Well timed challenge completion ensures that initiatives keep inside funds and fulfill the expectations of stakeholders. The important path methodology is a challenge administration method that’s integral to reaching these aims.
CPM was developed within the late Nineteen Fifties by James E. Kelley of Remington Rand and Morgan R. Walker of DuPont to handle the challenges of complicated challenge scheduling. It’s helpful for initiatives with interdependent actions, the place delays in a single activity can have cascading results on subsequent duties and the challenge’s completion date.
On this information, I clarify the idea of CPM, analyze its advantages, and present you the right way to implement and calculate important paths. Whether or not managing a small challenge or a large-scale enterprise operation, understanding and implementing CPM can considerably improve the probability of success.
What’s the important path methodology?
The important path methodology is a step-by-step challenge administration method used to determine the sequence of duties that should be accomplished on time for the whole challenge to be completed by the deadline. These duties type the “critical path,” which is the longest stretch of dependent actions that determines the shortest doable challenge period.
CPM focuses on probably the most essential duties that can not be delayed with out affecting the challenge timeline. By calculating the important path, challenge managers can decide the minimal challenge period and determine which duties have flexibility (float) and which don’t. This methodology additionally highlights potential bottlenecks and helps challenge managers prioritize duties important for on-time challenge completion.
This data permits for higher useful resource allocation, threat administration, and scheduling, guaranteeing the challenge stays on monitor.
Advantages of CPM
CPM permits challenge managers to concentrate on important duties, higher handle their time to keep away from delays, and be certain that the challenge stays on monitor. Other than well timed challenge completion, CPM additionally provides the next advantages.
Manages funds
CPM permits challenge managers to optimize useful resource allocation by offering a exact sequence of important duties, subsequently decreasing pointless bills. As an illustration, if you determine float time in non-critical duties, you’ll be able to reassign assets like staff to important features which are not on time, thus avoiding pointless time beyond regulation prices.
This proactive method ensures that each greenback is spent the place it has probably the most affect. CPM’s structured timeline additionally makes it simpler to plan for materials deliveries simply in time, which minimizes storage prices and reduces the probability of tying up capital in extra stock.
Identifies important duties
CPM provides a transparent view of the duties which are important to the challenge’s success, which helps challenge managers set priorities and permits for the proactive administration of potential delays. This focus ensures that the challenge stays on monitor and reduces the chance of lacking deadlines. It additionally helps determine potential dangers early on in order that proactive measures could be taken to mitigate them.
Visualizes the challenge timeline
Usually depicted by way of a community diagram or flowchart, CPM highlights the sequence and period of every activity inside a challenge. This visible illustration permits challenge managers to simply see how duties are interrelated and which of them are important to the challenge’s general timeline. This readability simplifies the planning course of, making allocating assets and anticipating potential delays simpler.
Improves staff communication
By clearly defining the important path and activity dependencies, CPM enhances communication throughout the challenge staff. Every individual is aware of which duties are important, who’s chargeable for them, and the affect of delays. This shared understanding fosters collaboration, reduces misunderstandings, and ensures the staff is aligned towards the challenge’s objectives.
The right way to calculate the important path
Calculating the important path includes a number of steps that require an in depth understanding of the challenge’s duties and dependencies. Right here’s a step-by-step information:
Step 1: Record all duties (actions) required for the challenge
Establish and listing all of the duties required to finish the challenge. Every activity operate or exercise must be clearly outlined and its anticipated period must be included.
Step 2: Decide dependencies (sequence of actions)
Establish the dependencies between duties to grasp which duties should precede others. Mapping these dependencies is important for comprehending the sequence of actions.
Step 3: Estimate activity durations
Assign a period to every activity. This may be completed utilizing historic information, knowledgeable judgment, or estimation methods just like the Program Analysis and Overview Approach (PERT).
Mission managers also can use the Ahead Go and Backward Go methods to calculate duties’ earliest and newest begin and end instances. These methods are integral to figuring out the important path and guaranteeing the challenge stays on schedule.
