North Korean hackers are utilizing a brand new Linux variant of the FASTCash malware to contaminate the fee change methods of monetary establishments and carry out unauthorized money withdrawals.
Earlier variants of FASTCash focused Home windows and IBM AIX (Unix) methods, however a brand new report by safety researcher HaxRob reveals a beforehand undetected Linux model that targets Ubuntu 22.04 LTS distributions.
Cash-stealing historical past
CISA first warned in regards to the FASTCash ATM cash-out scheme in December 2018, attributing the exercise to the state-backed North Korean hacking group generally known as ‘Hidden Cobra.’
In accordance with the company’s investigations, the menace actors have been utilizing FASTCash in operations since a minimum of 2016, stealing tens of thousands and thousands of {dollars} per incident in simultaneous ATM withdrawal assaults in 30 international locations or extra.
In 2020, the U.S. Cyber Command highlighted the menace as soon as once more, linking the revived FASTCash 2.0 exercise to APT38 (Lazarus).
A yr later, indictments had been introduced for 3 North Koreans allegedly concerned in these schemes, accountable for the theft of over $1.3 billion from monetary institutes worldwide.
Cashing out from Linux
The most recent variant noticed by HaxRob was first submitted to VirusTotal in June 2023 and options intensive operational similarities to earlier Home windows and AIX variants.
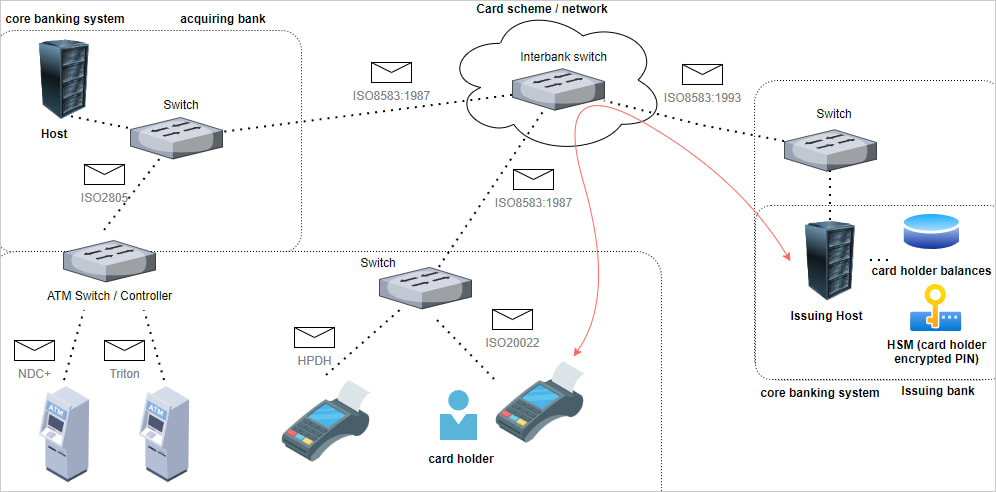
It comes within the type of a shared library that’s injected right into a working course of on a fee change server with the assistance of the ‘ptrace’ system name, hooking it into community features.
These switches are intermediaries dealing with the communication between ATMs/PoS terminals and the financial institution’s central methods, routing transaction requests and responses.
The malware intercepts and manipulates ISO8583 transaction messages used within the monetary business for debit and bank card processing.
Particularly, the malware targets messages that concern declines of the transactions on account of inadequate funds within the cardholder’s account and replaces the “decline” response with “approve.”
Supply: doubleagent.internet
The manipulated message additionally incorporates a random amount of cash between 12,000 and 30,000 Turkish Lira ($350 – $875) to authorize the requested transaction.
As soon as the manipulated message is distributed again to the financial institution’s central methods containing the approval codes (DE38, DE39) and the quantity (DE54), the financial institution approves the transaction, and a cash mule performing on behalf of the hackers withdraws the money from an ATM.
As of its discovery, the Linux variant of FASTCash had no detections on VirusTotal, which means it may evade most traditional safety instruments, permitting the menace actors to carry out transactions undeterred.
HaxRob additionally stories {that a} new Home windows model was submitted on VT in September 2024, indicating that the hackers are actively engaged on evolving all of the items of their toolset.
