sort of malware illustrates how attackers are creating Linux malware that was beforehand remoted to Home windows because the enterprise more and more adopts Linux.
Indicators of compromise (IoCs) related to Bootkitty have been shared on this GitHub repository.