- Ahead Go method: Decide every activity’s earliest doable begin and end instances. This course of helps schedule duties as early as doable, minimizing challenge period.
- Backward Go method: Outline every activity’s newest begin and end instances, guaranteeing that the challenge is accomplished by its deadline. This course of permits PMs to determine the pliability within the schedule and the most recent doable begin instances with out delaying the challenge.
Step 4: Draw a community diagram of the important path
Utilizing the data from the earlier steps, create a community diagram (often known as a challenge schedule community diagram). On this diagram, duties are represented as nodes and dependencies are proven as arrows connecting the nodes. This visible instrument helps for example the sequence of duties and their interrelationships clearly.
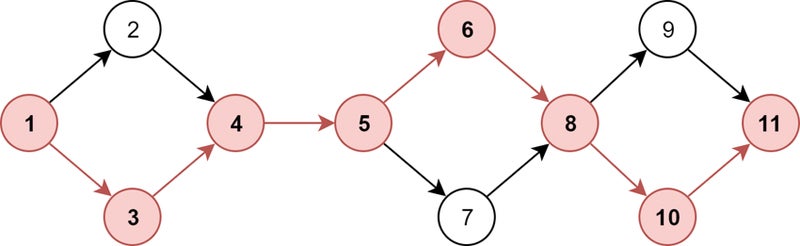
Step 5: Establish the important path
The important path is the longest sequence of actions within the community diagram that should be accomplished so as to end the challenge, and it represents the shortest doable time for completion.
To determine the important path, calculate the earliest begin (ES) and earliest end (EF) instances for every activity, adopted by the most recent begin (LS) and newest end (LF) instances.
- Calculate ES and EF: Start at first of the community diagram and calculate the earliest time every activity can begin and end. The earliest begin time is the earliest time a activity can start, contemplating the completion of previous duties. The earliest end time is calculated by including the duty period to its earliest begin time (EF = ES + activity period).
- Calculate LS and LF: Work backward from the challenge completion date to find out the most recent time every activity can begin and end with out delaying the challenge. The newest begin time is calculated by subtracting the duty period from its newest end time (LS = LF – activity period).
- Calculate Float (Slack) for every activity: Float, or Slack, is the period of time a activity could be delayed with out affecting the challenge’s completion date. It’s calculated by subtracting the earliest begin time from the most recent begin time (Float = LS – ES). Duties with zero float are on the important path, that means any delay in these duties will delay the challenge.
Step 6: Analyze and regulate
Overview the important path and determine any potential points or bottlenecks. Regulate the schedule as wanted to optimize the challenge timeline. If important duties are liable to delay, take into account reassigning assets or adjusting the challenge plan to maintain the challenge on monitor.
Examples of important path methodology
To raised perceive how CPM works, listed below are two real-world examples the place it may very well be carried out to help a challenge.
Creating a web site
On this occasion, you might be managing the challenge to create a company web site. The challenge contains planning, designing, creating, testing, and launching the web site.
Duties and durations
- A. Mission Planning (2 days)
- B. Necessities Gathering (3 days): Begins after A
- C. Design Mockup Creation (5 days): Begins after B
- D. Design Approval (2 days): Begins after C
- E. Web site Improvement (10 days): Begins after D
- F. Content material Creation (7 days): Begins after B
- G. Content material Integration (3 days): Begins after E and F
- H. Testing (4 days): Begins after G
- I. Last Approval (2 days): Begins after H
- J. Web site Launch (1 day): Begins after I
Essential path calculation
Step 1: Establish all doable paths.
- Path 1: A → B → C → D → E → G → H → I → J
- Path 2: A → B → F → G → H → I → J
Step 2: Calculate the period of every path.
- Path 1: A (2 days) + B (3 days) + C (5 days) + D (2 days) + E (10 days) + G (3 days) + H (4 days) + I (2 days) + J (1 day) = 32 days
- Path 2: A (2 days) + B (3 days) + F (7 days) + G (3 days) + H (4 days) + I (2 days) + J (1 day) = 22 days
Step 3: Decide the important path.
