WordPress websites are being hacked to put in malicious plugins that show faux software program updates and errors to push information-stealing malware.
Over the previous couple of years, information-stealing malware has grow to be a scourge to safety defenders worldwide as stolen credentials are used to breach networks and steal knowledge.
Since 2023, a malicious marketing campaign referred to as ClearFake has been used to show faux internet browser replace banners on compromised web sites that distribute information-stealing malware.
In 2024, a brand new marketing campaign referred to as ClickFix was launched that shares many similarities with ClearFake however as an alternative pretends to be software program error messages with included fixes. Nonetheless, these “fixes” are PowerShell scripts that, when executed, will obtain and set up information-stealing malware.
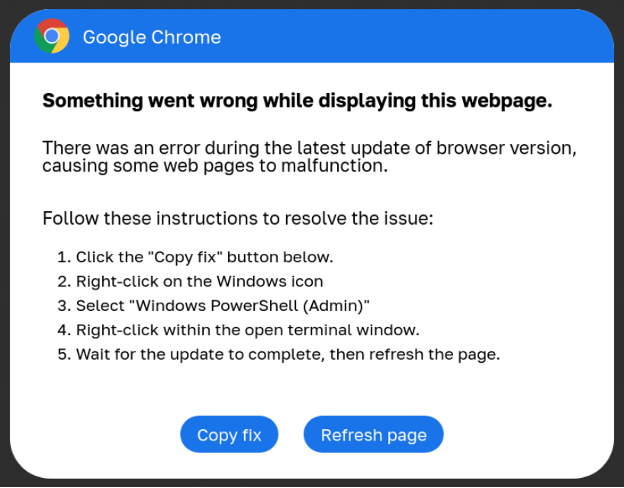
Supply: BleepingComputer
ClickFix campaigns have grow to be more and more widespread this yr, with menace actors compromising websites to show banners exhibiting faux errors for Google Chrome, Google Meet conferences, Fb, and even captcha pages.
Malicious WordPress plugins
Final week, GoDaddy reported that the ClearFake/ClickFix menace actors have breached over 6,000 WordPress websites to put in malicious plugins that show the faux alerts related to these campaigns.
“The GoDaddy Security team is tracking a new variant of ClickFix (also known as ClearFake) fake browser update malware that is distributed via bogus WordPress plugins,” explains GoDaddy safety researcher Denis Sinegubko.
“These seemingly legitimate plugins are designed to appear harmless to website administrators but contain embedded malicious scripts that deliver fake browser update prompts to end-users.”
The malicious plugins make the most of names just like legit plugins, reminiscent of Wordfense Safety and LiteSpeed Cache, whereas others use generic, made-up names.
The listing of malicious plugins seen on this marketing campaign between June and September 2024 are:
| LiteSpeed Cache Traditional | Customized CSS Injector |
| MonsterInsights Traditional | Customized Footer Generator |
| Wordfence Safety Traditional | Customized Login Styler |
| Search Rank Enhancer | Dynamic Sidebar Supervisor |
| search engine marketing Booster Professional | Simple Themes Supervisor |
| Google search engine marketing Enhancer | Type Builder Professional |
| Rank Booster Professional | Fast Cache Cleaner |
| Admin Bar Customizer | Responsive Menu Builder |
| Superior Person Supervisor | search engine marketing Optimizer Professional |
| Superior Widget Handle | Easy Publish Enhancer |
| Content material Blocker | Social Media Integrator |
Web site safety agency Sucuri additionally famous {that a} faux plugin named “Universal Popup Plugin” can also be a part of this marketing campaign.
When put in, the malicious plugin will hook numerous WordPress actions relying on the variant to inject a malicious JavaScript script into the HTML of the location.
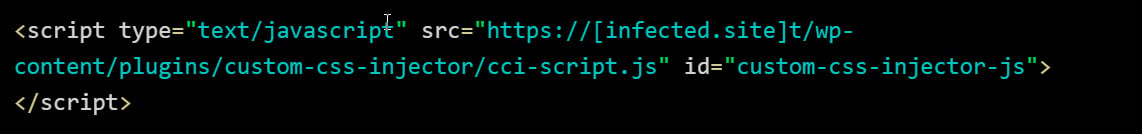
Supply: GoDaddy
When loaded, this script will try to load an additional malicious JavaScript file saved in a Binance Sensible Chain (BSC) good contract, which then masses the ClearFake or ClickFix script to show the faux banners.
