A Linux malware named “perfctl” has been focusing on Linux servers and workstations for no less than three years, remaining largely undetected by excessive ranges of evasion and the usage of rootkits.
In accordance with Aqua Nautilus researchers who found perfctl, the malware possible focused thousands and thousands of Linux servers lately and probably brought about infections in a number of hundreds of them.
That is primarily based on quite a few reviews by victims of the malware submitted to on-line dialogue boards, all containing indicators of compromise completely related to perfctl exercise.
In accordance with Aqua Nautilus, the first objective of perfctl is for cryptomining, utilizing the compromised servers to mine the hard-to-trace Monero cryptocurrency. Nonetheless, it may very well be simply used for extra damaging operations.
An infection chain
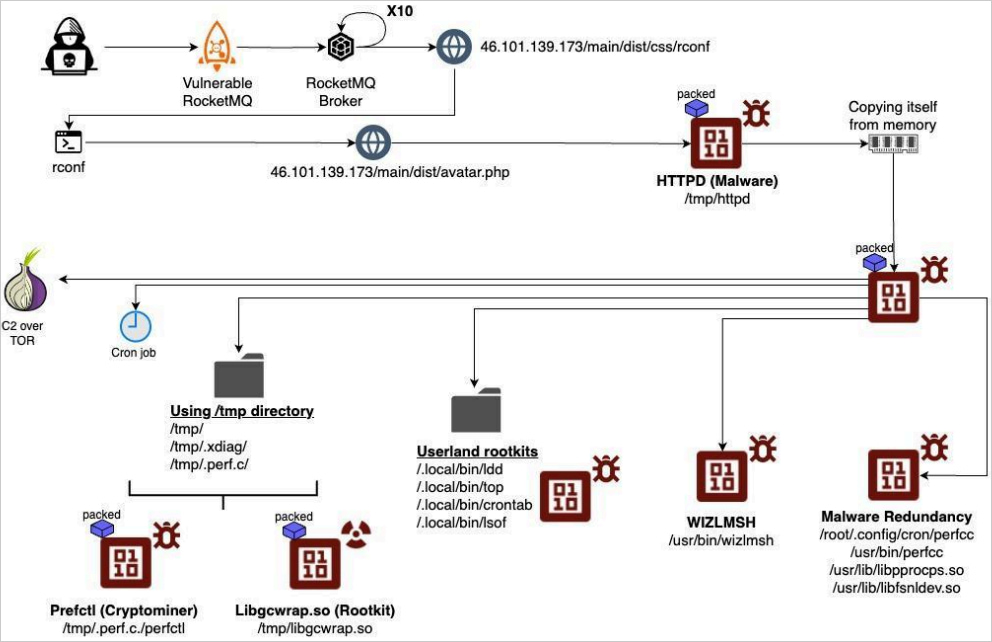
Aqua Nautilus believes that the risk actors exploit misconfigurations or uncovered secrets and techniques to breach Linux servers. These misconfigurations vary from publicly accessible information that include credentials to uncovered login interfaces.
Supply: Aqua Nautilus
The researchers have additionally noticed exploitation of CVE-2023-33246, a distant command execution impacting Apache RocketMQ variations 5.1.0 and older, and CVE-2021-4034 (PwnKit), an elevation of privilege flaw in Polkit.
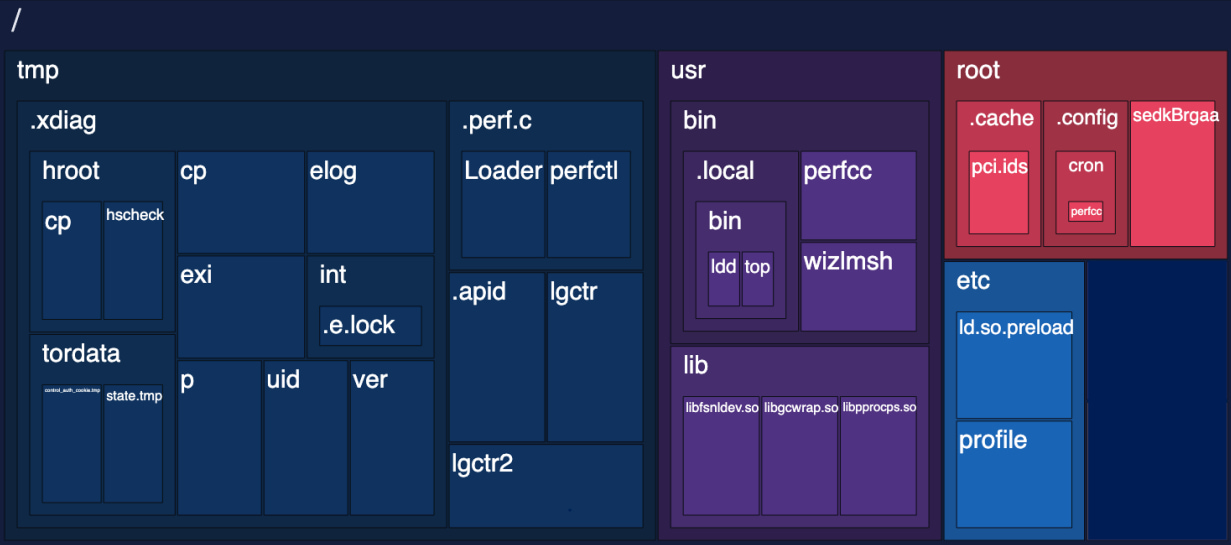
As soon as preliminary entry is established, the packed and obfuscated payload, named “httpd,” is downloaded from the attacker’s server and executed. It then copies itself within the /tmp listing underneath the “sh” identify after which deletes the unique binary.
