Ransomware actors have had a tough begin this yr, as stats from cybersecurity agency Coveware present firms are more and more refusing to pay extortion calls for, resulting in a document low of 28% of firms paying ransom within the first quarter of 2024.
This determine was 29% in This fall 2023, and Coveware’s stats present that diminishing funds have remained regular since early 2019.
This lower is because of organizations implementing extra superior protecting measures, mounting authorized strain to not meet the crooks’ monetary calls for, and cybercriminals repeatedly breaching guarantees to not publish or resale stolen knowledge if a ransom is paid.
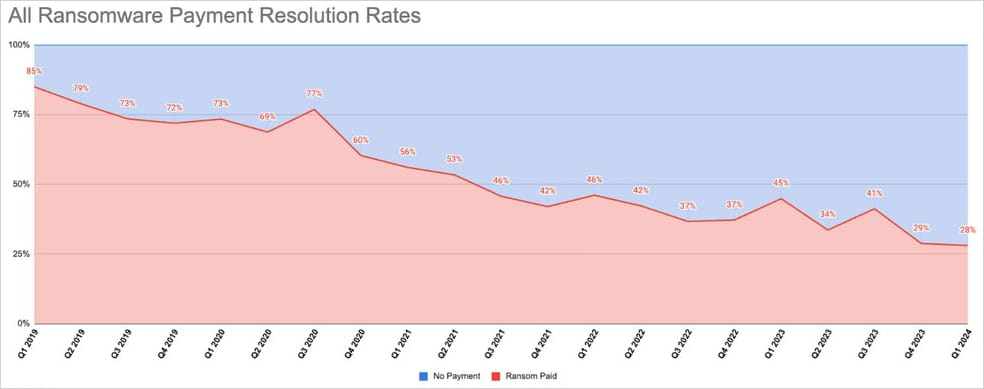
Supply: Coveware
Nonetheless, it’s important to notice that regardless of the drop within the fee charge, the quantity paid to ransomware actors is greater than ever earlier than, reaching $1.1 billion final yr, in accordance with a Chainalysis report.
This is because of ransomware gangs hitting extra organizations by escalating their assault frequency and demanding extra substantial figures for not exposing stolen secrets and techniques and offering victims with a decryption key.
Regarding Q1 2024, Coveware reviews a 32% quarter-over-quarter (QoQ) drop within the common ransom fee, now at $381,980, and a 25% QoQ enhance within the median ransom fee, which stands at $250,000.
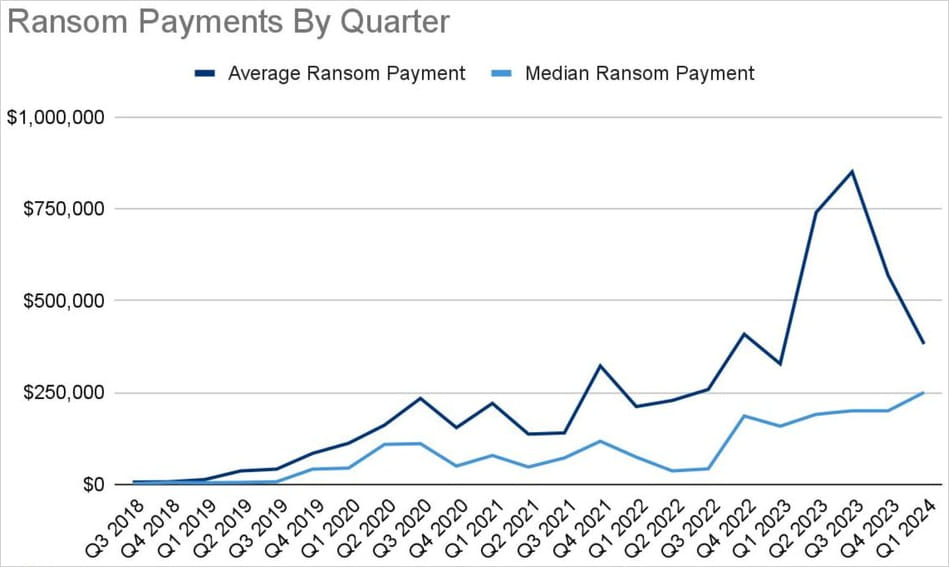
Supply: Coveware
This simultaneous drop in common and rise in median ransom funds signifies a lower in high-figure funds and a rise in reasonable quantities. This could possibly be brought on by ransom calls for changing into extra modest and/or fewer high-value targets succumbing to extortion.
