A malware botnet generally known as ‘Ebury’ has contaminated virtually 400,000 Linux servers since 2009, with roughly 100,000 nonetheless compromised as of late 2023.
ESET researchers have been following the financially motivated malware operation for over a decade now, warning about important updates within the payload’s capabilities in 2014 and once more in 2017.
Under are the Ebury infections logged by ESET since 2009, exhibiting a notable development within the quantity of infections over time.
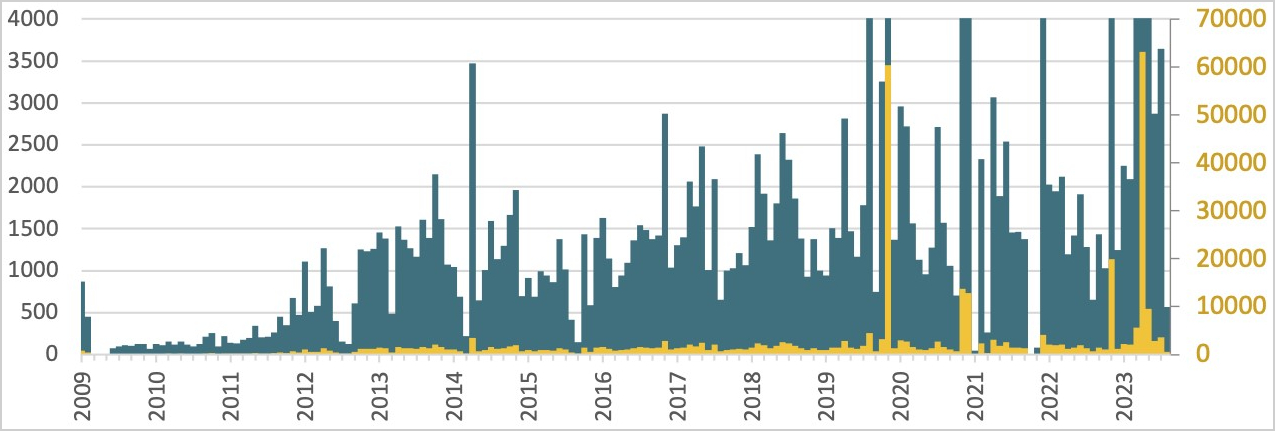
Supply: ESET
Within the newest replace printed right now, ESET stories {that a} latest legislation enforcement motion allowed them to achieve perception into the malware operation’s actions over the previous fifteen years.
“While 400,000 is a massive number, it’s important to mention that this is the number of compromises over the course of almost 15 years. Not all of those machines were compromised at the same time,” explains ESET.
“There is a constant churn of new servers being compromised while others are being cleaned up or decommissioned. The data at our disposal doesn’t indicate when the attackers lost access to the systems, so it’s difficult to know the size of the botnet at any specific point in time.”
Ebury’s newest ways
Latest Ebury assaults present a choice by the operators to breach internet hosting suppliers and carry out provide chain assaults to purchasers renting digital servers on the compromised supplier.
The preliminary compromise is carried out by way of credential stuffing assaults, utilizing stolen credentials to log into the servers.
As soon as a server is compromised, the malware exfiltrates a listing of inbound/outband SSH connections from wtmp and the known_hosts file and steals SSH authentication keys, which are then used to attempt to log into different methods.
“When the known_hosts file contains hashed information, the perpetrators try to brute force its content,” reads ESET’s detailed report.
“Out of 4.8 million known_hosts entries collected by Ebury operators, about two million had their hostname hashed. 40% (about 800,000) of those hashed hostnames were guessed or brute forced.”
Alternatively, and the place potential, the attackers may additionally exploit identified vulnerabilities within the software program working on the servers to achieve additional entry or elevate their privileges.
