Corporations that use non-public cases of huge language fashions (LLMs) to make their enterprise information searchable by a conversational interface face dangers of knowledge poisoning and potential information leakage if they don’t correctly implement safety controls to harden the platforms, specialists say.
Living proof: This week, Synopsys disclosed a cross-site request forgery (CSRF) flaw that impacts purposes primarily based on the EmbedAI part created by AI supplier SamurAI; it might enable attackers to idiot customers into importing poisoned information into their language mannequin, the application-security agency warned. The assault exploits the open supply part’s lack of a protected cross-origin coverage and failure to implement session administration, and will enable an attacker to have an effect on even a personal LLM occasion or chatbot, says Mohammed Alshehri, the Synopsys safety researcher who discovered the vulnerability.
The dangers are much like these dealing with builders of software program purposes, however with an AI twist, he says.
“There’re products where they take an existing AI implementation [and open source components] and merge them together to create something new,” he says. “What we want to highlight here is that even after the integration, companies should test to ensure that the same controls we have for Web applications are also implemented on the APIs for their AI applications.”
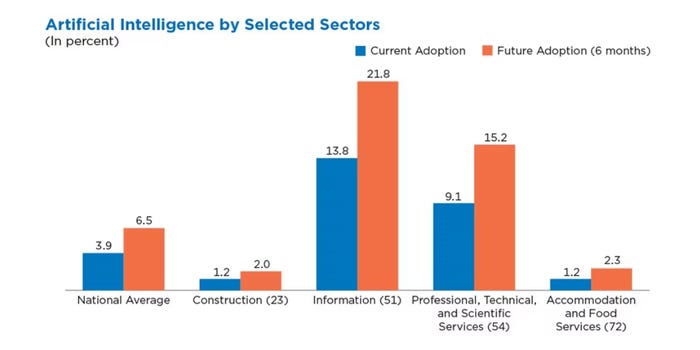
The analysis underscores that the push to combine AI into enterprise processes does pose dangers, particularly for firms which are giving LLMs and different generative-AI purposes entry to giant repositories of knowledge. Total, solely 4% of US firms have adopted AI as a part of their enterprise operations, however some industries have increased adoption charges, with the knowledge sector at 14% and the skilled providers sector at 9%, in accordance with a survey by the US Census Bureau performed in October 2023.
The data and professional-services industries have had the best AI adoption. Supply: US Census Bureau
The dangers posed by the adoption of next-gen synthetic intelligence and machine studying (AI/ML) will not be essentially as a result of fashions, which are inclined to have smaller assault surfaces, however the software program elements and instruments for growing AI purposes and interfaces, says Dan McInerney, lead AI menace researcher with Shield AI, an AI software safety agency.
“There’s not a lot of magical incantations that you can send to an LLM and have it spit out passwords and sensitive info,” he says. “But there’s a lot of vulnerabilities in the servers that are used to host LLMs. The [LLM] is really not where you’re going to get hacked — you’re going to get hacked from all the tools you use around the LLM.”
Sensible Assaults Towards AI Elements
Such vulnerabilities have already turn into actively exploited. In March, Oligo Safety reported on the invention of lively assaults in opposition to Ray, a well-liked AI framework, utilizing a beforehand found safety concern, one in every of 5 vulnerabilities that had been found by analysis teams at Shield AI and Bishop Fox, together with impartial researcher Sierra Haex. Anyscale, the corporate behind Ray, fastened 4 vulnerabilities however thought of the fifth to be a misconfiguration concern.
But, attackers managed to seek out lots of of deployments that inadvisedly uncovered a Ray server to the Web and compromised the techniques, in accordance with an evaluation revealed by Oligo Safety in March.
“This flaw has been under active exploitation for the last seven months, affecting sectors like education, cryptocurrency, biopharma and more,” the corporate said. “All organizations using Ray are advised to review their environments to ensure they are not exposed and to analyze any suspicious activity.”
In its personal March advisory, Anyscale acknowledged the assaults and launched a instrument to detect insecurely configured techniques.
Non-public Does Not Imply Protected
Whereas the vulnerability within the Ray framework uncovered public-facing servers to assault, even non-public AI-powered LLMs and chatbots might face exploitations. In Could, AI-security agency Shield AI launched the most recent tranche of vulnerabilities found by its bug bounty neighborhood, Huntr, encompassing 32 points from important distant exploits to low-severity race situations. Some assaults might require entry to the API, however others may very well be carried out by malicious paperwork and different vectors.
In its personal analysis, Synopsys researcher Alshehri found the cross-site request forgery (CSRF) concern, which provides an attacker the power to poison an LLM by a watering gap assault.
“Exploitation of this vulnerability could affect the immediate functioning of the model and can have long-lasting effects on its credibility and the security of the systems that rely on it,” Synopsys said in its advisory. “This can manifest in various ways, including the spread of misinformation, introduction of biases, degradation of performance, and potential for denial-of-service attacks.”
Through the use of a personal occasion of a chatbot service or internally internet hosting an LLM, many firms imagine they’ve minimized the chance of exploitation, says Tyler Younger, CISO at BigID, an information administration agency.
“Most enterprises are leaning toward leveraging private LLM chatbots on top of those LLM algorithms, simply because it offers that comfort, just like hosting something in your own cloud, where you have control over who can access the data,” he says. “But there are risks … because the second you have an inherent trust, you start pumping more and more data in there, and you have overexposure. All it takes is one of those accounts to get compromised.”
New Software program, Similar Outdated Vulnerabilities
Corporations must assume that the present crop of AI techniques and providers have had solely restricted safety design and evaluation, as a result of the platforms usually are primarily based on open-source elements which have small groups and restricted oversight, says Synopsys’s Alshehri. Actually, in February, the Hugging Face AI open supply mannequin repository was discovered to be riddled with malicious code-execution fashions.
“The same way we do regular testing and those code reviews with black-box and white-box testing, we need to do that … when it comes to adopting these new technologies,” he says.
Corporations which are implementing AI techniques primarily based on inside information ought to phase the information — and the ensuing LLM cases — in order that solely staff are allowed entry to only these LLM providers that had been constructed on the information to which they’ve entry. Every assortment of customers with a selected privilege stage would require a separate LLM skilled on their accessible information.
“You cannot just give the LLM access to a giant dump of data and say, ‘OK, everyone has access to this,’ because that’s the equivalent of giving everyone access to a database with all the data inside of it, right?” says Shield AI’s McInerney. “So you got to clean the data.”
Lastly, firms want to attenuate the elements they’re utilizing to develop their AI instruments after which repeatedly replace these software program property and implement controls to make exploitation tougher, he says.