The Iranian state-backed risk actor tracked as APT42 is using social engineering assaults, together with posing as journalists, to breach company networks and cloud environments of Western and Center Jap targets.
APT42 was first documented by Mandiant in September 2022, who reported that the risk actors have been energetic since 2015, having carried out no less than 30 operations in 14 nations.
The espionage group, which is believed to be affiliated with Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps Intelligence Group (IRGC-IO), has been noticed focusing on non-governmental organizations, media shops, academic institutes, activists, and authorized providers.
Google risk analysts following APT42’s operations report that the hackers use malicious emails to contaminate their targets with two customized backdoors, particularly “Nicecurl” and “Tamecat,” which offer command execution and knowledge exfiltration capabilities.
Crafting on-line personas
APT42 assaults depend on social engineering and spear-phishing, with the final word aim of infecting targets’ gadgets with customized backdoors, permitting the risk actors to realize preliminary entry to the organizations’ networks.
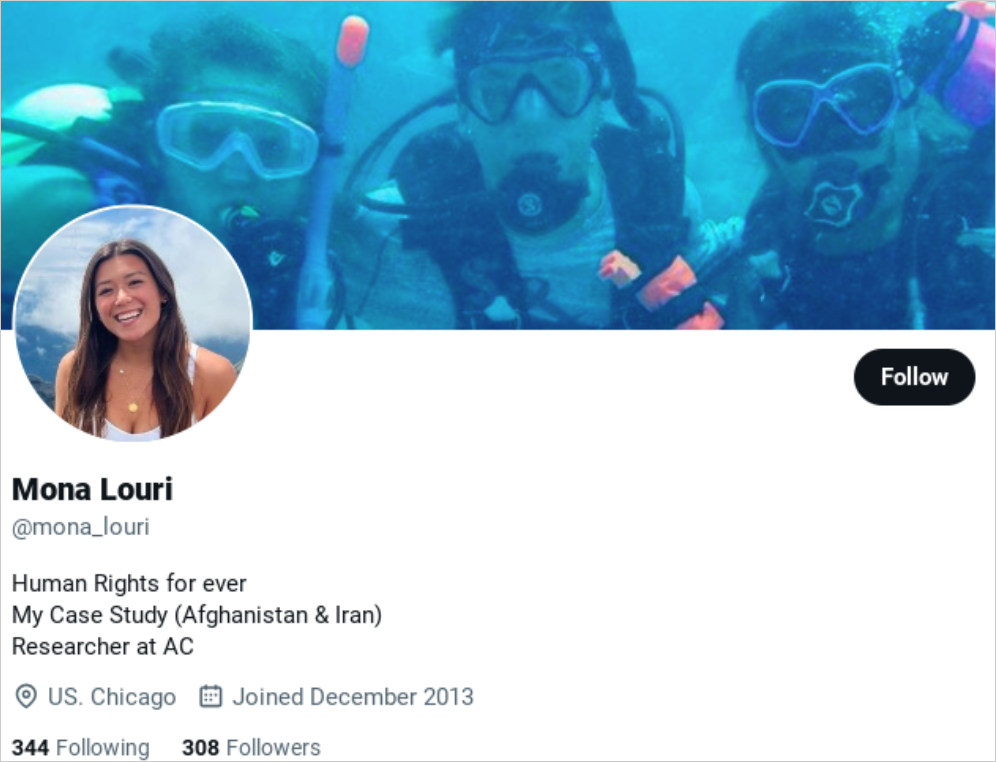
The assault begins with emails from on-line personas posing as journalists, NGO representatives, or occasion organizers despatched from domains that “typosquat” (use comparable URLs) to these of professional organizations.
Supply: Google
The media organizations impersonated by APT42 embrace the Washington Submit (U.S.), The Economist (UK), The Jerusalem Submit (IL), Khaleej Occasions (UAE), Azadliq (Azerbaijan), with Mandiant stating that the assaults usually use typosquatted domains like “washinqtonpost[.]press”.
