A malicious crypto mining marketing campaign codenamed ‘REF4578,’ has been found deploying a malicious payload named GhostEngine that makes use of weak drivers to show off safety merchandise and deploy an XMRig miner.
Researchers at Elastic Safety Labs and Antiy have underlined the weird sophistication of those crypto-mining assaults in separate studies and shared detection guidelines to assist defenders establish and cease them.
Nevertheless, neither report attributes the exercise to recognized menace actors nor shares particulars about targets/victims, so the marketing campaign’s origin and scope stay unknown.
GhostEngine
Whereas it’s unclear how servers are initially breached, the menace actor’s assault begins with the execution of a file named ‘Tiworker.exe,’ which masquerades as a reliable Home windows file.
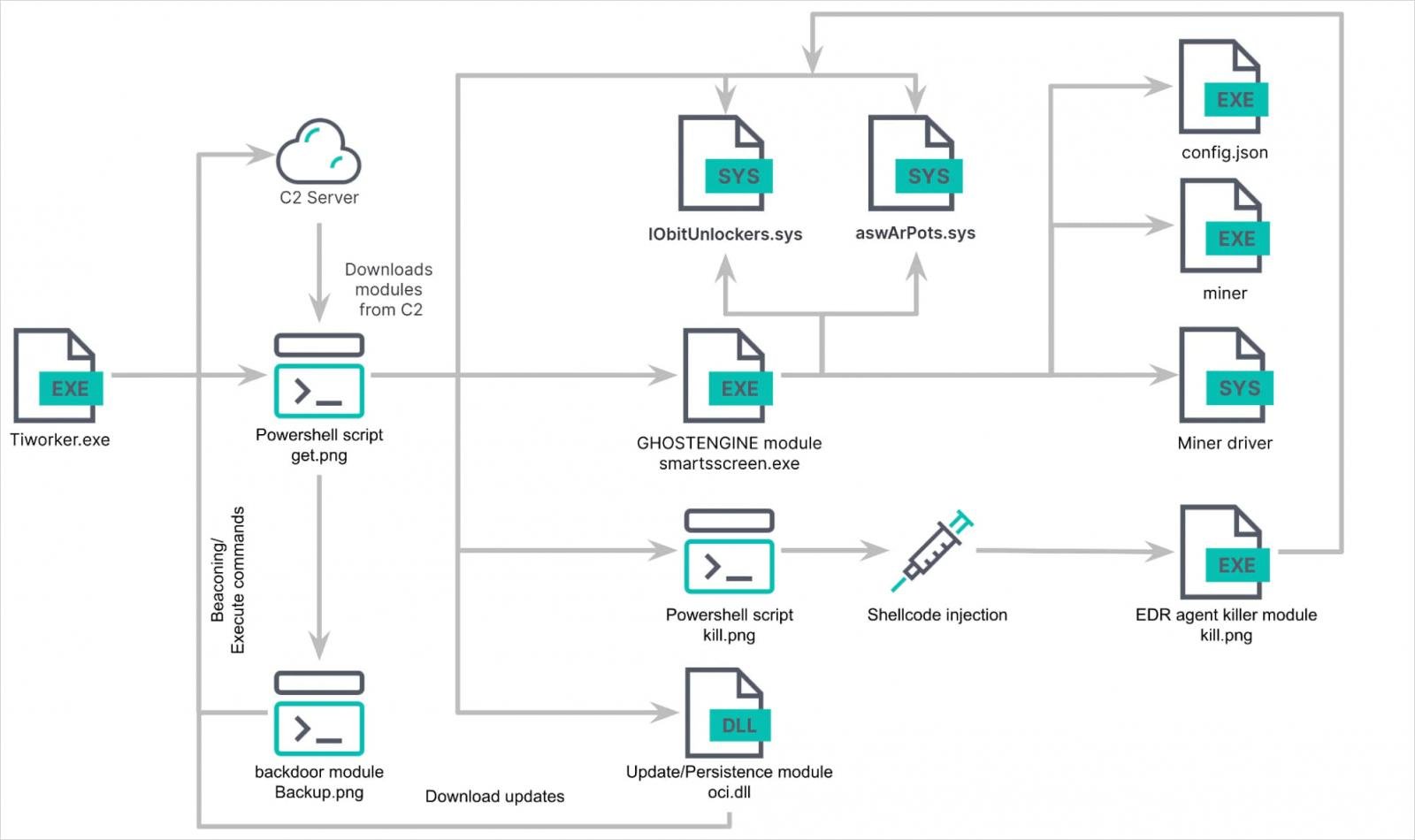
This executable is the preliminary staging payload for GhostEngine, a PowerShell script that downloads varied modules to conduct completely different behaviors on an contaminated system.
