KEY SUMMARY POINTS
- Focus Shift to Nuclear Business: The Lazarus Group, linked to North Korea, has shifted its targets to the nuclear business, marking a possible escalation from its earlier give attention to protection, aerospace, and cryptocurrency.
- Pretend Job Posting Ways: Their assaults, noticed in January 2024, make use of faux job postings (Operation DreamJob) to ship malicious recordsdata disguised as job assessments, having access to victims’ methods.
- Superior Malware Strategies: The group makes use of subtle instruments like Ranid Downloader and a novel plugin-based malware, “CookiePlus,” which operates in reminiscence, making it more durable for safety methods to detect.
- Exploitation of Vulnerabilities: Lazarus continues refining its ways, exploiting vulnerabilities like Google Chrome zero-day and leveraging modern malware like “RustyAttr” on macOS.
- Name for Warning: The rising sophistication and exercise of the Lazarus Group underscore the necessity for heightened cybersecurity measures, significantly in delicate industries.
Securelist by Kaspersky has revealed its newest risk intelligence report targeted on the actions of the infamous Lazarus hacking group, which, as we all know it, has hyperlinks to the North Korean authorities.
In response to Securelist’s analysis, the Lazarus Group has shifted its focus to concentrating on people inside the nuclear business these days. This means an upcoming escalation of their operations, as they beforehand targeting sectors like protection, aerospace, and cryptocurrency.
“We observed a similar attack in which the Lazarus group delivered archive files containing malicious files to at least two employees associated with the same nuclear-related organization over the course of one month,” the report learn.
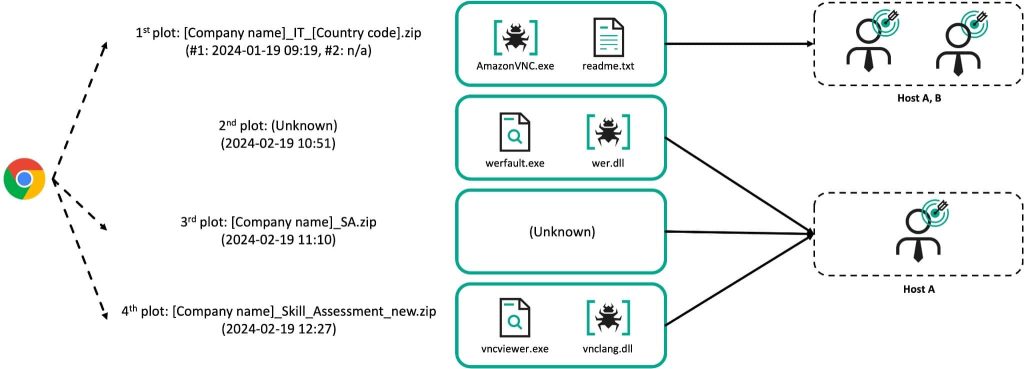
The assaults noticed by Kaspersky occurred in January 2024 and adopted the sample of utilizing faux job postings, a tactic often called the DeathNote marketing campaign or “Operation DreamJob.”
This entails creating faux job postings and engaging potential victims with tempting profession alternatives. Throughout the “interview” course of, malicious recordsdata are subtly launched, typically disguised as official evaluation checks.
The assault begins with an preliminary file disguised as job assessments for outstanding firms, which comprises a ZIP archive with malicious executables or trojanized official instruments like VNC viewers.
As soon as executed, the trojan prompts the sufferer to enter an IP handle offered by the attackers through separate communication channels like messenger apps. This grants the attackers unauthorized entry to the compromised machine, enabling them to maneuver laterally inside the community and doubtlessly steal delicate knowledge or disrupt important operations.
An XOR key’s generated based mostly on the IP handle to decrypt the interior assets of the VNC executable and unzip the information. The unzipped knowledge is then downloaded by Ranid Downloader, which fetches additional malicious payloads like MISTPEN, RollMid, LPEClient, Charamel Loader, ServiceChanger, and CookiePlus. The payload sort (DLL or shellcode) is decided by a flag inside the knowledge construction. The execution outcomes of those plugins are encrypted and despatched again to the C2 server.
A key innovation in these latest assaults is the introduction of “CookiePlus,” a novel plugin-based malware. This downloader operates primarily in reminiscence, loading malicious payloads dynamically. This evasive method makes it more durable for conventional safety options to detect and mitigate the risk.
The event of CookiePlus demonstrates the Lazarus Group’s steady efforts to refine its instruments and evade detection. By introducing new modular malware and adapting their ways, they intention to keep up a persistent presence inside focused networks and obtain their targets.
The group has been significantly lively these days. In November Group-IB found the Lazarus group’s new trojan, “RustyAttr,” which hides malicious code in prolonged attributes on macOS methods and in October the group exploited a Google Chrome zero-day vulnerability to focus on cryptocurrency traders with a misleading NFT recreation. This requires steady vigilance to safeguard your digital property.
RELATED TOPICS
- Lazarus Exploits Chrome 0-Day with Pretend NFT Sport
- North Korean Hackers Workforce Up with Play Ransomware
- Lazarus’ Magecart assault steal card knowledge from EU, US websites
- Lazarus Hits Blockchain Professionals with Pretend Video Conferencing
- Lazarus hackers suspected of concentrating on Indian area company