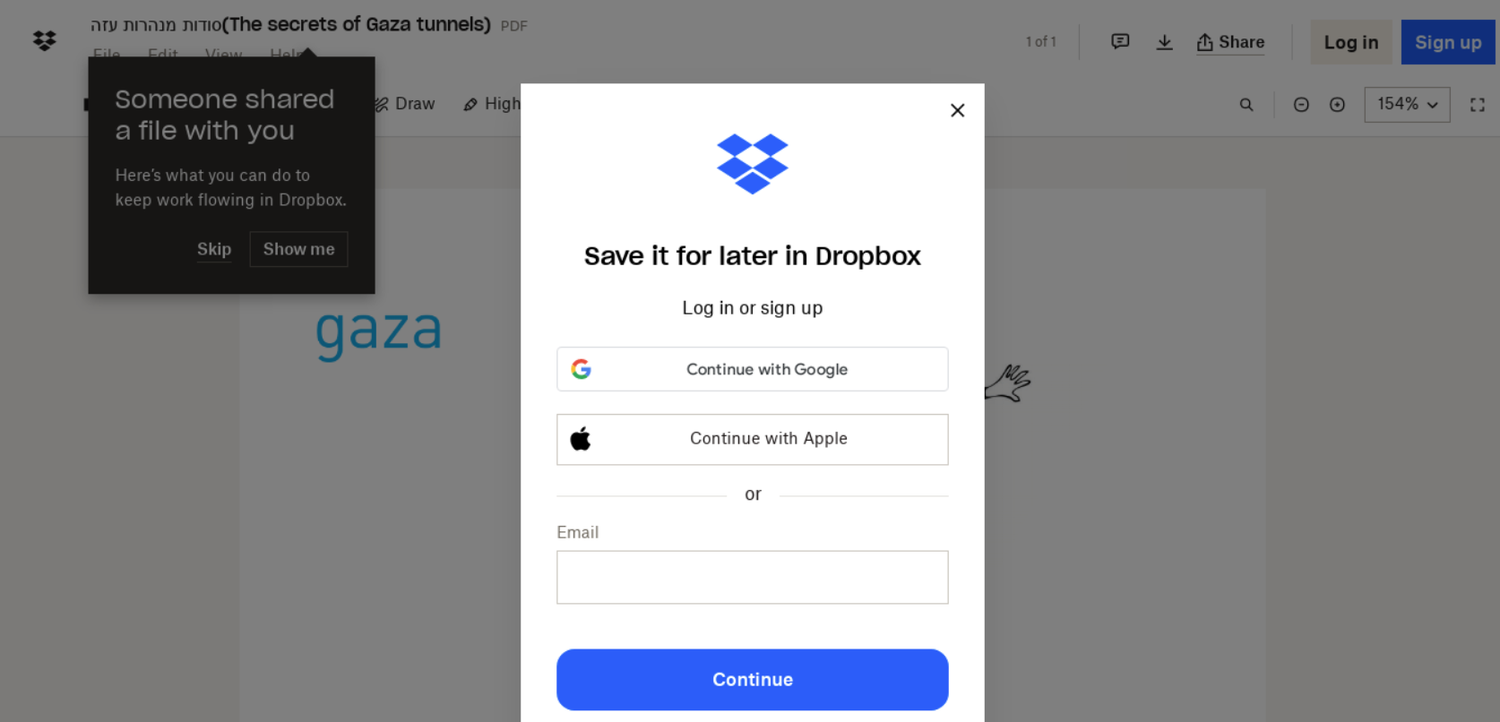
After the attackers change sufficient communication to construct belief with a sufferer, they ship a hyperlink to a doc associated to a convention or a information article, relying on the chosen lure matter.
