Our ancestors as soon as huddled in small, remoted communities, their faces illuminated by flickering fires.
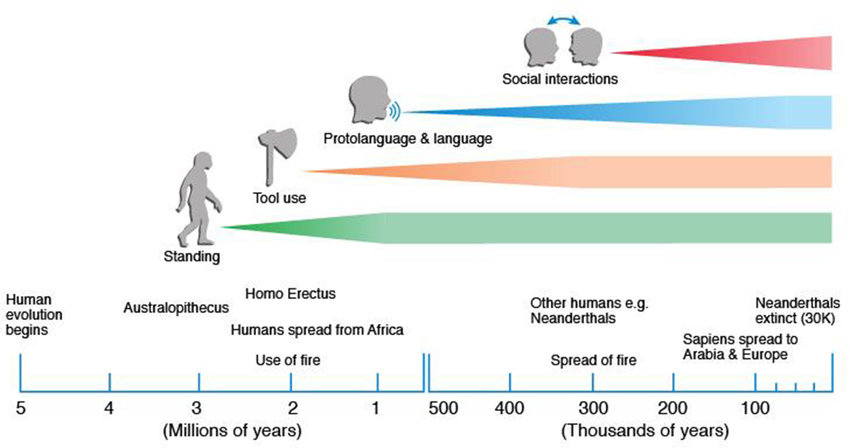
The primary proof of managed campfires for cooking and heat dates again some 700,000 years, although hominids had already existed for a number of million years by then.
Archaeological proof means that it wasn’t till the final 20,000 years or in order that people started to ‘settle down’ and have interaction in more and more advanced societal and cultural practices.
Solely within the final 20,000 years or so have people begun to ‘settle down’ and have interaction in more and more advanced societal and cultural practices.
Over 100,00 years earlier than that, homo erectus began to reside in small social teams, at which level we will observe modifications within the vocal tract, which point out primitive types of communication.
That is when early people started to translate and share their inner states, primarily constructing a primitive worldview through which somebody and one thing existed past the self.
Early types of communication and social bonding led to a cascade of modifications that thrust human evolution ahead, culminating within the formation and dominance of contemporary people, homo sapiens.
Little did early hominids know that the hearth round which they gathered was however a pale reflection of the hearth that burned inside them – the hearth of consciousness illuminating them on the trail to turning into human.
And little did they know that numerous generations later, their descendants would discover themselves gathered round a unique type of fireplace – the intense, electrical glow of their screens.
The primal roots of human thought
To know the character of this primitive thoughts, we should look to the work of evolutionary psychologists and anthropologists who’ve sought to reconstruct the cognitive world of our distant ancestors.
Certainly one of trendy evolutionary psychology’s key insights is that the human thoughts shouldn’t be a clean slate however a group of specialised cognitive modules formed by pure choice to resolve particular adaptive issues.
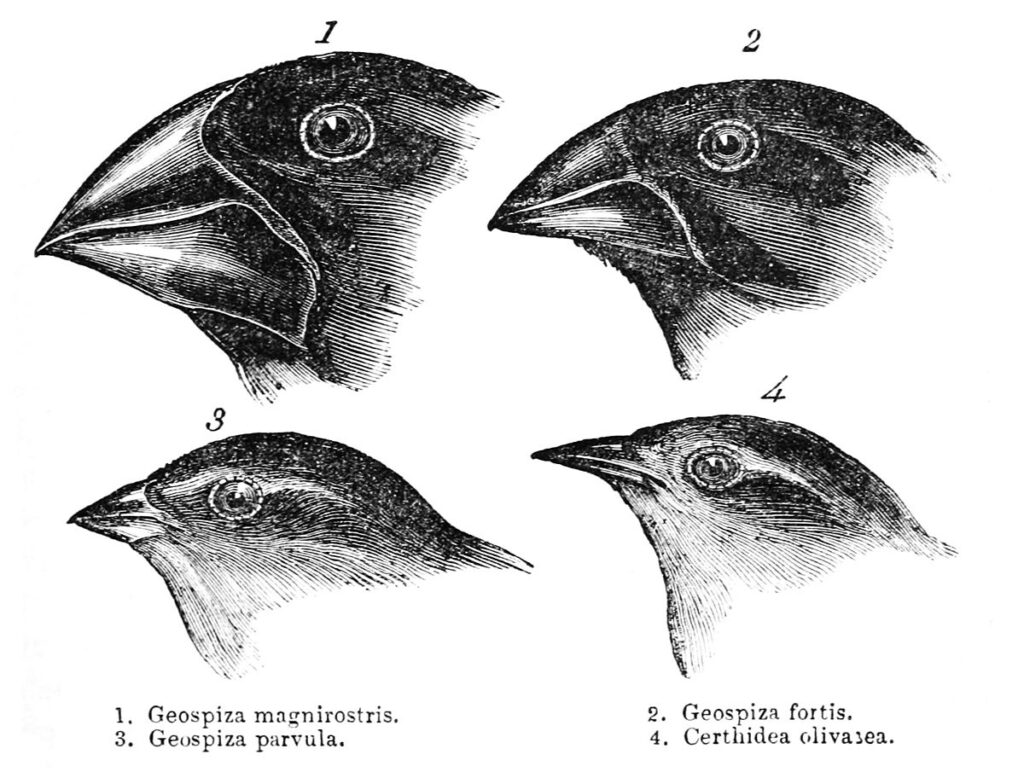
This isn’t unique to people. Darwin’s early evolutionary analysis noticed that the Galapagos finches, for instance, shared extremely specialised beaks that enabled them to occupy completely different ecological niches.
