A brand new assault referred to as ‘Browser Syncjacking’ demonstrates the opportunity of utilizing a seemingly benign Chrome extension to take over a sufferer’s machine.
The brand new assault technique, found by safety researchers at SquareX, entails a number of steps, together with Google profile hijacking, browser hijacking, and, finally, machine takeover.
Regardless of the multi-stage course of, the assault is stealthy, requires minimal permissions, and nearly no sufferer interplay apart from to put in what seems to be a professional Chrome extension.
Syncjacking phases
The assault begins with the creation of a malicious Google Workspace area the place the attacker units up a number of consumer profiles with security measures reminiscent of multi-factor authentication disabled. This Workspace area will probably be used within the background to create a managed profile on the sufferer’s machine.
A browser extension, made to look as a great tool with professional performance, is then printed on the Chrome Net Retailer.
Utilizing social engineering, the attacker tips the sufferer into putting in the extension, which then quietly logs them into one of many attacker’s managed Google Workspace profiles in a hidden browser window working within the background.
The extension then opens a professional Google help web page. Because it has Learn and Write privileges to webpages, it injects content material into the web page, telling the consumer to allow Chrome sync.
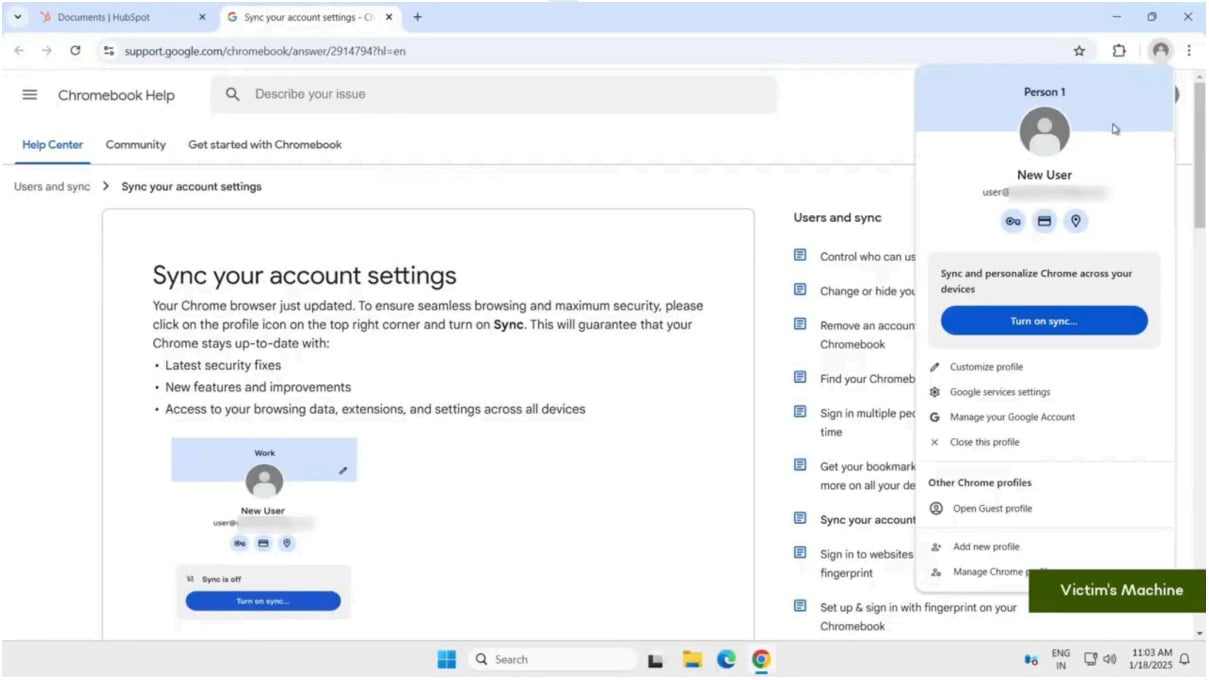
Supply: SquareX
As soon as synced, all saved information, together with passwords and searching historical past, turns into accessible to the attacker, who can now use the compromised profile on their very own machine.
