A brand new Android malware named NGate can steal cash from cost playing cards by relaying to an attacker’s machine the info learn by the near-field communication (NFC) chip.
Particularly, NGate allows attackers to emulate victims’ playing cards and make unauthorized funds or withdrawal money from ATMs..
The marketing campaign has been energetic since November 2023 and is linked to a current report from ESET on the elevated use of progressive net apps (PWAs) and superior WebAPKs to steal banking credentials from customers within the Czechia.
In analysis revealed at the moment, the cybersecurity firm says that NGate malware was additionally used through the marketing campaign in some circumstances to carry out direct money theft.
Stealing card knowledge by way of NFC chip
The assaults begin with malicious texts, automated calls with pre-recorded messages, or malvertising to trick victims into putting in a malicious PWA, and later WebAPKs, on their units.
These net apps are promoted as pressing safety updates and use the official icon and login interface of the focused financial institution to steal consumer entry credentials.
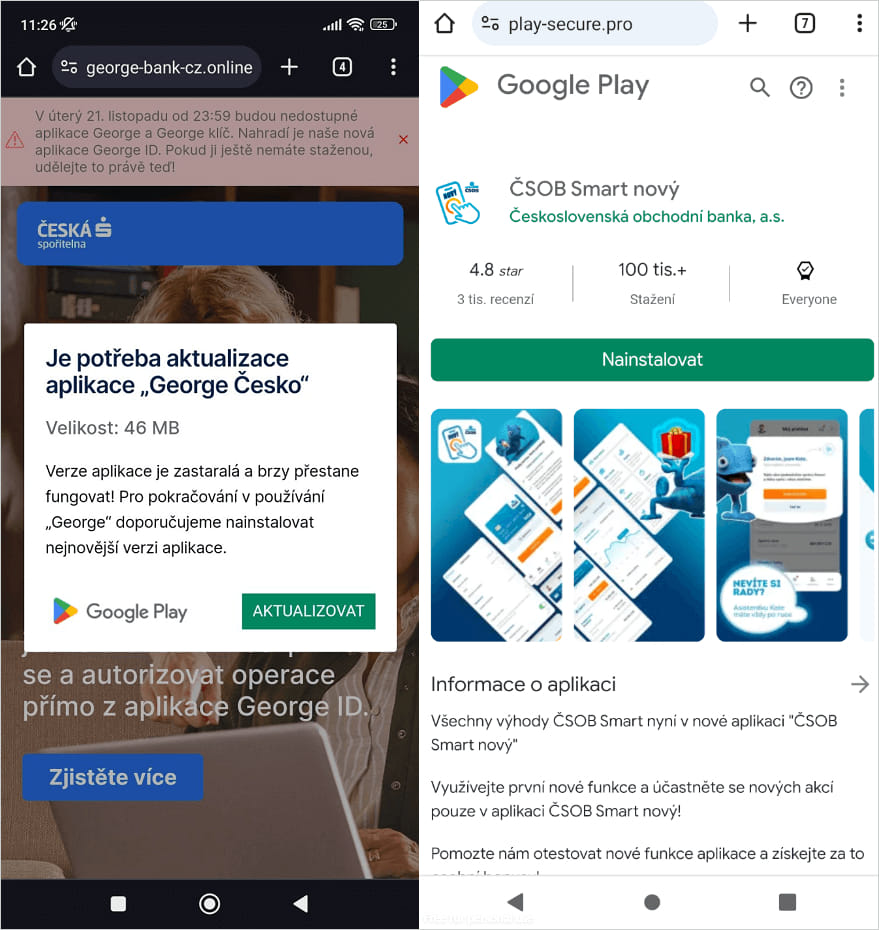
Supply: ESET
These apps don’t require any permission when put in. As a substitute, they abuse the API of the online browser they run in to get the required entry to the machine’s {hardware} parts.
As soon as the phishing step is finished by way of the WebAPK, the sufferer is tricked into additionally putting in NGate by way of a subsequent step within the second assault section.
Upon set up, the malware prompts an open-source part known as ‘NFCGate‘ that was developed by college researchers for NFC testing and experimentation.
The device helps on-device capturing, relaying, replaying, and cloning options, and doesn’t all the time require the machine to be “rooted” as a way to work.
NGate makes use of the device to seize NFC knowledge from cost playing cards in shut proximity to the contaminated machine after which relay it to the attacker’s machine, both instantly or via a server.
The attacker might save this knowledge as a digital card on their machine and replay the sign on ATMs that use NFC to withdraw money, or make a cost at a point-of-sale (PoS) system.
