Menace actors are utilizing Area Identify System (DNS) tunneling to trace when their targets open phishing emails and click on on malicious hyperlinks, and to scan networks for potential vulnerabilities.
DNS tunneling is the encoding of information or instructions which can be despatched and retrieved through DNS queries, primarily turning DNS, a elementary community communication element, right into a covert communications channel.
The menace actors encode the information in varied methods, similar to Base16 or Base64 or customized textual encoding algorithms, to allow them to be returned when querying DNS data, similar to TXT, MX, CNAME, and Deal with data.
Hackers generally use DNS tunneling to bypass community firewalls and filters, using the method for command and management (C2) and Digital Personal Community (VPN) operations. There are additionally authentic DNS tunneling purposes, similar to for bypassing censorship.
Supply: Unit 42
Palo Alto Networks’ Unit 42 safety analysis crew not too long ago found extra use of DNS tunneling in malicious campaigns involving sufferer monitoring and community scanning.
TrkCdn marketing campaign
The primary marketing campaign, tracked as “TrkCdn,” focuses on monitoring sufferer interactions with phishing electronic mail content material.
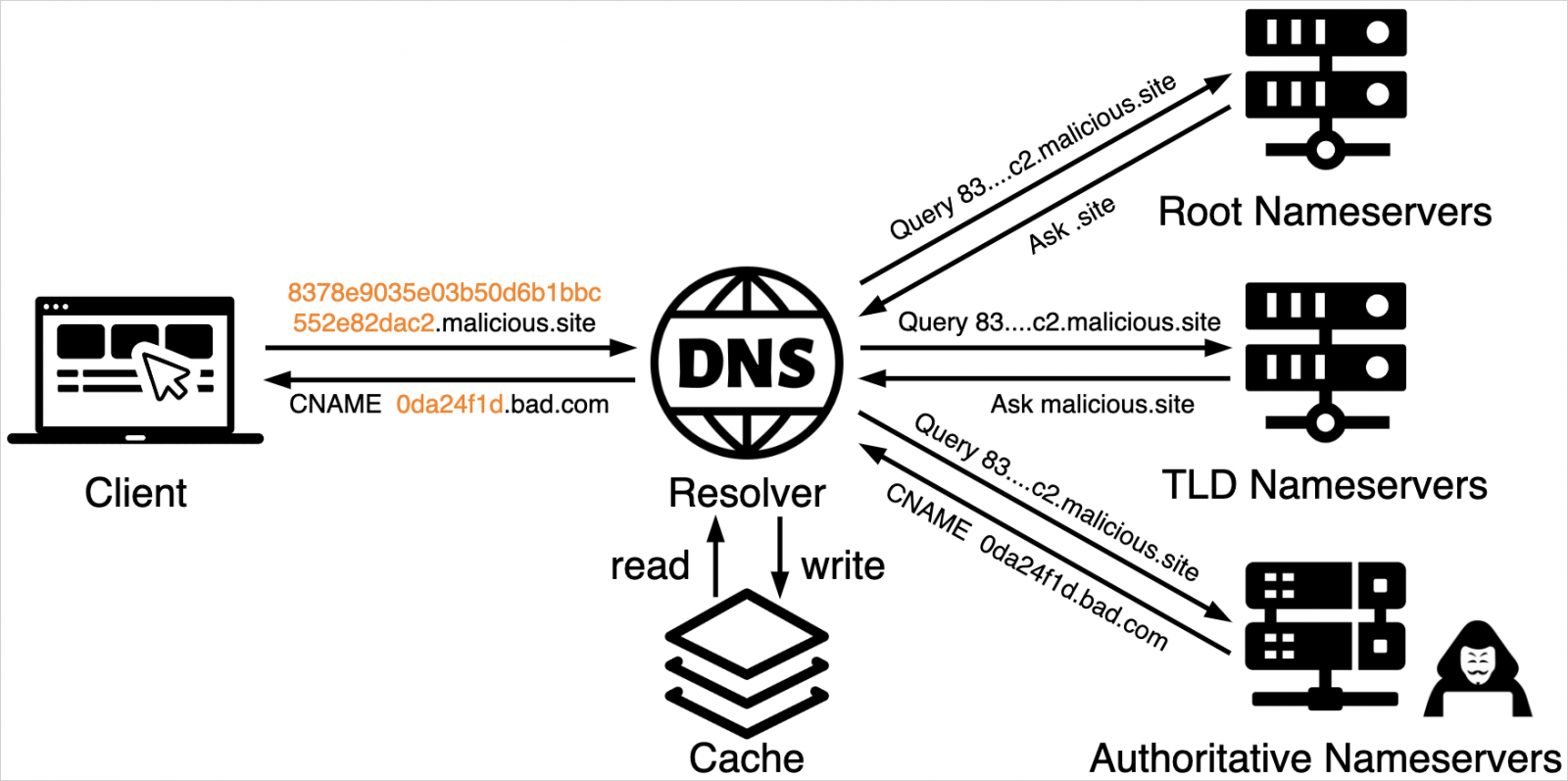
The attackers embed content material in an electronic mail that, when opened, performs a DNS question to attacker-controlled subdomains whose FQDN incorporates encoded content material.
For instance, 4e09ef9806fb9af448a5efcd60395815.trk.simitor[.]com. with 4e09ef9806fb9af448a5efcd60395815 being the md5 hash of unit42@not-a-real-domain[.]com, which resolves to a CNAME to a major authoritative title server.
“Hence, even though the FQDNs vary across different targets, they are all forwarded to the same IP address used by cdn.simitor[.]com,” explains the researchers.
“This authoritative title server then returns a DNS end result that results in an attacker-controlled server that delivers attacker-controlled content material. This content material can embody commercials, spam, or phishing content material.
This method permits the attackers to judge their methods, refine them, and ensure the supply of malicious payloads to their victims.
Supply: Unit 42
Unit 42’s report additionally highlights an identical marketing campaign that makes use of DNS tunneling to trace the supply of spam messages, dubbed “SpamTracker.”
The SecShow marketing campaign
The second marketing campaign noticed by the analysts, codenamed “SecShow,” makes use of DNS tunneling to scan community infrastructures.
The attackers embed IP addresses and timestamps into DNS queries to map out community layouts and uncover potential configuration flaws that may be exploited for infiltration, information theft, or denial of service.
The DNS queries used on this marketing campaign had been periodically repeated to allow real-time information gathering, detect standing adjustments, and check the response of various community elements to unsolicited DNS requests.
Menace actors go for DNS tunneling over extra conventional strategies like monitoring pixels and common community scanning instruments for a number of causes, together with the power to bypass safety instruments, keep away from detection, and preserve operational versatility.
Unit 42 proposes that organizations implement DNS monitoring and evaluation instruments to watch and analyze logs for uncommon visitors patterns and anomalies, similar to atypical or high-volume requests.
Moreover, it is advisable to restrict the DNS resolvers within the community to deal with solely the required queries, decreasing the potential of DNS tunneling misuse.