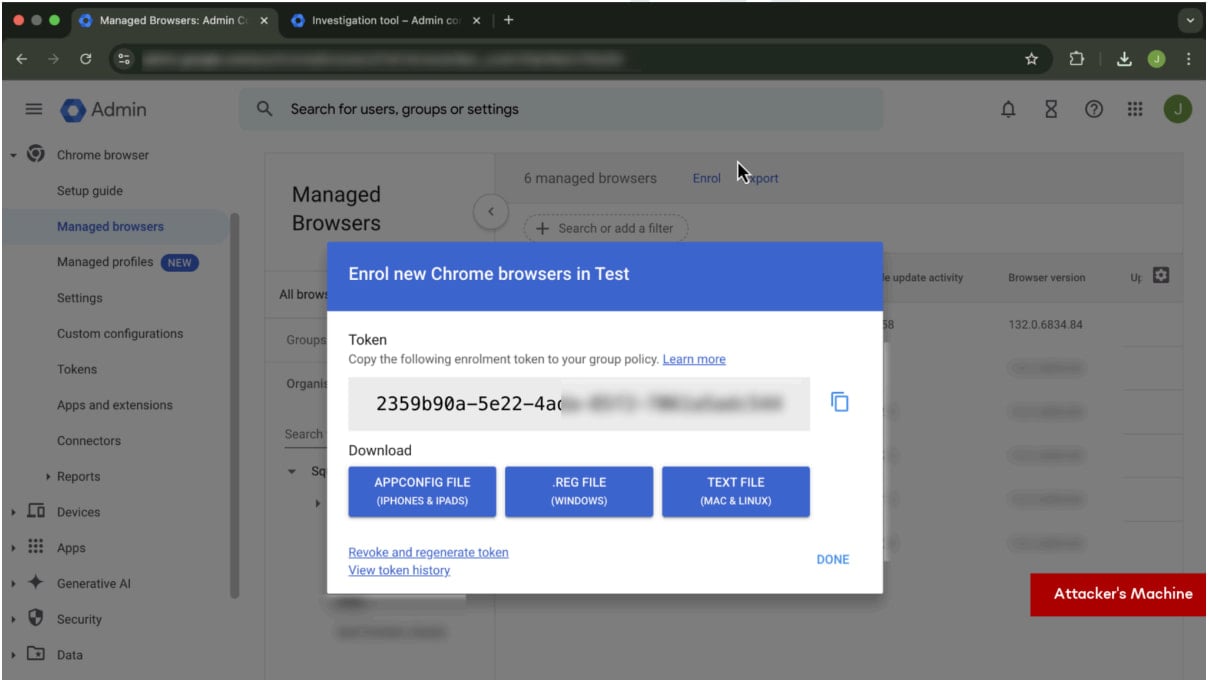
Supply: SquareX
With the sufferer’s profile beneath management, the attacker strikes to take over the browser, which, in SquareX’s demo, is completed via a pretend Zoom replace.
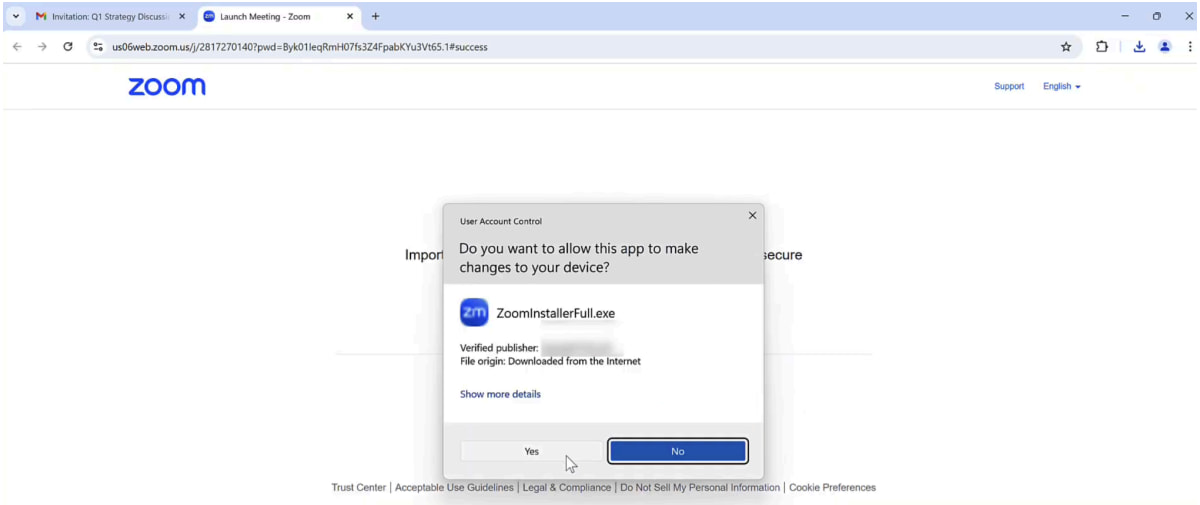
Supply: SquareX
Within the situation highlighted by the researchers, an individual might obtain a Zoom invite, and after they click on it and go to the Zoom webpage, the extension will as an alternative inject malicious content material stating that the Zoom shopper must be up to date.