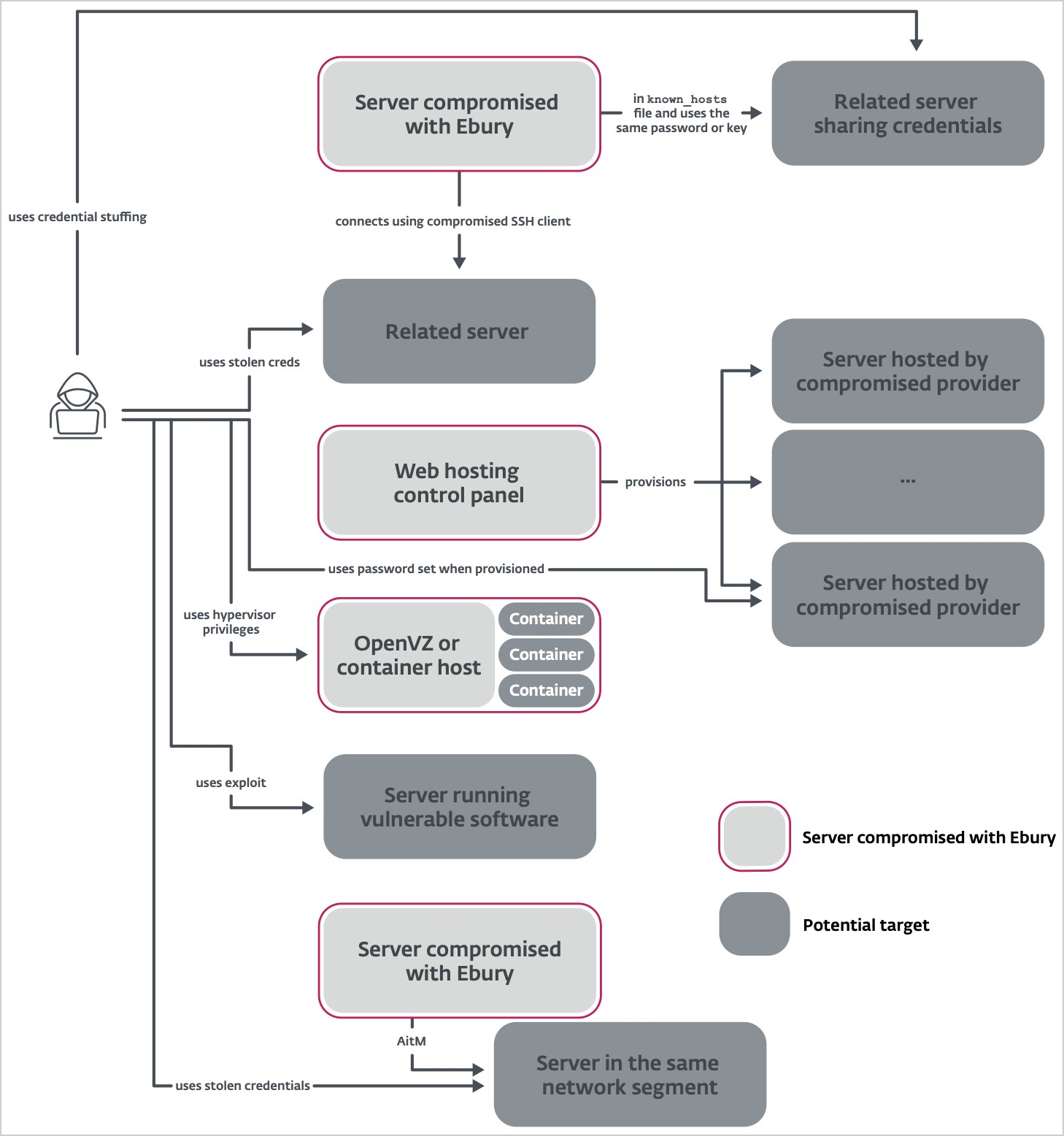
Supply: ESET
The internet hosting supplier’s infrastructure, together with OpenVZ or container hosts, will be leveraged to deploy Ebury throughout a number of containers or digital environments.
Within the subsequent section, the malware operators intercept SSH site visitors on the focused servers inside these information facilities through the use of Tackle Decision Protocol (ARP) spoofing to redirect site visitors to a server below their management.
