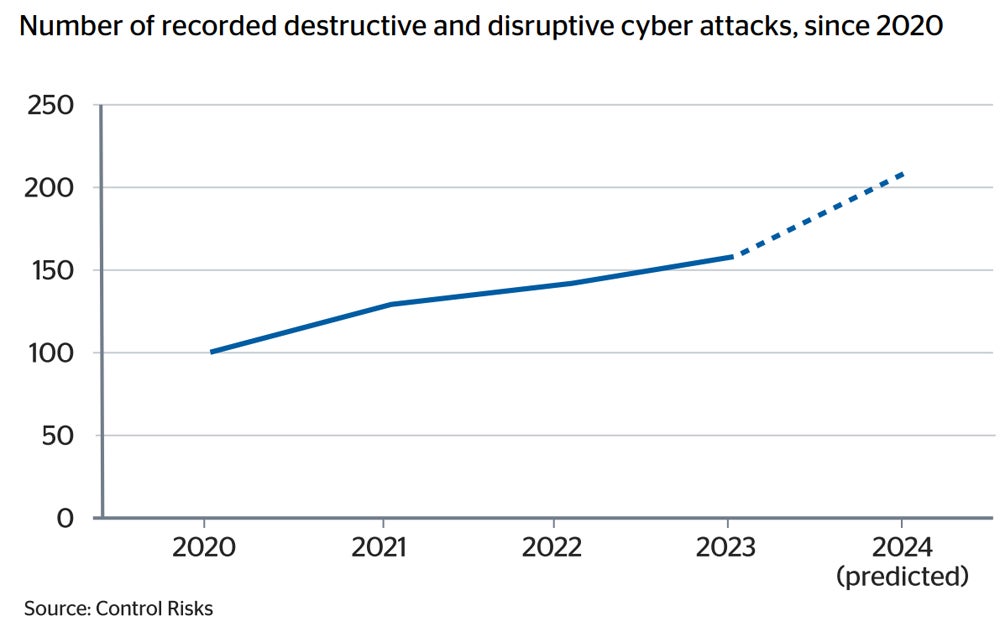
On the primary day of Cybersecurity Consciousness Month within the U.S., analysis has revealed that the variety of vital international cyber assaults in 2024 will likely be double that of 2020.
A brand new report from insurer QBE, Related Enterprise: digital dependency fuelling danger, predicts that organisations will likely be hit by 211 disruptive and harmful cyber assaults this 12 months.
Disruptive incidents are reversible and solely affect information availability, integrity, or entry — corresponding to distributed denial-of-service assaults. Conversely, harmful assaults are irreversible and goal to have a bodily affect on folks, just like the Triton malware, which disabled security methods at petrochemical vegetation.
The variety of disruptive and harmful cyber assaults in 2020 was 103, indicating a possible 105% improve in simply 4 years.
The information for the report was collected by the consultancy Management Dangers. They listed a choice of “strategically important” open-source and incident response instances slightly than information loss or easy system compromise kind incidents.
Examples of those vital assaults from the final 4 years embody the:
SEE: Ransomware Cheat Sheet: All the things You Want To Know In 2024
Nonetheless, QBE informed TechRepublic that the true figures for disruptive and harmful assaults are seemingly far larger than what’s reported.
“As technology interdependencies grow, we expect more cyber incidents to disrupt many companies in a single attack, meaning businesses are more likely to experience a disruptive cyber event,” the authors wrote.
“Malicious actors can also target specific companies to cause greater damage, whether they’re extorting ransoms or destabilising geopolitical rivals.”
Ransomware attackers goal operational tech and huge corporations for larger paydays
The report finds that operational know-how operators and huge organisations are prime targets for ransomware attackers.
In addition to having strict uptime necessities, OT organisations managing vital infrastructure are recognized for counting on legacy units, as changing know-how whereas sustaining regular operations is each difficult and expensive.
Proof from NCC Group submitted for a U.Okay. authorities report on the specter of ransomware to nationwide safety discovered that “OT systems are much more likely to include components that are 20 to 30 years old and/or use older software that is less secure and no longer supported.”
This makes OT corporations each accessible and more likely to pay a ransom, as downtime could have extreme penalties. Certainly, the QBE report claimed that ransomware assaults in opposition to industrial sector organisations surged by 50% from 2022 to 2023.
One other group more likely to concede to an attacker’s calls for are the executives of huge corporations, as they view operational disruption as extra expensive. In line with QBE, a mean of 61% of organisations with annual revenues of $5 billion payout ransoms after an assault, in contrast with 25% of these with annual revenues beneath $10 million.
These techniques have confirmed profitable. The typical ransomware payout of 2023 was $2 million, a five-fold improve over 2022. The report’s authors say that profitable legislation enforcement operations — for instance, the LockBit, BlackCat, and Hive takedowns — have led attackers to hone in on wealthier targets to allow them to maximise ransom funds earlier than they stopped.
Moreover, now that takedowns have gotten extra frequent, specialists say that ransomware teams could view authorities retaliation as “inevitable,” and due to this fact haven’t any reservations about focusing on giant or vital organisations.
Researchers behind the QBE report predict that the variety of ransomware victims will rise by 11% from 2023 to 2025, with manufacturing, healthcare, IT, schooling, and authorities sectors most in danger.
One other ransomware method the report highlights that attackers use for optimum affect is focusing on IT provide chains. One purpose is as a result of variety of corporations reliant on their companies making uptime extra vital, as with CNI. However the different is as a result of they create the chance to hit many organisations throughout sectors via a single assault.
Over three-quarters of third-party incidents in 2023 are attributable to only three provide chain vulnerabilities, the report finds.
Synthetic intelligence as a supply of each concern and hope for U.Okay. enterprise safety
In addition to the brand new report, QBE additionally surveyed 311 IT resolution makers within the U.Okay. in September about their safety considerations, with AI, after all, being the most popular matters.
It revealed {that a} small, however vital, 15% portion thought AI would elevate the chance of cyber assault. That is vital, as 69% of medium-to-large U.Okay. companies mentioned that they had already confronted disruption from cyber occasions previously 12 months.
In June, HP intercepted an e-mail marketing campaign spreading malware with a script that “was highly likely to have been written with the help of GenAI.” AI can decrease the barrier to entry for cyber crimes, as less-skilled criminals can use it to generate deepfakes, to scan networks for entry factors, for reconnaissance, and extra.
At first of the 12 months, a finance employee in Hong Kong paid out $25 million to hackers that used AI to impersonate the chief monetary officer. They mimicked the executives voice throughout cellphone calls to authorise the switch.
SEE: Report Reveals the Impression of AI on Cyber Security Panorama
However, 32% of U.Okay. companies informed QBE that they really feel AI will enhance their cyber safety, and the Management Dangers researchers mentioned it’ll increase the effectivity of safety and defensive actions.
David Warr, the QBE Insurance coverage Portfolio Supervisor for Cyber, mentioned: “AI is each a hindrance and a assist to the cyber panorama. As AI turns into extra broadly accessible, cybercriminals and cyber activists can launch larger-scale assaults at a sooner tempo. This elevated functionality in scale and pace introduced on by AI may threaten the cyber area. Nonetheless, managed and managed use of AI can even assist detect cyber vulnerabilities.
“Companies in the U.K. and around the world both big and small should be building up their resilience to both mitigate against cyber threats and be prepared to act in the event of a cyber-attack.”