Nonetheless, this obtain is an executable file containing an enrollment token, giving the attackers full management over the sufferer’s browser.
“Once enrolled, the attacker gains full control over the victim’s browser, allowing them to silently access all web apps, install additional malicious extensions, redirect users to phishing sites, monitor/modify file downloads and many more,” explains the SquareX researchers.
By leveraging Chrome’s Native Messaging API, the attacker can set up a direct communication channel between the malicious extension and the sufferer’s working system.
This permits them to browse directories, modify recordsdata, set up malware, execute arbitrary instructions, seize keystrokes, extract delicate information, and even activate the webcam and microphone.
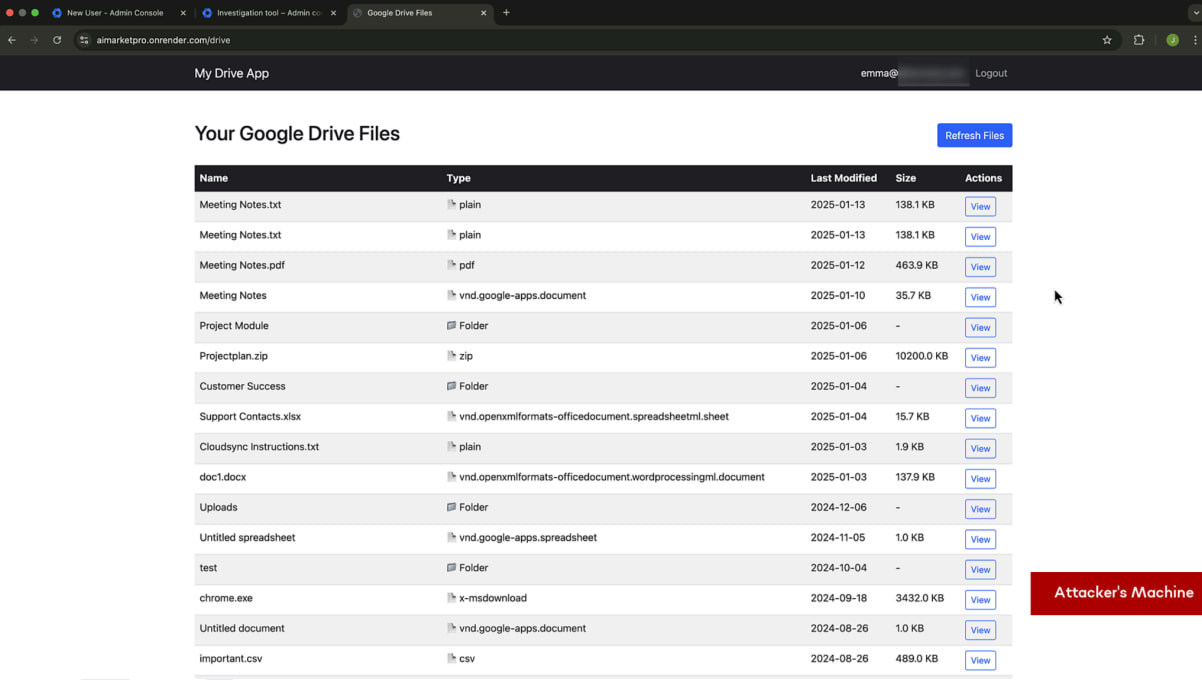
Supply: SquareX
SquareX highlights the stealth and potent nature of the assault, underlining how troublesome it might be for many customers to appreciate one thing’s off.
“Unlike previous extension attacks that involve elaborate social engineering, adversaries need only minimal permissions and a small social engineering step, with nearly no user interaction required to execute this attack,” describes the report.
“Unless the victim is extremely security paranoid and is technically savvy enough to constantly navigate the Chrome settings to look for managed browser labels, there is no real visual indication that a browser has been hijacked.”
Chrome extensions are sometimes perceived as remoted dangers, however current occasions like a wave of hijacks impacting professional extensions utilized by hundreds of thousands proved in any other case.
BleepingComputer contacted Google concerning the new assault and can replace our story if we obtain a reply.