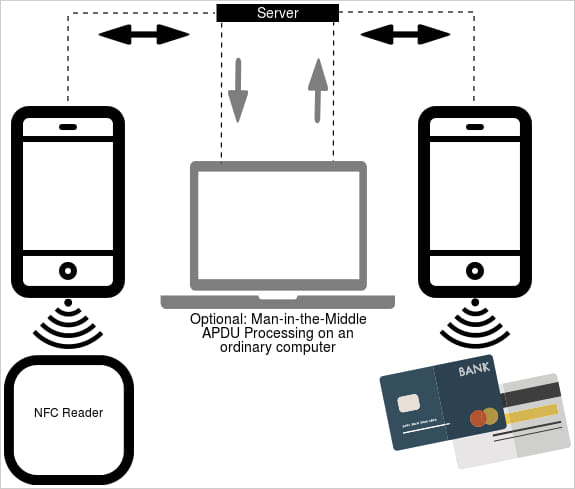
Supply: ESET
In a video demonstration, ESET’s malware researcher Lukas Stefanko additionally exhibits how the NFCGate part in NGate can be utilized to scan and seize card knowledge in wallets and backpacks. On this situation, an attacker at a retailer might obtain the info via a server and make a contactless cost utilizing the sufferer’s card.
Stefanko notes that the malware may also be used to clone the distinctive identifiers of some NFC entry playing cards and tokens to get into restricted areas.
Buying the cardboard PIN
A money withdrawal at most ATMs requires the cardboard’s PIN code, which the researchers say that it’s obtained by social engineering the sufferer.
After the PWA/WebAPK phishing step is finished, the scammers name the sufferer, pretending they’re a financial institution worker, informing them of a safety incident that impacts them.
They then ship an SMS with a hyperlink to obtain NGate, supposedly an app for use for verifying their present cost card and PIN.
As soon as the sufferer scans the cardboard with their machine and enters the PIN to “verify” it on the malware’s phishing interface, the delicate info is relayed to the attacker, enabling the withdrawals.
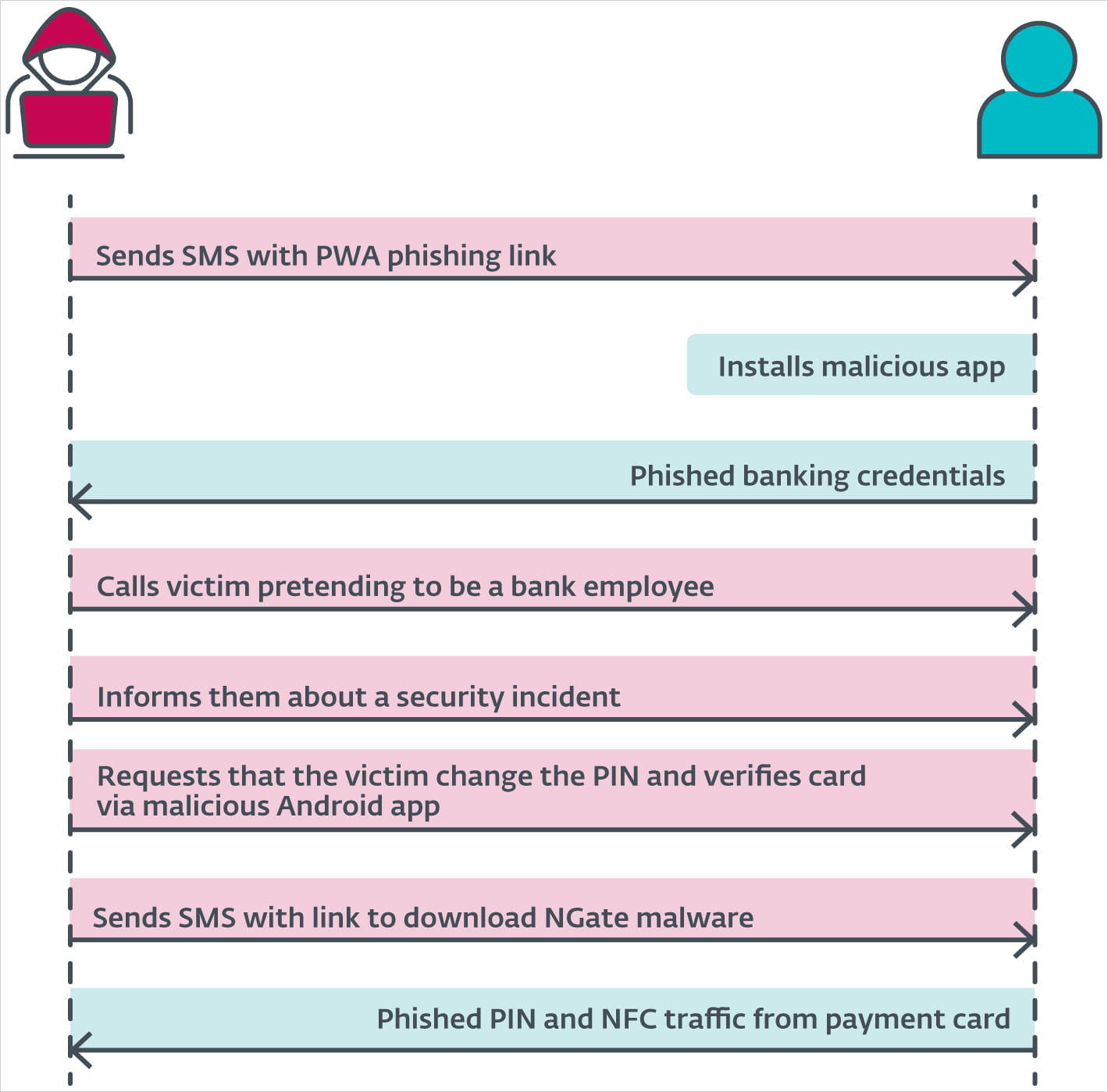
Supply: ESET
The Czech police already caught one of many cybercriminals performing these withdrawals in Prague, however because the tactic might achieve traction, posing a big danger for Android customers.
