A brand new malware named ‘Cuttlefish’ has been noticed infecting enterprise-grade and small workplace/residence workplace (SOHO) routers to observe information that passes by way of them and steal authentication info.
Lumen Applied sciences’ Black Lotus Labs examined the brand new malware and stories that Cuttlefish creates a proxy or VPN tunnel on the compromised router to exfiltrate information discreetly whereas bypassing safety measures that detect uncommon sign-ins.
The malware may carry out DNS and HTTP hijacking inside personal IP areas, interfering with inner communications and presumably introducing extra payloads.
Though Cuttlefish has some code that overlaps with HiatusRat, which has been beforehand noticed in campaigns that aligned with Chinese language state pursuits, there are not any concrete hyperlinks between the 2, and attribution was not possible.
Black Lotus Labs says the malware has been energetic since a minimum of July 2023. It’s at present operating an energetic marketing campaign concentrated in Turkey, with a number of infections elsewhere impacting satellite tv for pc telephone and information heart companies.
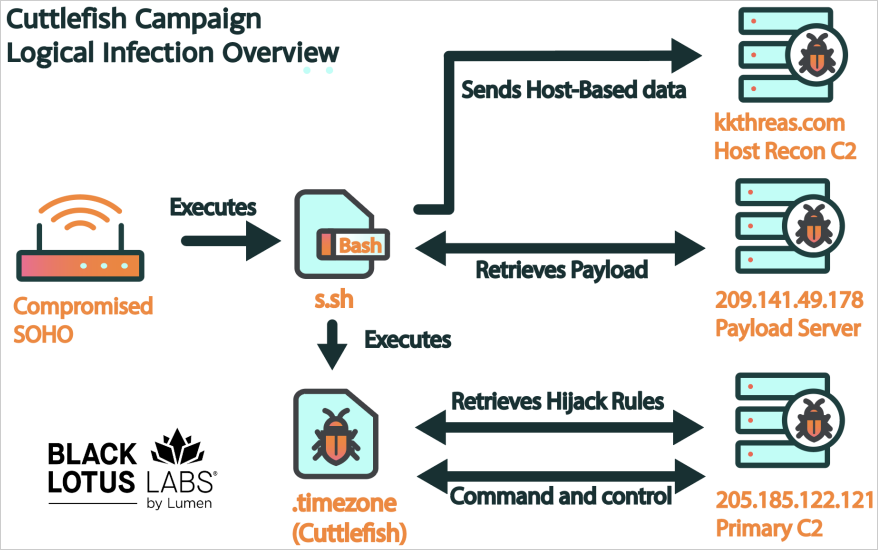
Cuttlefish infections
The strategy for the preliminary an infection of the routers has but to be decided, nevertheless it might contain exploiting identified vulnerabilities or brute-forcing credentials.
As soon as entry is gained to a router, a bash script (“s.sh”) is deployed and begins accumulating host-based information, together with particulars on listing itemizing, operating processes, and energetic connections.
The script downloads and executes the first Cuttlefish payload (“.timezone”), which is loaded into reminiscence to evade detection whereas the downloaded file is wiped from the file system.
Black Lotus Labs stories that Cuttlefish is obtainable in varied builds supporting ARM, i386, i386_i686, i386_x64, mips32, and mips64, overlaying most router architectures.
Supply: Black Lotus Labs
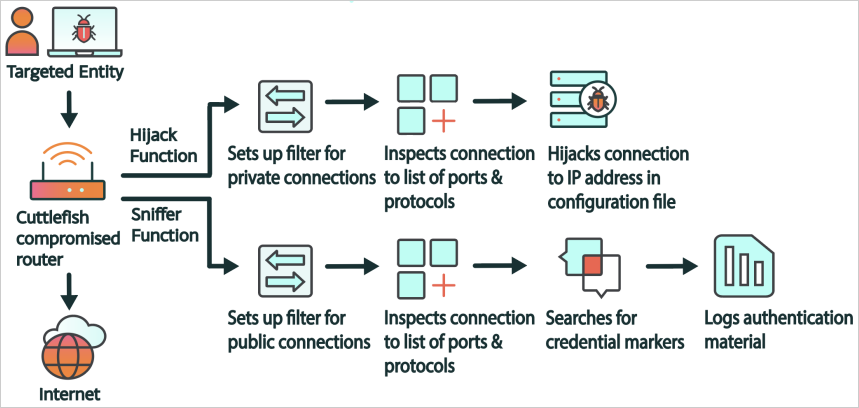
Monitoring your site visitors
Upon execution, Cuttlefish makes use of a packet filter to observe all connections by way of the gadget, and when it detects particular information, it performs a specific actions primarily based on rulesets that are frequently up to date from the attacker’s command and management (C2) server.
The malware passively sniffs packets looking for “credential markers” throughout the site visitors, reminiscent of usernames, passwords, and tokens particularly related to public cloud-based companies like Alicloud, AWS, Digital Ocean, CloudFlare, and BitBucket.
“This caught our attention as many of these services would be used to store data otherwise found within the network,” explains the Black Lotus Labs report.
“Capturing credentials in transit could allow the threat actors to copy data from cloud resourcesthat do not have the same type of logging or controls in place as traditional network perimeters.”
Knowledge matching these parameters is logged regionally, and as soon as it reaches a sure measurement (1048576 bytes), it’s exfiltrated to the C2 utilizing a peer-to-peer VPN (n2n) or proxy tunnel (socks_proxy) created on the gadget.
Supply: Black Lotus Labs
For site visitors destined to non-public IP addresses, DNS requests are redirected to a specified DNS server, and HTTP requests are manipulated to redirect site visitors to actor-controlled infrastructure utilizing HTTP 302 error codes.
“We suspect this capability enables Cuttlefish to hijack internal (a.k.a. “east-west”) traffic through the router, or site-to-site traffic where there is a VPN connection established between routers,” clarify the researchers.
“The additional function opens the door to secured resources that are not accessible via the public internet.”
Supply: Black Lotus Labs
Defending towards Cuttlefish
Cuttlefish is a severe menace to organizations worldwide because it allows attackers to bypass safety measures like community segmentation and endpoint monitoring and dwell undetected in cloud environments for prolonged durations.
Black Lotus Labs means that company community admins eradicate weak credentials, monitor for uncommon logins from residential IPs, safe site visitors with TLS/SSL, examine gadgets for rogue iptables or different irregular recordsdata, and routinely reboot them.
When establishing distant connections to high-value property, it’s advisable to make use of certificates pinning to stop hijacking.
For SOHO router customers, it is beneficial to reboot the gadgets frequently, apply the most recent obtainable firmware updates, change default passwords, block distant entry to the administration interface, and change them after they attain end-of-life (EoL).