From internet server entry logs analyzed by Sinegubko, the menace actors look like using stolen admin credentials to log into the WordPress website and set up the plugin in an automatic method.
As you may see from the picture beneath, the menace actors log in through a single POST HTTP request moderately than first visiting the location’s login web page. This means that it’s being achieved in an automatic method after the credentials have been already obtained.
As soon as the menace actor logs in, they add and set up the malicious plugin.
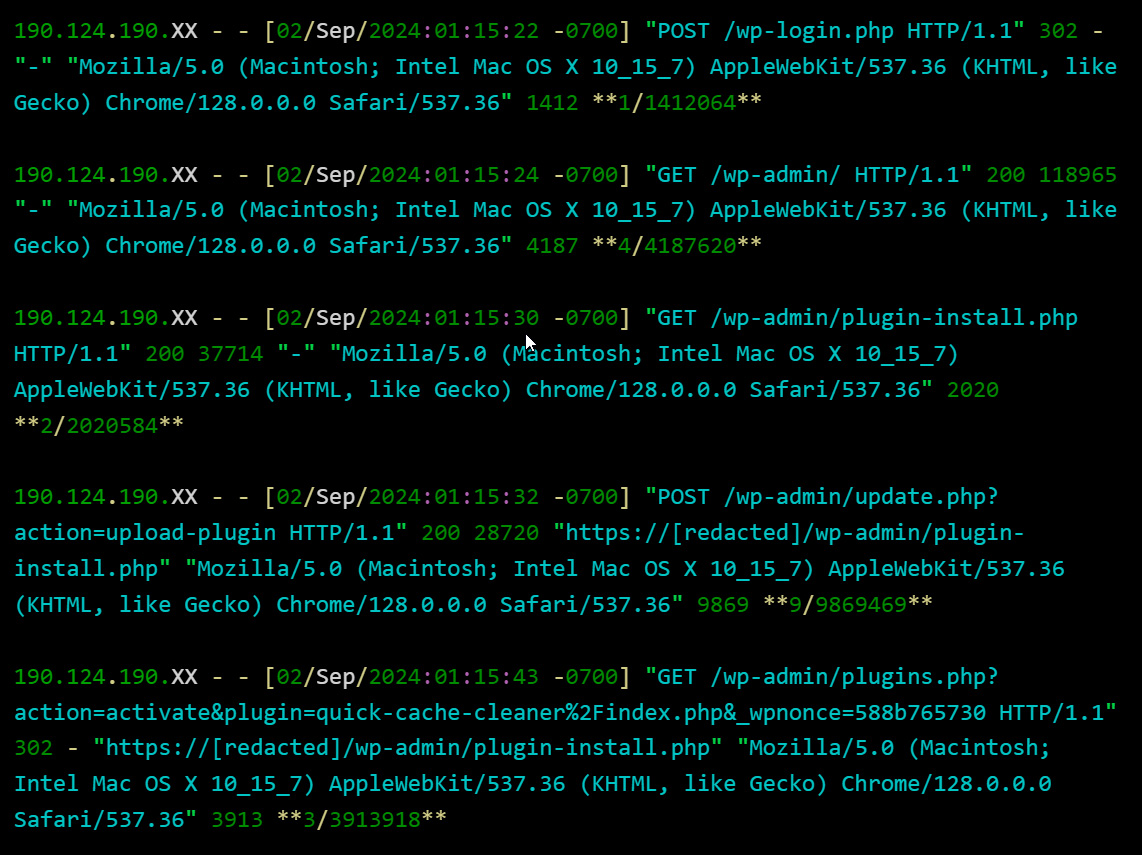
Supply: GoDaddy
Whereas it’s unclear how the menace actors are acquiring the credentials, the researcher notes it may very well be by means of earlier brute power assaults, phishing, and information-stealing malware.
If you’re a WordPress operation and are receiving reviews of pretend alerts being exhibited to guests, it’s best to instantly study the listing of put in plugins, and take away any that you just didn’t set up your self.
Should you discover unknown plugins, you also needs to instantly reset the passwords for any admin customers to a novel password solely used at your website.
