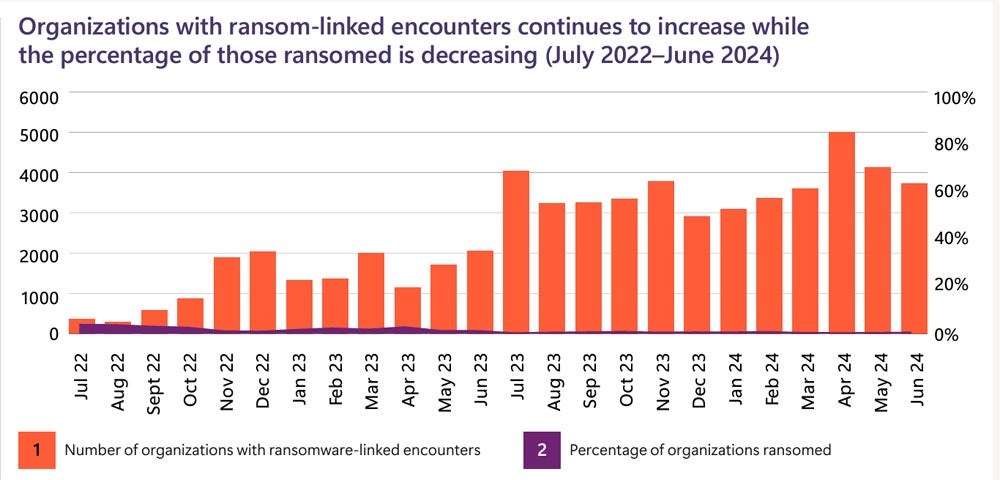
The variety of tried ransomware assaults on Microsoft prospects globally have grown dramatically within the final yr, based on Microsoft’s Digital Protection report, launched on Oct. 15. Nonetheless, developments in automated assault disruption applied sciences have led to fewer of those assaults reaching the encryption stage.
Microsoft reported 600 million cybercriminal and nation-state assaults occurring every day. Whereas ransomware makes an attempt elevated by 2.75 occasions, profitable assaults involving knowledge encryption and ransom calls for dropped by three-fold.
Important assault varieties embrace deepfakes, e-commerce theft
Microsoft says it “tracks more than 1,500 unique threat groups — including more than 600 nation-state threat actor groups, 300 cybercrime groups, 200 influence operations groups, and hundreds of others.” The highest 5 ransomware households — Akira, Lockbit, Play, Blackcat, and Basta — accounted for 51% of documented assaults.
In response to the report, attackers most frequently exploit social engineering, id compromises, and vulnerabilities in public-facing purposes or unpatched working techniques. As soon as inside, they typically set up distant monitoring instruments or tamper with safety merchandise. Notably, 70% of profitable assaults concerned distant encryption, and 92% focused unmanaged units.
Different main sorts of assaults included:
- Infrastructure assaults.
- Cyber-enabled monetary fraud.
- Assaults on e-commerce areas, the place bank card transactions don’t require the cardboard to be bodily current.
- Impersonation.
- Deepfakes.
- Account takeover.
- Identification and social engineering assaults — most (99%) of which have been password theft assaults.
- SIM swapping.
- Assist desk social engineering, the place attackers impersonate prospects to reset passwords or join new units.
- Credential phishing, significantly by way of phishing-as-a-service initiatives. Typically these are triggered by HTML or PDF attachments containing malicious URLs.
- DDoS assaults, which precipitated a worldwide outage earlier this yr.
Antivirus tampering was additionally a significant participant within the earlier yr: Over 176,000 incidents Microsoft Defender XDR detected in 2024 concerned tampering with safety settings.
SEE: Ransomware actors can goal backup knowledge to attempt to pressure a cost.
Nation-state, financially motivated actors share ways
Each financially-motivated menace actors and nation-state actors more and more use the identical info stealers and command-and-control frameworks, Microsoft discovered. Curiously, financially-motivated actors now launch cloud id compromise assaults — a tactic beforehand related to nation-state attackers.
“This year, state-affiliated threat actors increasingly used criminal tools and tactics — and even criminals themselves — to advance their interests, blurring the lines between nation-state backed malign activity and cybercriminal activity,” the report said.
Microsoft tracks main menace actor teams from Russia, China, Iran, and North Korea. These nation-states might both leverage monetary menace actors for revenue or flip a blind eye to their actions inside their borders.
In response to Tom Burt, Microsoft’s company vice chairman of buyer safety and belief, the ransomware concern highlights the connection between nation-state actions and financially motivated cybercrime. This downside is exacerbated by international locations that both exploit these operations for revenue or fail to take motion in opposition to cybercrime inside their borders.
Knowledgeable Evan Dornbush, former NSA cybersecurity professional, gives views on the matter:
“This report signals one trend currently getting little attention and likely to define the future of cyber: the amount of money criminals can earn,” he mentioned in an electronic mail to TechRepublic. “Per the Microsoft report, government, as a sector, only makes up 12% of the aggressors’ targeting sets. The vast majority of victims are in the private sector.”
The sectors most focused by nation-state menace actors this yr have been:
- IT.
- Schooling .
- Authorities.
- Assume tanks and NGOs.
- Transportation.
Each attackers and defenders use generative AI
Generative AI introduces a brand new set of questions. Microsoft recommends limiting generative AI’s entry to delicate knowledge and making certain that knowledge governance insurance policies are utilized to its use. The report outlines AI’s vital impacts on cybersecurity:
- Each attackers and defenders more and more use AI instruments.
- Nation-state actors can generate misleading audio and video with AI.
- AI spear phishing, résumé swarming, and deepfakes at the moment are widespread.
- Standard strategies of limiting overseas affect operations might now not work.
- AI insurance policies and rules can mitigate some threat related to using AI instruments.
- Though many governments agree on a necessity for safety as an necessary issue within the improvement of AI, completely different governments pursue it in several methods.
“The sheer volume of attacks must be reduced through effective deterrence,” Burt defined, “and while the industry must do more to deny the efforts of attackers via better cybersecurity, this needs to be paired with government action to impose consequences that further discourage the most harmful cyberattacks.”
How organizations can stop widespread cyberattacks
The Microsoft report accommodates actions organizations can take to stop particular sorts of assaults. TechRepublic distilled some actionable insights that apply throughout the board:
- Disrupt assaults on the method layer, which implies implementing insurance policies similar to for multi-factor authentication and assault floor discount.
- Equally, use “secure-by-default” settings, which make multi-factor authentication necessary.
- Use sturdy password safety.
- Check pre-configured safety settings, similar to safety defaults or managed Conditional Entry insurance policies, in report-only mode to know their potential influence earlier than going stay.
- Classify and label delicate knowledge, and have DLP, knowledge lifecycle, and Conditional Entry insurance policies round high-risk knowledge and high-risk customers.
Microsoft put its Safe Future Initiative in place this yr, after the Chinese language intrusion into Microsoft authorities electronic mail accounts in July 2023.