As soon as a person logs right into a compromised server by way of SSH, Ebury captures the login credentials.
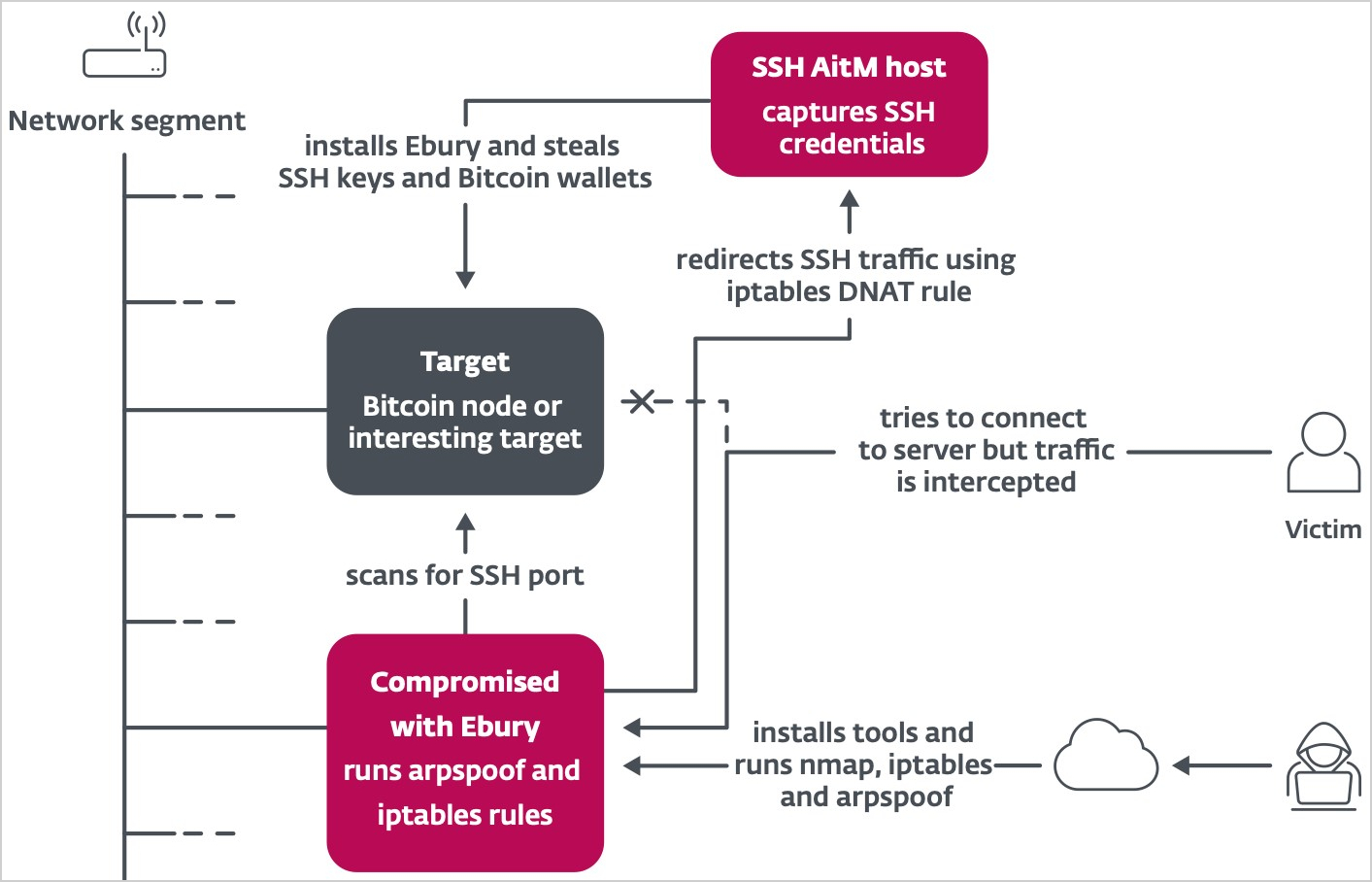
Supply: ESET
In instances the place servers host cryptocurrency wallets, Ebury makes use of the captured credentials to empty the wallets mechanically.
