SUMMARY
- A consumer on X (@NSA_Employee39) claimed to find a zero-day exploit for 7-Zip, alleging a essential buffer overflow vulnerability.
- The exploit purportedly concerned a crafted .7z archive with a malformed LZMA stream to execute arbitrary code.
- Cybersecurity specialists and 7-Zip creator Igor Pavlov dismissed the declare, citing non-existent features and failed copy makes an attempt.
- Researchers steered the exploit code may need been generated by an AI, undermining its credibility.
- The incident highlights the persistent risk of zero-day exploits and the significance of sturdy cybersecurity measures.
The cybersecurity neighborhood not too long ago confronted a stir attributable to a consumer on the social media platform X (formally Twitter), claiming to own a zero-day exploit for the favored file archiver 7-Zip.
On your info, this consumer, below the deal with @NSA_Employee39, alleged that that they had found a essential vulnerability that would enable attackers to execute arbitrary code on a sufferer’s system by exploiting a buffer overflow throughout the 7-Zip software program. The consumer supplied a code snippet on Pastebin, purportedly demonstrating this exploit.
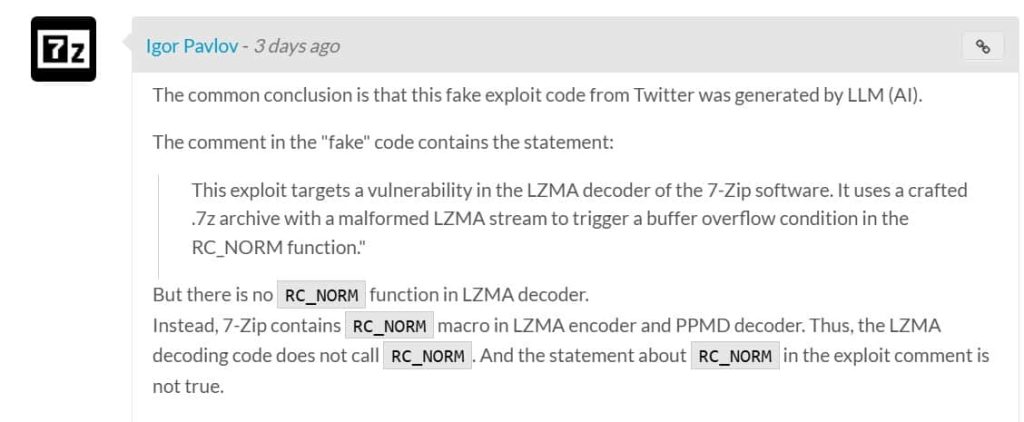
“This exploit targets a vulnerability in the LZMA decoder of the 7-Zip software. It uses a crafted .7z archive with a malformed LZMA stream to trigger a buffer overflow condition in the RC_NORM function. By aligning offsets and payloads, the exploit manipulates the internal buffer pointers to execute shellcode which results in arbitrary code execution,” the consumer wrote on Pastebin.
Regardless of the preliminary consideration, cybersecurity specialists rapidly started to specific doubts in regards to the exploit’s validity. Makes an attempt to duplicate the exploit proved unsuccessful, resulting in scepticism in regards to the code’s effectiveness.
The declare was later dismissed by 7-Zip’s creator, Igor Pavlov, who said that the alleged vulnerability depends on a operate (“RC_NORM”) that doesn’t exist within the 7-Zip LZMA decoder. Pavlov steered that the code was doubtless generated by an AI mannequin, additional undermining its credibility.
Moreover, safety researcher @LowLevelTweets reported being unable to breed the claimed exploit, stating that it produced no crashes, hangs, or timeouts throughout their testing. These findings counsel that the reported 7-Zip zero-day could also be a false alarm, doubtlessly arising from artificially generated code or a misunderstanding of the software program’s inner workings.
Whereas this explicit incident proved to be a false alarm, the specter of zero-day exploits stays a critical concern. These vulnerabilities are extremely harmful as they’re unknown to software program builders and thus lack any pre-existing defences.
Final month, Hackread reported a Home windows zero-day vulnerability permitting attackers to steal NTLM credentials by a misleading methodology. The vulnerability affected numerous Home windows programs, together with Home windows Server 2022, Home windows 11 (as much as v24H2), Home windows 10 (a number of variations), Home windows 7 and Server 2008 R2.
To remain secure from zero-day exploits, complete safety software program is necessary as it will possibly present important safety towards numerous threats, together with viruses, malware, and zero-day exploits. These options usually embrace options like real-time risk detection, superior risk defences, and robust privateness options to guard customers from cybersecurity threats.