Concerning preliminary infiltration strategies, there is a rising variety of instances the place that is unknown, reaching almost half of all reported instances within the first quarter of 2024.
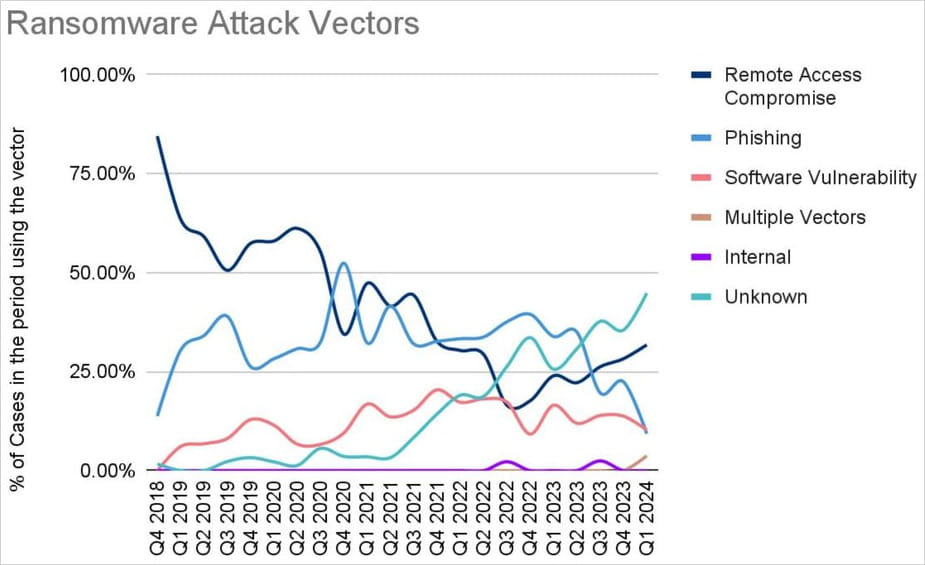
Coveware
From these which were decided, distant entry and vulnerability exploitation play the biggest function, with the CVE-2023-20269, CVE-2023-4966, and CVE-2024-1708-9 flaws being the extra broadly exploited in Q1 by ransomware operators.
Legislation enforcement impact
Coveware reviews that the FBI’s LockBit disruption has had a large affect on the once-leading operation, as mirrored of their assault statistics. The operation additionally introduced turbulence to different main gangs, resulting in fee disputes and exit scams, equivalent to we noticed with BlackCat/ALPHV.
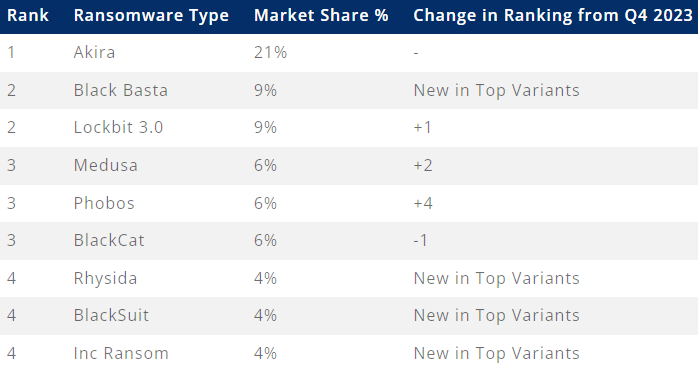
Supply: Coveware
Furthermore, these legislation enforcement operations have weakened the arrogance of different ransomware associates towards RaaS operators, with many deciding to function independently.
“We have already seen an increase in Babuk forks in recent attacks, and several former RaaS affiliates using the ubiquitous, and almost free, Dharma / Phobos services,” explains Coveware within the report.
In line with the safety agency, associates, in lots of instances, determined to stop cybercrime altogether.
“Most participants in the cyber extortion ecosystems are not hardened criminals, rather they are individuals with STEM skills that live in jurisdictions lacking both extradition treaties, and sufficient legitimate economic opportunities to put their skills to use,” continued Coveware.
“Some of these people will view the increased risk of getting in trouble along with the risk of getting cut out of their income as enough reason to quit.”
On this risky house, Akira tops the record with essentially the most energetic ransomware when it comes to assaults launched within the first quarter of the yr, remaining in place #1 for 9 months now.
The FBI reported this week that Akira is accountable for breaches in at the very least 250 organizations, pocketing $42 million in ransom funds.
