An virtually 6-year-old vulnerability within the Lighttpd internet server utilized in Baseboard Administration Controllers has been missed by many system distributors, together with Intel and Lenovo.
The safety situation may result in the exfiltration of course of reminiscence addresses, which may assist attackers bypass safety mechanisms like Handle Area Format Randomization (ASLR).
Lighttpd is an open-source internet server recognized for being light-weight, quick, and environment friendly, making it best for high-traffic web sites whereas consuming minimal system assets.
Throughout current scans of Baseboard Administration Controllers (BMC), researchers at Binarly firmware safety agency found a remotely exploitable heap out-of-bounds (OOB) learn vulnerability by way of the Lighttpd internet server processing “folded” HTTP request headers.
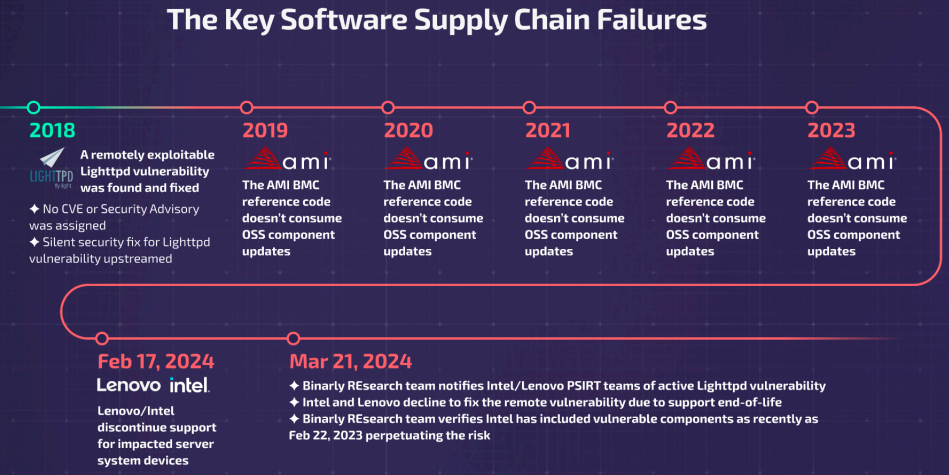
Though the vulnerability was addressed in August 2018, the maintainers of Lighthttpd patched it silently in model 1.4.51 with out assigning a monitoring ID (CVE).
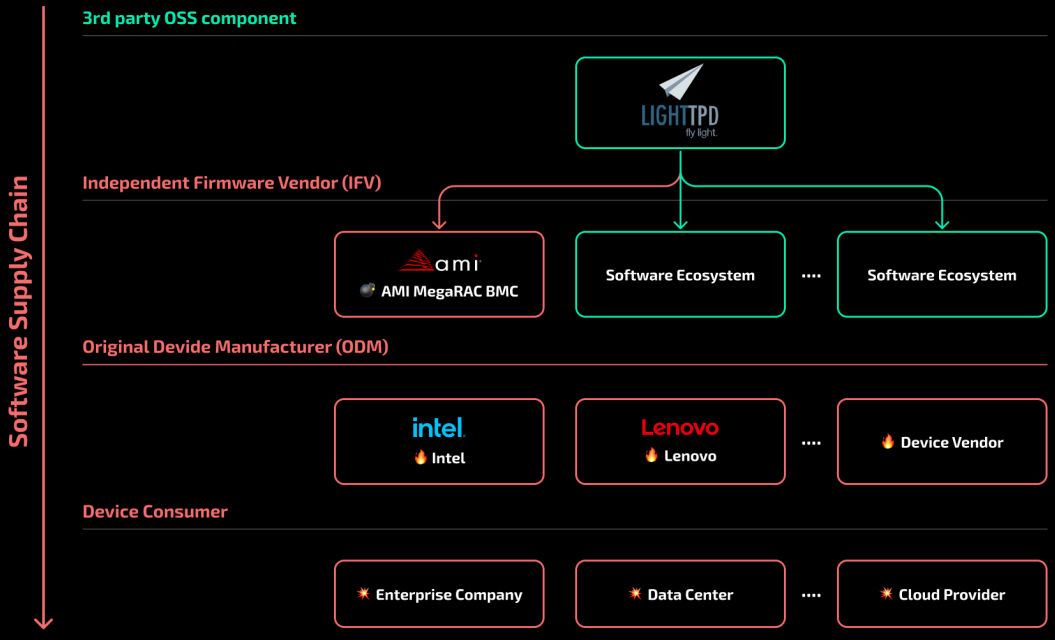
This led the builders of AMI MegaRAC BMC to overlook the repair and fail to combine it into the product. The vulnerability thus trickled down the provision chain to system distributors and their prospects.