ESET says Ebury focused no less than 200 servers utilizing this methodology all through 2023, together with Bitcoin and Ethereum nodes.
The monetization methods differ, although, they usually additionally embody stealing bank card data entered into fee websites, redirecting net site visitors to generate income from advertisements and affiliate applications, utilizing compromised servers to ship spam, and promoting the captured credentials.
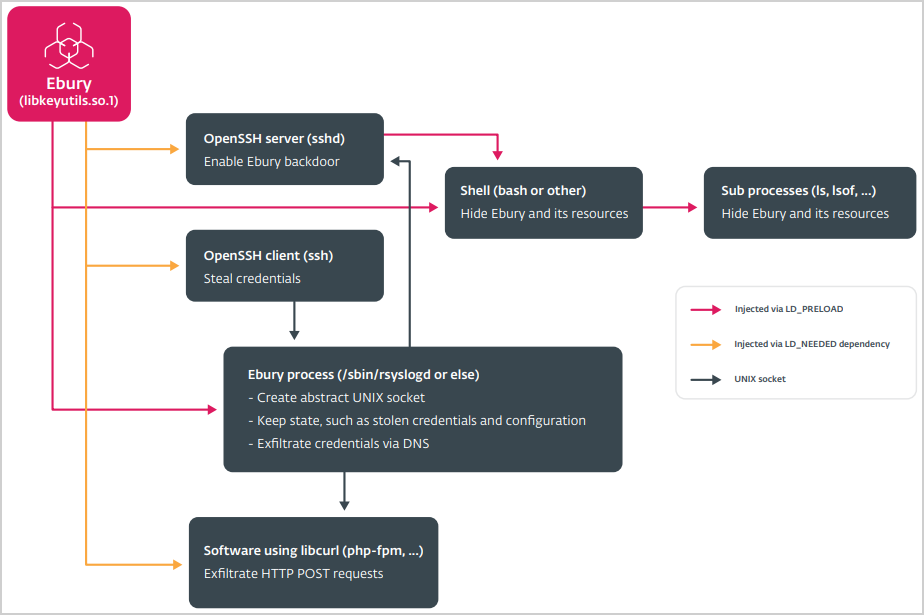
Supply: ESET
In late 2023, ESET says it noticed the introduction of latest obfuscation strategies and a brand new area era algorithm (DGA) system that enables the botnet to evade detection and enhance its resilience towards blocks.
The malware modules unfold by way of the Ebury botnet, primarily based on ESET’s newest observations, are:
- HelimodProxy: Proxies uncooked site visitors and relays spam by modifying the mod_dir.so Apache module, permitting the compromised server to run arbitrary instructions and assist spam campaigns.
- HelimodRedirect: Redirects HTTP site visitors to attacker-controlled web sites by modifying varied Apache and nginx modules to redirect a small proportion of net site visitors to malicious websites.
- HelimodSteal: Exfiltrates delicate data from HTTP POST requests by including an enter filter that intercepts and steals information submitted by way of net varieties, resembling login credentials and fee particulars.
- KernelRedirect: Modifies HTTP site visitors on the kernel stage to redirect guests through the use of a Linux kernel module that hooks into Netfilter, altering the Location header in HTTP responses to redirect customers to malicious URLs.
- FrizzySteal: Intercepts and exfiltrates HTTP requests by hooking into libcurl, enabling it to seize and steal information from HTTP requests made by the compromised server.