When Tiworker.exe is executed, it is going to obtain a PowerShell script named ‘get.png’ from the attacker’s command and management (C2) server, which acts as GhostEngine’s major loader.
This PowerShell script downloads further modules and their configurations, disables Home windows Defender, permits distant companies, and clears varied Home windows occasion logs.
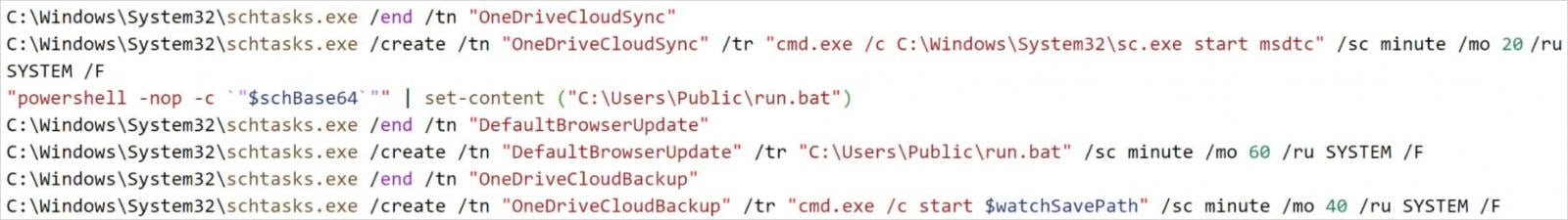
Subsequent, get.png verifies that the system has at the least 10MB of free area, which is essential for furthering the an infection, and creates scheduled duties named ‘OneDriveCloudSync,’ ‘DefaultBrowserUpdate,’ and ‘OneDriveCloudBackup,’ for persistence.
Supply: Elastic Safety
The PowerShell script will now obtain and launch an executable named smartsscreen.exe, which acts as GhostEngine’s major payload.
This malware is accountable for terminating and deleting EDR software program and downloading and launching the XMRig to mine for cryptocurrency.
To terminate EDR software program, GhostEngine masses two weak kernel drivers: aswArPots.sys (Avast driver), which is used to terminate EDR processes, and IObitUnlockers.sys (Iobit driver) to delete the related executable.
A listing of the processes focused by the EDR terminator is proven beneath:

Supply: Elastic Safety
For persistence, a DLL named ‘oci.dll’ is loaded by a Home windows service named ‘msdtc’. When began, this DLL will obtain a recent copy of ‘get.png’ to put in the most recent model of GhostEngine on the machine.
Although Elastic hasn’t seen spectacular figures from the only fee ID they examined, it is attainable that every sufferer comes with a novel pockets, so the general monetary acquire might be important.
Supply: Elastic Safety
Defending towards GhostEngine
Elastic researchers counsel defenders look out for suspicious PowerShell execution, uncommon course of exercise, and community site visitors pointing to crypto-mining swimming pools.
Moreover, deploying weak drivers and creating related kernel mode companies must be handled as crimson flags in any surroundings.
An aggressive measure is to dam file creation from weak drivers like aswArPots.sys and IobitUnlockers.sys.
Elastic Safety has additionally offered YARA guidelines within the report to assist defenders establish GhostEngine infections.
