The hunt to create a helpful quantum pc reached a major milestone on the finish of 2024 with Google’s announcement of its Willow chip. The chip guarantees decreased noise and fewer errors because the variety of qubits grows — a essential step to advance towards superior quantum computing. Regardless of some debate on when these programs will really turn into obtainable, consultants nonetheless advise planning and migrating to post-quantum applied sciences.
The shift from immediately’s expertise, the place including extra qubits provides extra noise, to a future the place rising the variety of qubits exponentially reduces the quantity of noise — an achievement often called “threshold scalability” — conquers a serious obstacle to quantum computer systems. Making a 1,000-qubit quantum pc requires foundational developments past immediately’s noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) computer systems to create dependable logical qubits that can be utilized in simply scaled architectures.
The Google announcement marks “a significant leap forward,” says Karl Holmqvist, founder and CEO at Lastwall, an identification companies supplier centered on quantum resilience.
“Companies should be starting to get concerned about a usable quantum computer now,” Holmqvist says. “This is not because there is proof of a cryptographically relevant quantum computer yet. It is because there are active campaigns that are currently taking place to capture encrypted data and store it until there is a system that can break our asymmetric encryption.”
The risk posed by quantum computer systems appears to be changing into extra actual daily. Along with Google’s Willow chip announcement, Microsoft introduced in November that it had reached a 24-qubit milestone with Atom Computing utilizing lasers, whereas Japanese researchers from the Riken Quantum Pc Analysis Middle introduced a “general-purpose” optical quantum pc.
The longer term implications may very well be dire. The Hudson Institute, a free-market assume tank, warns that quantum computer systems pose a systemic cyber-risk to monetary programs; it printed two papers describing dangers of disruption to the US monetary system and cryptocurrencies.
Much less Than a Decade Away?
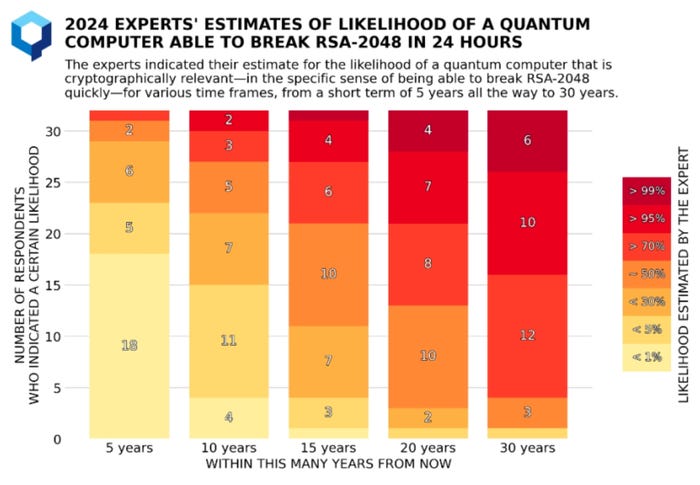
Quantum computing is a kind of applied sciences that many have perennially predicted is solely a decade away. Presently, the median estimate amongst consultants is that inside 15 years, a quantum pc will be capable of break RSA-2048 in 24 hours, in line with the “Quantum Threat Timeline Report 2024.”
The center-of-the-road estimate of when quantum computer systems will pose an encryption risk is lower than 15 years. Supply: International Danger Institute
Whereas many consultants see the opportunity of a helpful quantum pc in lower than a decade — based mostly on three key areas: {hardware} development, error correction, and algorithm growth — helpful quantum computer systems nonetheless have a protracted strategy to go earlier than they turn into attainable. For instance, whereas Google’s work on Willow is a serious step towards making error correction — primarily a theoretical subject earlier than this decade — extra achievable in bigger quantum computing chips, reaching this step is simply the second milestone out of six listed on its quantum pc street map.
As well as, gauging the chance is tough, with phrases equivalent to “threshold scalability” and “quantum supercomputers” muddying the waters, says Rebecca Krauthamer, co-founder and CEO of QuSecure.
“There’s so much complicated vocabulary when it comes to quantum, the thing that people need to look out for is when they start seeing quantum computers beginning to solve problems that they recognize,” Krauthamer says. “So whether it’s improved battery technology, or route optimization for self-driving cars, or optimized portfolio management, or breaking encryption — that’s the time everybody should have already migrated to post-quantum technologies, and not just post-quantum but crypto-agile management of cryptography.”
But the shortage of serious advantages for the personal sector might put a damper on growth. The Boston Consulting Group, for instance, factors out that quantum computing applications have had issue changing effort into worth.
“Quantum computing today provides no tangible advantage over classical computing in either commercial or scientific applications,” BCG acknowledged in a July evaluation. “Though experts agree that there are clear scientific and commercial problems for which quantum solutions will one day far surpass the classical alternative, the newer technology has yet to demonstrate this advantage at scale.”
Consultants Nonetheless Urge Preparation
As well as, the purpose at which nation-states might use quantum computer systems to interrupt encryption may very well be sooner, rising the chance for some industries. Quantinuum, for instance, accelerated its street map for totally fault-tolerant quantum computing to 2030 and warns that quantum safe options will seemingly be essential earlier than 2035.
“Given where we stand today, the need to complete migration to PQC [post-quantum computing] to effectively protect sensitive data needs to be prioritized,” says Duncan Jones, head of cybersecurity for Quantinuum.
Quantinuum expects incremental advances within the subsequent few years. That features enhancements in error correction and qubit scaling, continued analysis into purposes equivalent to quantum decryption, and, in consequence, higher adoption of PQC applied sciences, equivalent to post-quantum encryption, quantum key distribution, and quantum random quantity era (QRNG), says the corporate’s Jones.
“Organizations implementing quantum-safe strategies today should focus on PQC migration while ensuring their cryptographic foundations are as strong as possible through the use of QRNGs,” he says. “This approach provides immediate security benefits while preparing for future quantum-safe technologies.”
Google acknowledges that whereas its error correction breakthrough is critical, there’s a distinction between principle and follow.
“We still have a long way to go before we reach our goal of building a large-scale, fault-tolerant quantum computer,” two members of the Google Quantum AI group acknowledged in a weblog publish. “The engineering challenge ahead of us is immense.”