Supply: Binarly
Affect and standing
BMCs are microcontrollers embedded on server-grade motherboards, together with techniques utilized in information facilities and cloud environments, that allow distant administration, rebooting, monitoring, and firmware updating on the system.
Binarly discovered that AMI failed to use the Lighttpd repair from 2019 till 2023, resulting in the roll-out of numerous units weak to the remotely exploitable bug all through these years.
“According to Binarly Transparency Platform data, we see multiple products from Intel, Lenovo, and Supermicro are impacted,” Binarly instructed BleepingComputer.
“Based on our data, nearly 2000+ devices are impacted in the field. In reality, this number is even bigger.”
Supply: Binarly
The menace analysts assigned three inner identifiers to the Lighttpd vulnerability primarily based on its influence on completely different distributors and units:
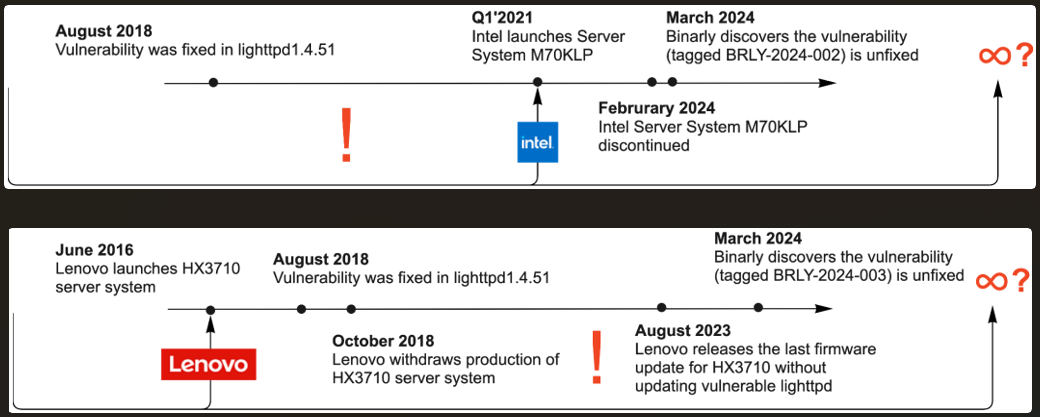
- BRLY-2024-002: Particular vulnerability in Lighttpd model 1.4.45 utilized in Intel’s M70KLP sequence firmware model 01.04.0030 (newest), impacting sure Intel server fashions.
- BRLY-2024-003: Particular vulnerability in Lighttpd model 1.4.35 inside Lenovo BMC firmware model 2.88.58 (newest) utilized in Lenovo server fashions HX3710, HX3710-F, and HX2710-E.
- BRLY-2024-004: Basic vulnerability in Lighttpd internet server variations earlier than 1.4.51, permitting delicate information studying from the server’s course of reminiscence.
Among the many distributors with impacted units are Intel and Lenovo, who Binarly notified of the issue of their units. The firmware safety firm notes some Intel techniques launched as lately as February 22, 2023, embody the weak part.
Nevertheless, each distributors stated the impacted fashions had reached end-of-life (EOL) and not obtain safety updates, which means that they may possible stay weak till decommissioned.
Supply: Binarly
In accordance with Binarly, there’s a “massive number” of weak and publicly accessible BMC units which have reached end-of-life and can stay weak perpetually as a result of lack of patches.
Binarly’s report offers technical particulars concerning the vulnerability and the way it works, which may permit an attacker to develop an exploit. The researchers observe that that is one other instance of gaps within the firmware provide chain that introduce safety dangers that would lengthen over a number of years.
Lack of transparency and failing to boost consciousness concerning the vulnerability from the Lighttpd maintainers additionally provides to the issue, resulting in distributors failing to combine the required fixes in due time.
