Medical imaging is a fancy area the place deciphering outcomes might be difficult.
AI fashions can help medical doctors by analyzing photographs which may point out disease-indicating anomalies.
Nonetheless, there’s a catch: these AI fashions normally give you a single resolution when, in actuality, medical photographs typically have a number of interpretations.
In case you ask 5 consultants to stipulate an space of curiosity, like a small lump in a lung scan, you may find yourself with 5 completely different drawings, as they might all have their very own opinions on the place the lump begins and ends, for instance.
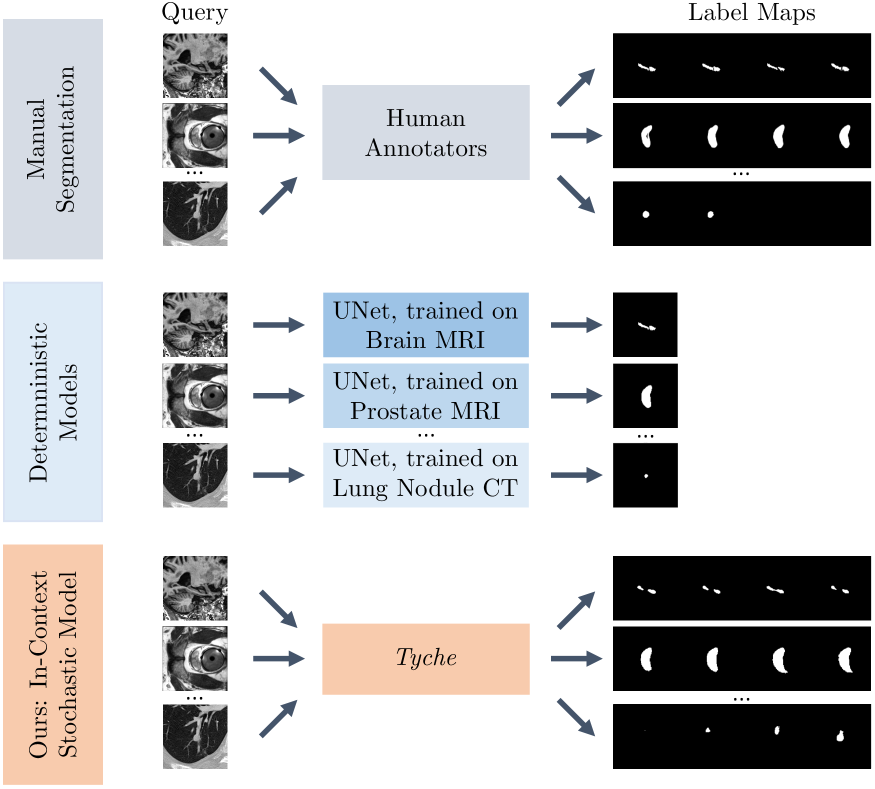
To sort out this downside, researchers from MIT, the Broad Institute of MIT Harvard, and Massachusetts Normal Hospital have created Tyche, an AI system that embraces the anomaly in medical picture segmentation.
Segmentation includes labeling particular pixels in a medical picture that symbolize necessary buildings, like organs or cells.
Marianne Rakic, an MIT pc science PhD candidate and lead writer of the examine, explains, “Having options can help in decision-making. Even just seeing that there is uncertainty in a medical image can influence someone’s decisions, so it is important to take this uncertainty into account.”
Named after the Greek goddess of probability, Tyche generates a number of potential segmentations for a single medical picture to seize ambiguity.
Every segmentation highlights barely completely different areas, permitting customers to decide on probably the most appropriate one for his or her wants.
Rakic tells MIT Information, “Outputting multiple candidates and ensuring they are different from one another really gives you an edge.”
So, how does Tyche work? Let’s break it down into 4 easy steps:
- Studying by instance: Customers give Tyche a small set of instance photographs, referred to as a “context set,” that present the segmentation activity they wish to carry out. These examples can embrace photographs segmented by completely different human consultants, serving to the mannequin perceive the duty and the potential for ambiguity.
- Neural community tweaks: The researchers modified an ordinary neural community structure to permit Tyche to deal with uncertainty. They adjusted the community’s layers in order that the potential segmentations generated at every step might “communicate” with one another and the context set examples.
- A number of potentialities: Tyche is designed to output a number of predictions primarily based on a single medical picture enter and the context set.
- Rewarding high quality: The coaching course of was tweaked to reward Tyche for producing the very best prediction. If the consumer asks for 5 predictions, they will see all 5 medical picture segmentations produced by Tyche, even when one is likely to be higher.
One in every of Tyche’s largest strengths is its adaptability. It might probably tackle new segmentation duties with no need to be retrained from scratch.
Usually, AI fashions for medical picture segmentation use neural networks that require intensive coaching on massive datasets and machine studying experience.
In distinction, Tyche can be utilized “out of the box” for numerous duties, from recognizing lung lesions in X-rays to figuring out mind abnormalities in MRIs.
Quite a few research have been carried out in AI medical imaging, together with main breakthroughs in breast most cancers screening and AI diagnostics that match and even beat medical doctors in deciphering photographs.
Seeking to the long run, the analysis staff plans to discover utilizing extra versatile context units, presumably together with textual content or a number of sorts of photographs.
In addition they wish to develop methods to enhance Tyche’s worst predictions and allow the system to advocate the most effective segmentation candidates.