Qilin ransomware is evolving, now concentrating on Google Chrome credentials. Learn the way this new tactic expands their assault arsenal and the way organizations can defend themselves. Uncover mitigation methods and the significance of strong safety measures.
Cybersecurity researchers at Sophos have uncovered a regarding improvement within the Qilin ransomware operation: Credential harvesting by way of Google Chrome browsers.
In accordance with the corporate, whereas investigating the Synovis breach Sophos X-Ops crew recognized that the attackers stole credentials saved in Google Chrome browsers on a subset of the community’s endpoints.
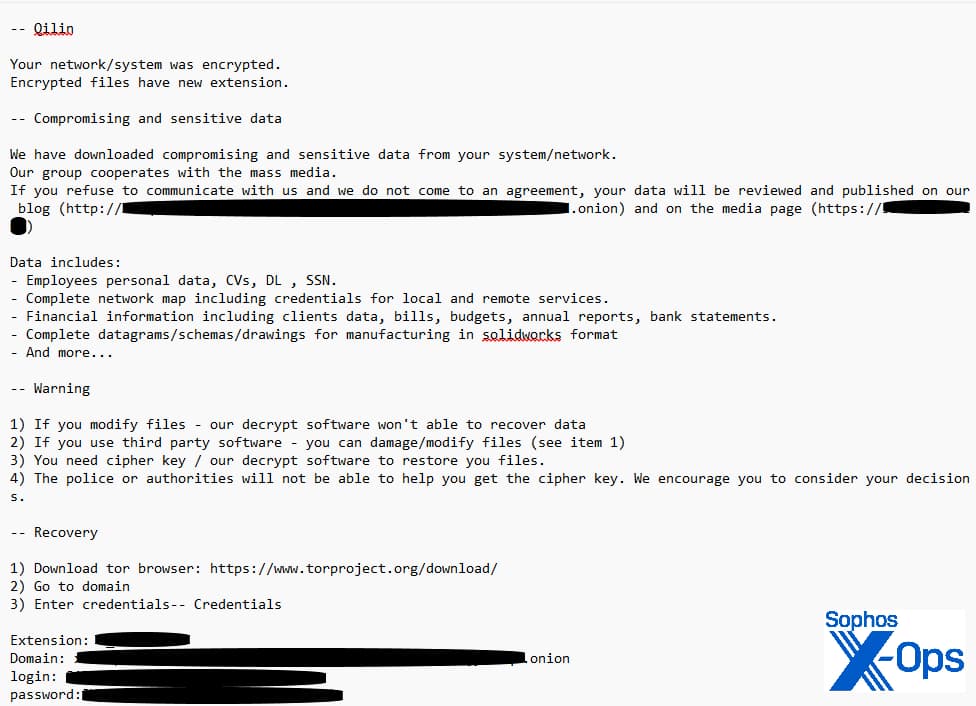
In your data, on June 3, 2024, the Qilin ransomware gang focused Synnovis, an outsourced lab service supplier for NHS hospitals in South-East London, claiming to have stolen hospital and affected person knowledge and demanding $50 million in ransom. After failed negotiations, the gang publicly leaked their whole exfiltrated dataset.
Qilin assaults have traditionally concerned “double extortion,” stealing knowledge, encrypting programs, and threatening to disclose/promote it if the sufferer doesn’t pay the ransom, which Sophos calls Turning the Screws method.
Nevertheless, this discovery marks a big shift in Qilin’s techniques because it focused credentials saved on contaminated networks’ Google Chrome, a browser that occupies round 65% of the browser market. This will likely have far-reaching penalties as attackers can entry monetary accounts, e mail, cloud storage, or enterprise functions utilizing compromised credentials.
The Sophos IR crew noticed this exercise in July 2024 on a single area controller throughout the goal’s Lively Listing area. Different area controllers in that area had been affected otherwise by Qilin, highlighting the potential for comparable assaults sooner or later.
Researchers analyzed a Qilin assault that started with compromised VPN credentials, suggesting the preliminary entry might have been bought from an Preliminary Entry Dealer (IAB). This 18-day dormancy interval signifies a calculated method, permitting the attackers to map the community, establish crucial property, and plan their subsequent transfer.
The credential theft itself leverages a customized stealer designed to focus on Google Chrome. As soon as the ransomware positive factors a foothold, it deploys Group Coverage Objects (GPO) to automate the method throughout the community. This automation considerably will increase the effectivity of the assault and ensures a wider attain throughout the compromised atmosphere.
“A successful compromise of this sort would mean that not only must defenders change all Active Directory passwords; they should also (in theory) request that end users change their passwords for dozens, potentially hundreds, of third-party sites for which the users have saved their username-password combinations in the Chrome browser. The defenders of course would have no way of making users do that,” Sophos’ researchers defined in a weblog put up.
First showing in October 2022, Qilin has rapidly gained notoriety for its RaaS (Ransomware-as-a-Service) mannequin, providing its malicious instruments to different cybercriminals. It’s believed to be linked to Russia-based risk actors and has focused varied industries, together with road newspapers, automotive components giants, and even Australian courtroom providers.
The evolving techniques of Qilin ransomware spotlight the significance of steady risk monitoring and adaptation of safety methods. Organizations should implement MFA (multi-factor authentication) on distant entry options to boost safety, use strong endpoint safety options to detect and stop suspicious behaviour, and commonly backup knowledge and patch all community programs, together with working programs and net browsers.