The brand new course of assumes the identical identify (“sh”), basically mixing with regular Linux system operations.
Extra copies are created in different system places, comparable to “/root/.config,” “/usr/bin/” and “usr/lib” to make sure persistence within the case of a cleanup.
Supply: Aqua Nautilus
Predominant operation and evasion mechanisms
When launched, perfctl opens a Unix socket for inner communications and establishes an encrypted channel with the risk actor’s servers over TOR, making it unattainable to decipher the alternate.
It then drops a rootkit named ‘libgcwrap.so’ which hooks into varied system features to switch authentication mechanisms and intercept community visitors as wanted to facilitate evasion.
Extra userland rootkits are additionally deployed, changing the ldd, prime, crontab, and lsof utilities with trojanized variations, once more, stopping direct detection of the malware’s actions.
Lastly, an XMRIG miner is dropped onto the system and executed to mine Monero utilizing the server’s CPU sources.
Supply: Aqua Nautilus
The cryptominer communicates with the set mining swimming pools over TOR, so the community visitors is obscured, and the earnings can’t be traced.
In some instances, Aqua Nautilus has additionally seen the deployment of proxy-jacking software program giving the attackers a further monetization route, promoting unused community bandwidth by Bitping, Repocket, Speedshare, and different comparable providers.
Most customers turn out to be suspicious that their servers are contaminated after they discover that the CPU is at 100% utilization as a result of it mining for cryptocurrency.
Nonetheless, the malware is very evasive, finishing up the mining actions till a consumer logs into the server, which causes it to cease instantly and wait till the server is idle once more.
“I only became aware of the malware because my monitoring setup alerted me to 100% CPU utilization,” reported a consumer on Reddit.
“However, the process would stop immediately when I logged in via SSH or console. As soon as I logged out, the malware would resume running within a few seconds or minutes.”
Utilizing rootkits additionally makes it troublesome to take away because the processes are hidden from userland utilities and regular malware removing strategies, generally requiring customers to take it offline or boot by way of a dwell CD to examine the filesystem.
Nonetheless, because the an infection modifies and replaces authentic Linux information, the perfect suggestion is to wipe and reinstall the machine to make sure that nothing is left behind.
Detecting and stopping perfctl
Aqua Nautilus proposes a number of methods for detecting and stopping perfctl, which fall into 4 fundamental classes: system monitoring, community visitors evaluation, file and course of integrity monitoring, and proactive mitigation.
Relating to detection, the next ideas are supplied by Aqua Nautilus:
- Often examine /tmp, /usr, and /root directories for suspicious binaries masquerading as authentic system information.
- Monitor CPU utilization for spikes and processes like httpd and sh operating from sudden places.
- Scrutinize ~/.profile, ~/.bashrc, and /and so forth/ld.so.preload for unauthorized modifications.
- Seize and analyze community visitors for TOR-based connections to exterior IPs.
- Search for outbound connections to identified cryptomining swimming pools or proxy-jacking providers.
- Add the IPs shared within the report’s IoC part to a blocklist to disrupt communications with malicious hosts.
System admins ought to make sure that all identified flaws on internet-facing functions comparable to RocketMQ servers (CVE-2023-33246) and Polkit (CVE-2021-4043) are patched.
Additionally, it could be efficient to show off unused HTTP providers, use role-based entry controls, and apply the ‘noexec’ choice to essential directories like ‘/tmp’ and ‘/dev.shm.’
