F5 has fastened two high-severity BIG-IP Subsequent Central Supervisor vulnerabilities, which might be exploited to achieve admin management and create hidden rogue accounts on any managed belongings.
Subsequent Central Supervisor permits directors to manage on-premises or cloud BIG-IP Subsequent situations and companies by way of a unified administration person interface.
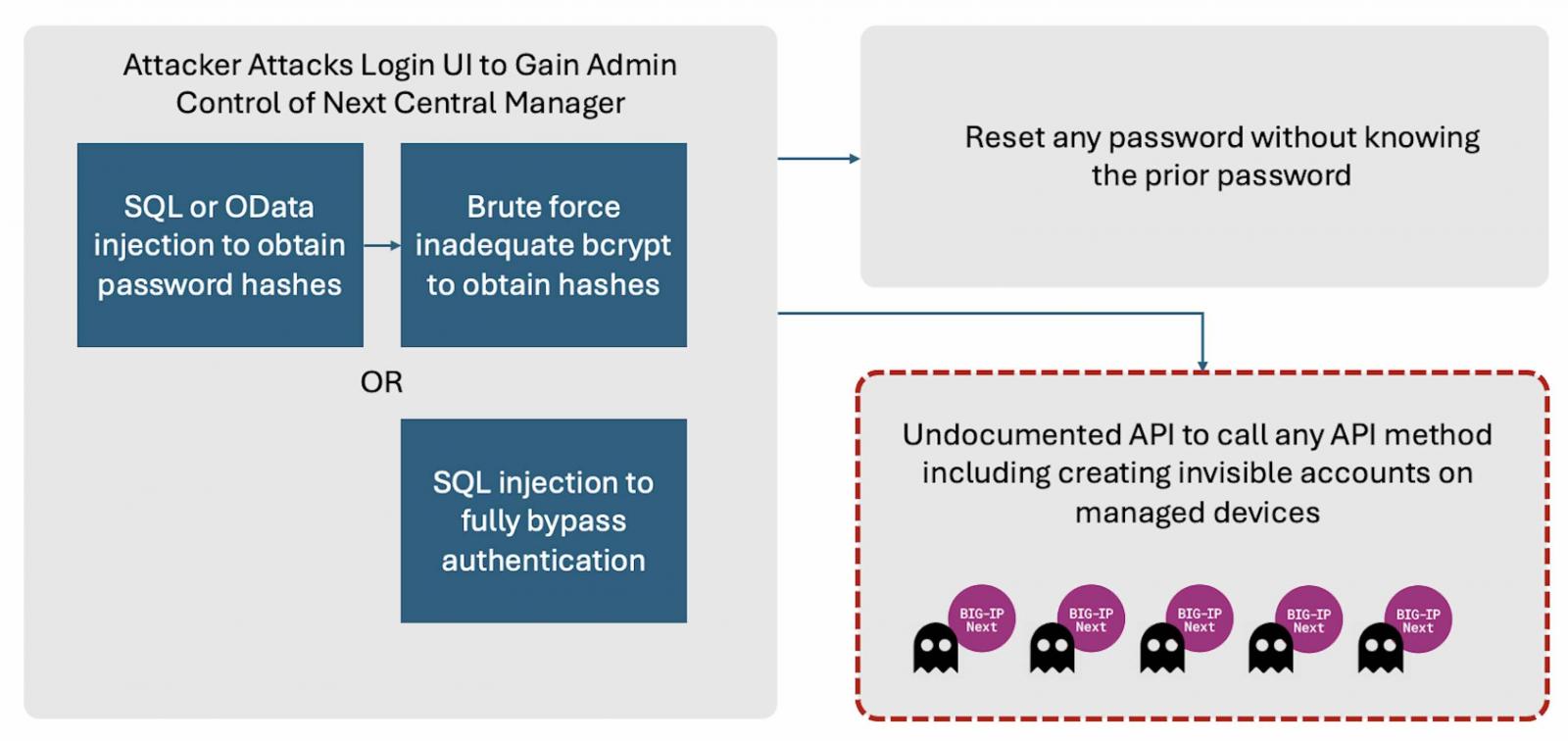
The failings are an SQL injection vulnerability (CVE-2024-26026) and an OData injection vulnerability (CVE-2024-21793) discovered within the BIG-IP Subsequent Central Supervisor API that might permit unauthenticated attackers to execute malicious SQL statements on unpatched units remotely.
SQL injection assaults contain injecting malicious SQL queries into enter fields or parameters in database queries. This exploits vulnerabilities within the software’s safety and permits unintended SQL instructions to execute, leading to unauthorized entry, information breaches, and system takeovers.
Provide chain safety agency Eclypsium, which reported the issues and shared a proof-of-concept exploit on Wednesday, says that rogue accounts created after compromising an unpatched occasion are usually not seen from Subsequent Central Supervisor and may thus be used for malicious persistence inside a sufferer’s atmosphere.
“The management console of the Central Manager can be remotely exploited by any attacker able to access the administrative UI via CVE 2024-21793 or CVE 2024-26026. This would result in full administrative control of the manager itself,” Eclypsium says.
“Attackers can then take advantage of the other vulnerabilities to create new accounts on any BIG-IP Next asset managed by the Central Manager. Notably, these new malicious accounts would not be visible from the Central Manager itself.”
PoC exploit and momentary mitigation accessible
Based on F5’s suggestions, directors who cannot instantly set up immediately’s safety updates ought to prohibit Subsequent Central Supervisor entry to trusted customers over a safe community to mitigate assault dangers.
Fortunately, in response to Eclypsium, there isn’t a proof that the 2 safety vulnerabilities have been exploited in assaults.
Whereas adoption charges for F5’s BIG-IP Subsequent Central Supervisor are at the moment unknown, Shodan at the moment tracks over 10,000 F5 BIG-IP units with administration ports uncovered on-line.
In November, F5 warned prospects that “skilled” attackers had been exploiting two vital BIG-IP vulnerabilities (CVE-2023-46747 and CVE-2023-46748) fastened one month earlier than to hack into unpatched units, executing malicious code and erasing indicators of the breach.
Two years in the past, CISA additionally cautioned of widespread exploitation of one other F5 BIG-IP flaw (CVE-2022-1388)—additionally permitting machine takeover—throughout authorities and personal sector networks and shared steering to dam the continuing assaults.