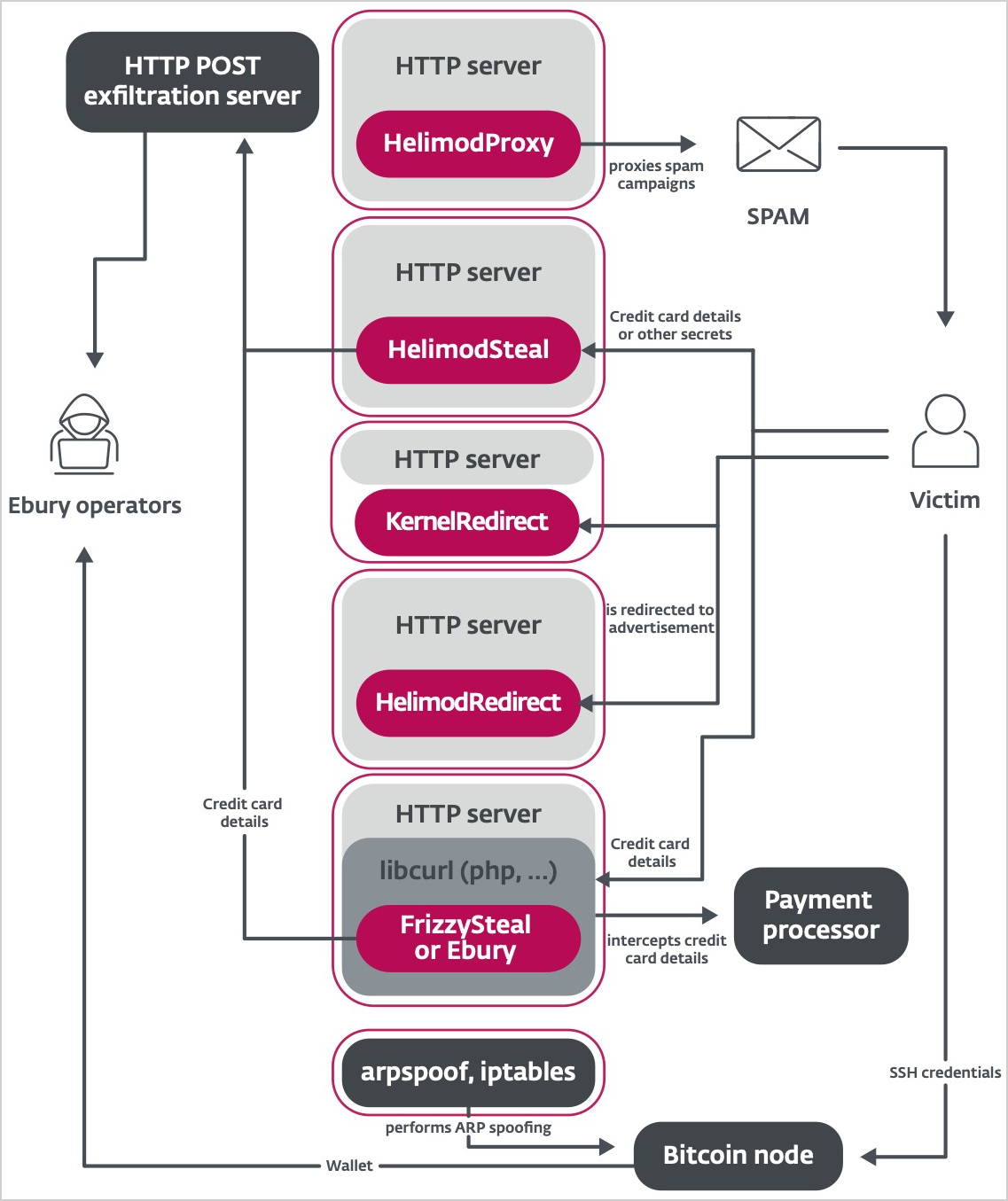
Supply: ESET
ESET’s newest investigation was carried out in collaboration with the Dutch Nationwide Excessive Tech Crime Unit (NHTCU), which not too long ago seized a backup server utilized by the cybercriminals.
The Dutch authorities say Ebury actors use pretend or stolen identities (by way of the Vidar Stealer), even assuming the monikers of different cybercriminals typically to mislead legislation enforcement.
The NHTCU is investigating proof present in that server, together with digital machines containing net looking artifacts resembling historical past and saved logins, however no concrete attributions have been made but.