- Essential path: Path 1
- Period: 32 days
The important path for creating this web site is Path 1, with a complete challenge period of 32 days. Duties on Path 2, corresponding to Content material Creation (F), don’t affect the general challenge period as they are often accomplished in parallel with out delaying the challenge, so long as they’re completed earlier than the Content material Integration (G) activity, which can also be a part of the important path.
Constructing a home
For this instance, you’re managing a challenge to construct a single-family house. All the blueprints have already been authorized, so your focus right here is on the bodily actions of building. The challenge contains laying the muse, framing, roofing, plumbing, electrical work, and inside ending.
Duties and durations
- A. Web site Preparation (3 days)
- B. Laying Basis (5 days): Begins after A
- C. Framing (7 days): Begins after B
- D. Roofing (4 days): Begins after C
- E. Plumbing (6 days): Begins after C
- F. Electrical Work (5 days): Begins after C
- G. Inside Ending (8 days): Begins after E and F
- H. Last Inspection (2 days): Begins after G
- I. Handover to Consumer (1 day): Begins after H
Essential path calculation
Step 1: Establish all doable paths.
- Path 1: A → B → C → D → G → H → I
- Path 2: A → B → C → E → G → H → I
- Path 3: A → B → C → F → G → H → I
Step 2: Calculate the period of every path.
- Path 1: A (3 days) + B (5 days) + C (7 days) + D (4 days) + G (8 days) + H (2 days) + I (1 day) = 3 + 5 + 7 + 4 + 8 + 2 + 1 = 30 days
- Path 2: A (3 days) + B (5 days) + C (7 days) + E (6 days) + G (8 days) + H (2 days) + I (1 day) = 3 + 5 + 7 + 6 + 8 + 2 + 1 = 32 days
- Path 3: A (3 days) + B (5 days) + C (7 days) + F (5 days) + G (8 days) + H (2 days) + I (1 day) = 3 + 5 + 7 + 5 + 8 + 2 + 1 = 31 days
Step 3: Decide the important path.
- Essential path: Path 2
- Period: 32 days
On this case, Path 2 is important as a result of it contains the longest sequence of dependent duties. Any delay in these duties will push again the whole challenge timeline.
CPM vs PERT
CPM and PERT are each challenge administration instruments used for planning and scheduling. They’ve distinct variations and aren’t interchangeable. Nonetheless, they will complement one another when used collectively.
CPM is deterministic, offering a hard and fast timeline primarily based on identified activity durations. It’s used when precision is required. It focuses on figuring out the longest sequence of dependent duties (the important path) to find out the challenge’s completion date. CPM is good for initiatives with well-defined duties and secure timelines.
Conversely, PERT is probabilistic, permitting for flexibility in planning by contemplating totally different outcomes. It’s helpful for initiatives with excessive uncertainty, permitting challenge managers to plan for various eventualities. PERT is decided utilizing three factors:
- Optimistic (O): The minimal time wanted if all the things goes completely.
- Most Probably (M): The period if the exercise takes place beneath regular circumstances.
- Pessimistic (P): The utmost time wanted if main issues happen.
FAQs
How do you calculate the important path?
The important path is calculated by figuring out all duties, figuring out their dependencies, estimating their durations, after which calculating the earliest and newest begin and end instances. Duties with zero float make up the important path, and any delay in these duties will delay the whole challenge.
What are the 4 key components of the important path methodology?
- Essential path evaluation.
- Float willpower.
- Early begin and early end calculation.
- Late begin and late end calculation.
Why is the important path methodology used?
CPM is used to determine the longest sequence of duties in a challenge. This permits challenge managers to concentrate on probably the most time-sensitive actions to make sure on-time challenge completion. It additionally helps with sensible challenge scheduling, useful resource administration, and the identification of potential delays.