Checkmarx researchers found PyPI malware posing as crypto pockets instruments. These malicious packages stole non-public keys and restoration phrases, concentrating on wallets like Metamask, Belief Pockets, and Exodus.
The cybersecurity researchers at Checkmarx uncovered a sequence of recent provide chain assaults that exploited the Python Bundle Index (PyPI) in September 2024 utilizing malicious packages to focus on cryptocurrency wallets.
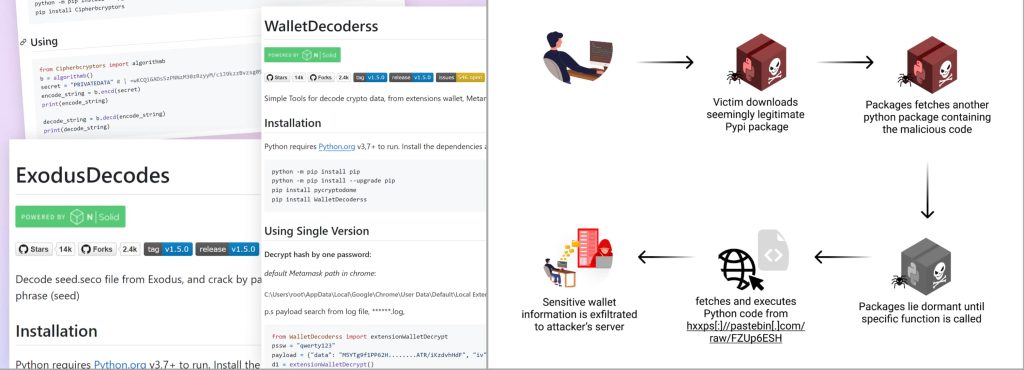
The assault concerned a brand new consumer on the platform who uploaded a number of malicious packages designed to steal delicate pockets information, together with non-public keys and mnemonic phrases. These packages recognized as “AtomicDecoderss,” “TrustDecoderss,” “WalletDecoderss,” and “ExodusDecodes,” focused cryptocurrency wallets together with Atomic, Belief Pockets, Metamask, Ronin, TronLink, and Exodus.
In accordance with the Checkmarx report shared with Hackread.com forward of publishing on Tuesday, every package deal got here with a professionally written README file, full with set up directions, utilization examples, and even “best practices” for digital environments.
Much more regarding, these paperwork included faux statistics, making the packages look like well-maintained and widespread initiatives, thus rising their credibility and obtain rely.
One of many key techniques utilized by the attacker was the distribution of performance throughout a number of dependencies. Six of the malicious packages relied on a dependency referred to as “cipherbcryptors,” which contained the core malicious code. Within the context of a cyberattack, dependencies confer with any exterior parts, methods, software program, or third-party providers that a company depends upon to operate correctly.
Additional evaluation revealed that risk actors closely obfuscated the code inside the “cipherbcryptors” package deal, making it tough for automated safety instruments and cybersecurity researchers to establish its malicious intent.
Not like others, these malicious packages didn’t begin infecting the system instantly upon set up. As an alternative, they remained inactive till the consumer tried to make use of sure options. As soon as the consumer started utilizing one of many options marketed by the risk actors, the malware would activate and entry the focused consumer’s cryptocurrency pockets.
It then stole vital data, resembling non-public keys and restoration phrases, that are wanted to regulate and entry cryptocurrency wallets. The stolen data was then encoded and despatched to a server managed by the attacker.
The impression of the sort of provide chain assault could be extreme for the victims. With entry to non-public keys and restoration phrases, attackers can rapidly drain cryptocurrency wallets. As a result of irreversible nature of blockchain transactions, as soon as funds are stolen, recovering them is sort of inconceivable.
Due to this fact, software program builders and unsuspecting customers must be cautious of such assaults, particularly when downloading packages from the PyPI platform, notably people who supply cryptocurrency-related providers and embody entry to wallets. Cybersecurity coaching for workers can be vital in defending in opposition to these assaults, making safety a matter of widespread sense.
RELATED TOPICS
- OpenSSF Launches Malicious Packages Repository
- Crypto Stealing PyPI Malware Hits Each Home windows, Linux Customers
- PyPI Suspends New Tasks, Customers On account of Malicious Packages
- Hackers Exploit PyPI to Infiltrate Programs with Python Packages
- Luna Grabber Malware Hits Roblox Devs By means of npm Packages