Supply: Google
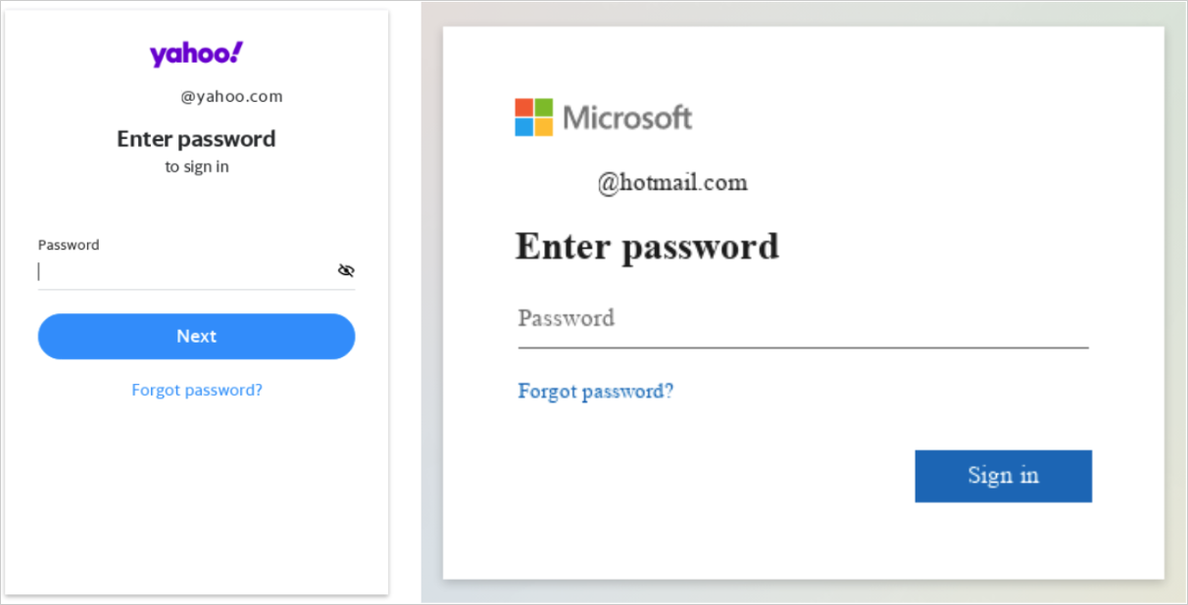
Clicking on the hyperlinks directs the targets to pretend login pages that mimic well-known providers like Google and Microsoft and even specialised platforms pertinent to the sufferer’s subject of labor.
These phishing websites harvest not solely the sufferer’s account credentials but in addition their multi-factor authentication (MFA) tokens.
Supply: Google
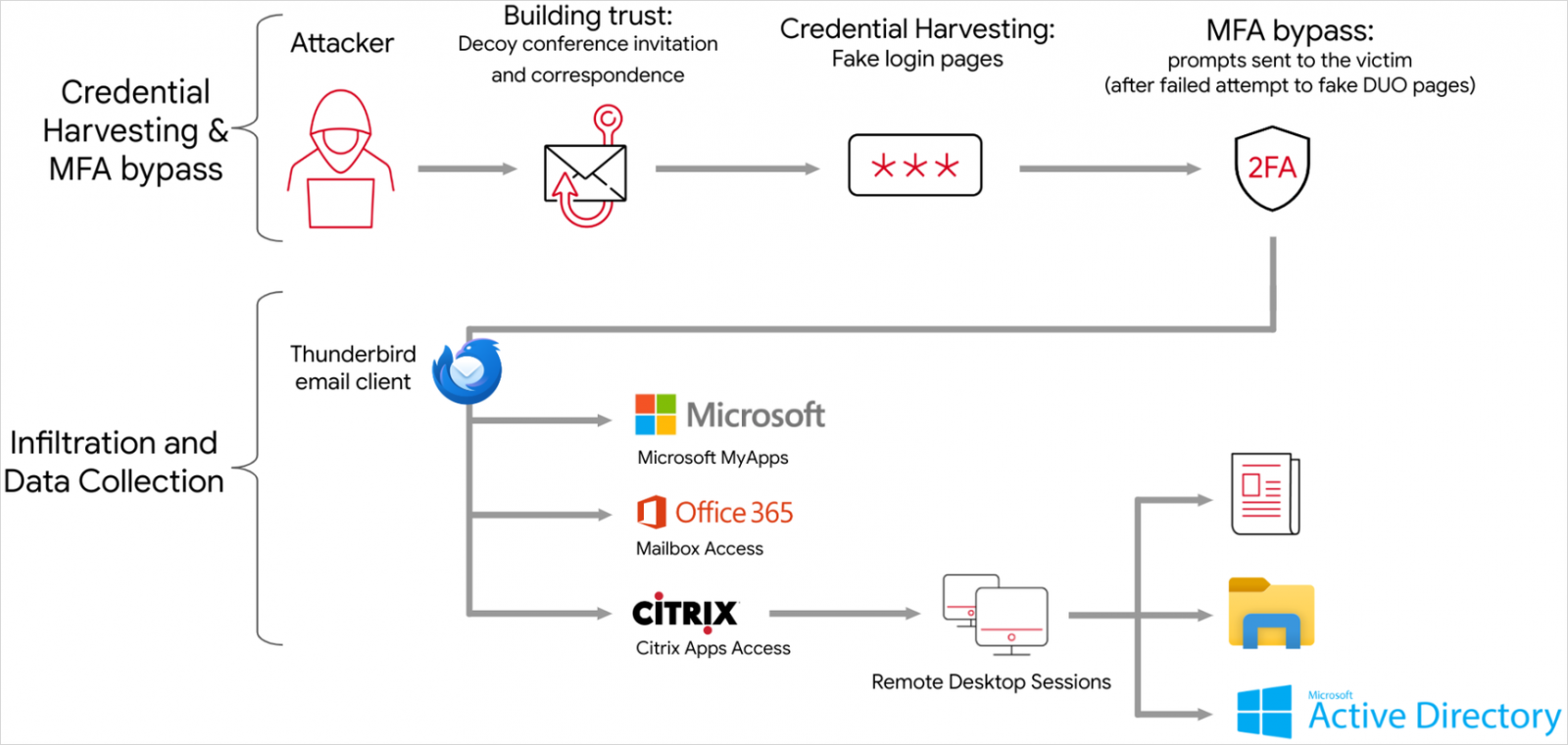
After stealing all knowledge required for hijacking the sufferer’s account, the hackers infiltrate the company community or cloud surroundings and accumulate delicate data akin to emails and paperwork.
Google studies that to evade detection and mix with regular operations, APT42 limits its actions to built-in options of the cloud instruments it has entry to, clears Google Chrome historical past after reviewing paperwork, and makes use of e-mail addresses that seem to belong to the victimized group to exfiltrate recordsdata to OneDrive accounts.
As well as, APT42 makes use of ExpressVPN nodes, Cloudflare-hosted domains, and ephemeral VPS servers throughout all interactions with the sufferer’s surroundings, making attribution tougher.
Supply: Google
Customized backdoor malware
APT42 makes use of two customized backdoors named Nicecurl and Tamecat, every tailor-made for particular capabilities inside cyberespionage operations.
Nicecurl is a VBScript-based backdoor able to performing command execution, downloading and executing further payloads, or performing knowledge mining on the contaminated host.
Tamecat is a extra complicated PowerShell backdoor that may execute arbitrary PS code or C# scripts, giving APT42 a lot operational flexibility to carry out knowledge theft and intensive system manipulation.
In comparison with Nicecurl, Tamecat obfuscates its C2 communication with base64, can replace its configuration dynamically, and assesses the contaminated surroundings earlier than execution to evade detection by AV instruments and different energetic safety mechanisms.
Each backdoors are deployed by way of phishing emails with malicious paperwork, usually requiring macro permissions to run. Nonetheless, if APT42 has cultivated belief with the sufferer, this requirement turns into much less of a barrier for the reason that sufferer is extra possible to manually disable security measures.
Related, if not the identical, malware was analyzed by Volexity in February, which additionally linked the assaults to Iranian risk actors.
The full record of Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) for the latest APT42 marketing campaign and YARA guidelines for detecting the NICECURL and TAMECAT malware may be discovered on the finish of Google’s report.