ESET additionally highlights the opportunity of cloning space entry tags, transport tickets, ID badges, membership playing cards, and different NFC-powered applied sciences, so direct cash loss is not the one dangerous situation.
In case you are not actively utilizing NFC, you possibly can mitigate the chance by disabling your machine’s NFC chip. On Android, head to Settings > Related units > Connection preferences > NFC and switch the toggle to the off place.
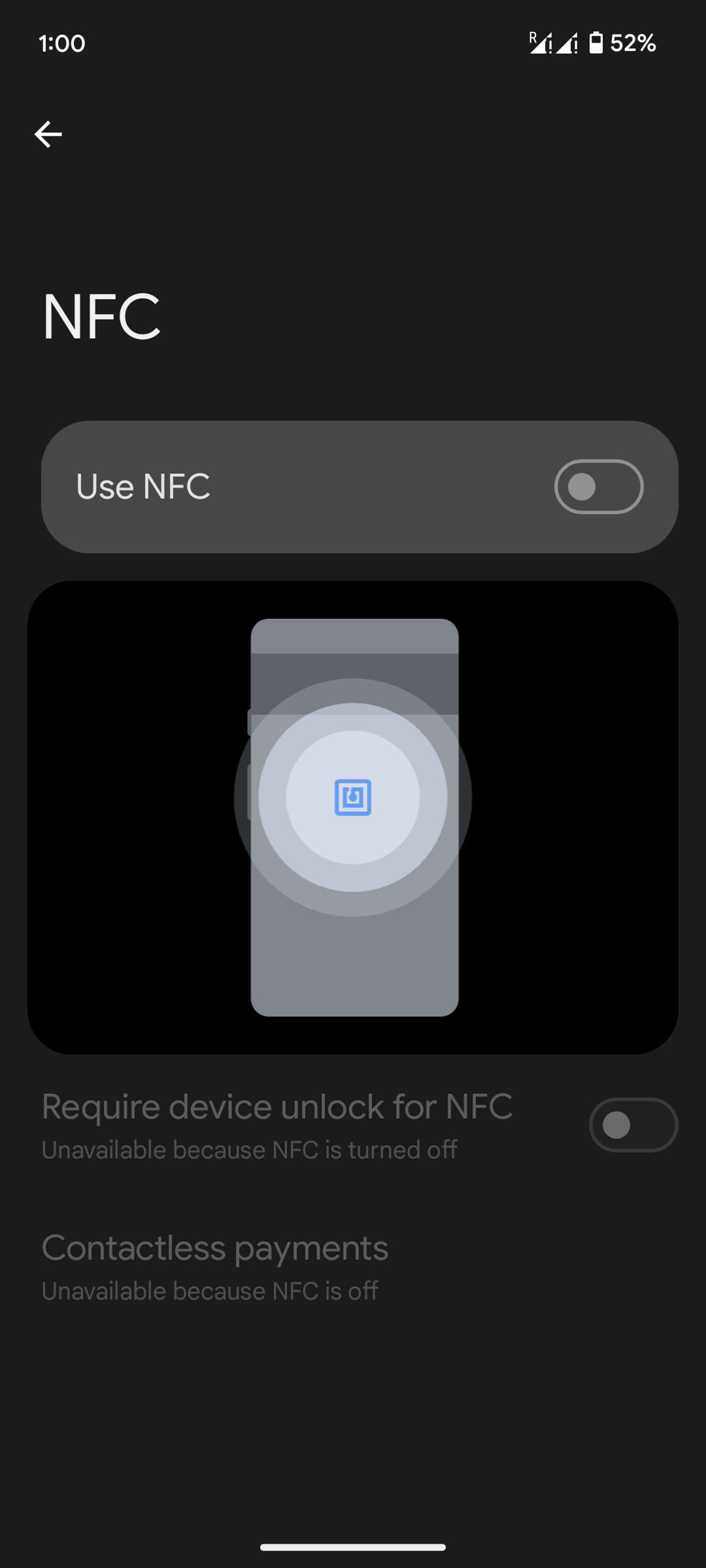
In the event you want NFC activated always, scrutinize all app permissions and prohibit entry solely to those who want it; solely set up financial institution apps from the establishment’s official webpage or Google Play, and make sure the app you are utilizing is not a WebAPK.
WebAPKs are often very small in dimension, are put in straight from a browser web page, don’t seem beneath ‘/knowledge/app’ like commonplace Android apps, and present atypically restricted info beneath Settings > Apps.
