Proof-of-concept exploit code is now public for a vulnerability in Microsoft’s Distant Registry shopper that could possibly be used to take management of a Home windows area by downgrading the safety of the authentication course of.
The vulnerability is tracked as CVE-2024-43532 and takes benefit of a fallback mechanism within the Home windows Registry (WinReg) shopper implementation that depends on outdated transport protocols if the SMB transport shouldn’t be current.
An attacker exploiting the safety problem might relay NTLM authentication to Lively Listing Certificates Companies (ADCS) to acquire a person certificates for additional area authentication.
The flaw impacts all Home windows server variations 2008 by 2022 in addition to Home windows 10 and Home windows 11.
Vulnerability and exploitation particulars
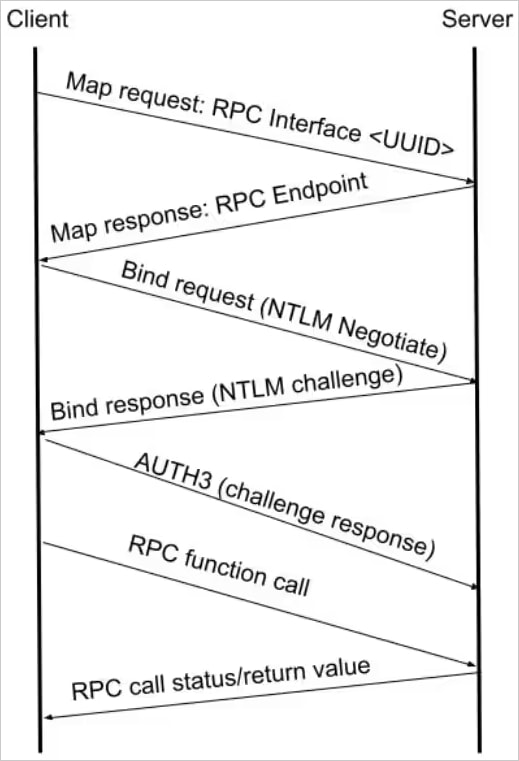
CVE-2024-43532 stems from how Microsoft’s Distant Registry shopper handles RPC (Distant Process Name) authentication throughout sure fallback eventualities when SMB transport is unavailable.
When this occurs, the shopper switches to older protocols like TCP/IP and makes use of a weak authentication stage (RPC_C_AUTHN_LEVEL_CONNECT), which does not confirm the authenticity or integrity of the connection.
An attacker might authenticate to the server and create new area administrator accounts by intercepting the NTLM authentication handshake from the shopper and forwarding it to a different service, such because the (ADCS).
Supply: Akamai
Efficiently exploiting CVE-2024-43532 outcomes into a brand new technique to perform a NTLM relay assault, one which leverages the WinReg element to relay authentication particulars that might result in area takeover.
Some risk actors have used NTLM relay assault strategies up to now to take management of Home windows domains. One instance is the LockFile ransomware gang, who focused organizations numerous organizations within the U.S. and Asia utilizing PetitPotam shortly after it was found.
The vulnerability was found by Akamai researcher Stiv Kupchik, who disclosed it to Microsoft on February 1. Nonetheless, Microsoft dismissed the report on April 25 “as documentation issue.”
In mid-June, Kupchik resubmitted the report with a greater proof-of-concept (PoC) and rationalization, which led to Microsoft confirming the vulnerability on July 8. Three months later, Microsoft launched a repair.
The researcher has now launched a working PoC for CVE-2024-43532 and defined the exploitation course of, from making a relay server to acquiring a person certificates from the goal, in the course of the No Hat safety convention in Bergamo, Italy.
Akamai’s report additionally offers a technique to find out if the Distant Registry service is enabled on a machine in addition to a YARA rule to detect shoppers that use a susceptible WinAPI.
The researchers additionally suggest utilizing Occasion Tracing for Home windows (ETW) to watch for particular RPC calls, together with these associated to the WinReg RPC interface.
