A Fb malvertising marketing campaign disguised as Bitwarden updates spreads malware, focusing on enterprise accounts. Customers are tricked into putting in malicious Chrome browser extensions.
Cybersecurity researchers at Bitdefender have uncovered a malicious promoting (malvertising) marketing campaign that exploits Meta’s promoting platform to distribute malware on Fb. This marketing campaign, detected on November 3, 2024, disguises the malware as a safety replace for the favored Bitwarden password supervisor. Though the marketing campaign has been taken down, consultants warn that comparable threats are more likely to resurface.
From Malicious Fb Advertisements to Faux Chrome Retailer
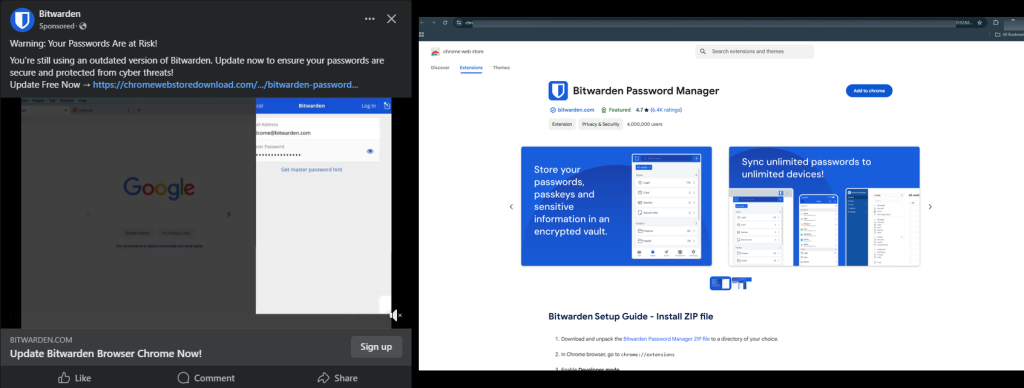
The marketing campaign makes use of misleading Fb adverts that seem like reliable safety updates for Bitwarden. These adverts warn customers concerning the danger of compromised passwords and trick them into putting in an pressing safety replace for the password supervisor. The adverts are designed to look genuine, utilizing Bitwarden’s branding and language to create a way of urgency.
When customers click on on these adverts, they’re redirected by way of a collection of internet sites earlier than reaching a phishing web page that mimics the official Chrome Net Retailer. This remaining web page notifies customers to put in a malicious browser extension disguised as a Bitwarden replace. The set up course of includes downloading a zipper file from Google Drive, unzipping it, and manually loading the extension into the browser.
In accordance with Bitdefender’s weblog put up shared with Hackead.com heard of its publishing on Monday, as soon as put in, the malicious Chrome extension requests permissions, enabling it to intercept and exploit the consumer’s on-line actions.
Some key permissions requested embody entry to all web sites, modification of community requests, and entry to storage and cookies. The extension’s manifest file reveals these permissions, indicating its potential to carry out varied malicious actions.
Researchers famous that the core of the assault lies throughout the background.js script, which prompts upon set up. This script performs a number of crucial duties information exfiltration which the collected information is distributed to a Google Script URL performing as a command-and-control server, cookie harvesting which permits attackers to seek for Fb cookies, notably the c_user cookie containing the consumer’s Fb ID. The script additionally gathers IP tackle and geolocation information and extracts private and enterprise data from Fb utilizing the Graph API.
Impacted Customers
The malware’s main targets are Fb enterprise accounts placing unsuspected people and organizations in danger. The malvertising marketing campaign has already reached 1000’s of customers, primarily in Europe, with the likelihood to develop globally.
If you happen to use Fb for enterprise functions and handle a enterprise account, it’s vital to remain cautious. If you happen to come throughout a malicious ad prompting you to put in updates, keep away from clicking on it. As an alternative, go to the official web site of the product to confirm and entry reliable safety updates.
RELATED TOPICS
- Faux Advertisements Supervisor Software program Goal Fb Accounts
- Faux LastPass Password Supervisor App Lurks on iOS App Retailer
- Faux League of Legends Obtain Advertisements Unfold Lumma Stealer
- PasswordState password supervisor’s replace hijacked to drop malware
- Faux Meta Advertisements Hijack Fb Accounts to Unfold SYS01 Infostealer