These diverse instruments correlated with numerous behaviors. One finch would possibly crack nuts with its massive, broad beak, whereas one other would possibly pry berries from a bush utilizing its razor-like invoice.
As psychologist Leda Cosmides and her colleagues, together with Steven Pinker, have argued in theories now summed as ‘evolutionary psychology,’ the mind’s modules function largely independently of each other, every processing domain-specific data.
Within the context of primitive historical past, this modular structure would have been extremely adaptive.
In a world the place survival relied on the flexibility to rapidly detect and reply to threats and alternatives within the atmosphere, a thoughts composed of specialised, domain-specific modules would have been extra environment friendly than a general-purpose, domain-general one.
Our distant ancestors inhabited this world. It was a world of quick sensations, primarily unconnected by an overarching narrative or sense of self.
Nevertheless, over the course of hundreds of years, hominid brains grew to become extra broadly interconnected, enabling instrument use, protolanguage, language, and social interplay.
In the present day, we all know that completely different elements of the mind change into closely built-in from delivery. fMRI research, resembling Raichle et al. (2001), present that data is shared between varied elements of the mind frequently at relaxation.
For instance, Holloway’s analysis (1996) on early hominid brains signifies modifications in mind structure over time supported enhanced integration. Stout and Chaminade (2007) explored how tool-making actions correlate with neural integration, suggesting that the calls for of those duties might have pushed the event of broader integrative neural capacities.
The necessity for advanced communication and summary reasoning elevated as people progressed from small-scale teams the place people had been intimately acquainted with each other’s experiences to bigger teams that always included people from completely different geographies, backgrounds, and appearances.
Language was maybe essentially the most highly effective catalyst for this cognitive revolution, creating shared that means by offering a way of encoding and transmitting advanced concepts and experiences throughout minds and generations.
People who might effectively talk and work with others gained benefits over these much less in a position. And gradually, people began to vocalize and talk simply because we might moderately than for any particular adaptive or survival worth.
Coming into the age of hyper-personalized realities
Allow us to re-center to the current day, the place expertise might once more current humanity with extremely individualized worlds in what could be described as a wierd circle again to the traditional thoughts.
AI and VR, for instance, are tailoring worlds to our particular person preferences and needs. By producing extremely sensible and context-aware textual content, photos, and even 3D fashions, we will create immersive environments, characters, and narratives extending past the pure world.
Furthermore, latest breakthroughs in edge computing and on-device AI processing have enabled VR gadgets to run subtle AI algorithms regionally with out counting on cloud-based servers.
This allows real-time, low-latency AI purposes inside VR environments, resembling dynamic object recognition, gesture monitoring, and speech interfaces.
In parallel, the most recent VR {hardware}, exemplified by the Apple Imaginative and prescient Professional, has seen big enhancements in show decision, refresh charges, and discipline of view, enhancing visible constancy and immersion.
Superior eye-tracking and hand-tracking applied sciences, powered by depth-sensing cameras and machine studying algorithms, now allow extra pure and intuitive interactions inside digital environments.
In 2016, Mark Zuckerberg strode by way of an occasion as attendees donned the Meta 2 headset, the ensuing picture turning into an iconic forwarding of VR’s perils to isolate folks of their private worlds.
is that this image an allegory of our future ? the folks in a digital actuality with our leaders strolling by us. pic.twitter.com/ntTaTN3SdR
— Nicolas Debock (@ndebock) February 21, 2016
VR didn’t take off again then; nonetheless, with the Apple Imaginative and prescient Professional, it’s on the cusp of a brand new period of mass adoption.
Many who’ve tried the Apple Imaginative and prescient Professional say it’ll ‘change everything,’ and carrying VR in public is already turning into widespread.
On this world, the idea of a shared actuality, a typical floor of expertise and understanding, might change into tenuous and fragmented.
VR’s influence on the mind
What units the hyper-personalized realities of the AI and VR age aside is their scope and granularity.
With machine studying, it’s now attainable to create digital worlds that aren’t simply superficially tailor-made to our tastes however basically formed by our cognitive quirks and idiosyncrasies.
As signaled by the Apple Imaginative and prescient Professional, we’re not simply content material shoppers however lively individuals in our personal personal realities.
However what are the impacts? Is all of it only a novelty?
A number of research have investigated the potential results of VR on cognitive processes, psychological well being, and social interactions.
A examine by Madary and Metzinger (2016), for instance, raised moral issues about using VR, notably relating to its influence on private id and autonomy.
The authors argued that VR’s immersive nature might result in a “loss of perspective” and a blurring of the boundaries between digital and actual experiences, doubtlessly affecting a person’s sense of self and decision-making processes.
A scientific evaluate by Spiegel (2018) examined VR use’s potential dangers and unwanted side effects. The findings instructed that extended publicity to VR environments might result in signs resembling eye pressure, complications, and nausea, collectively known as “cybersickness.”
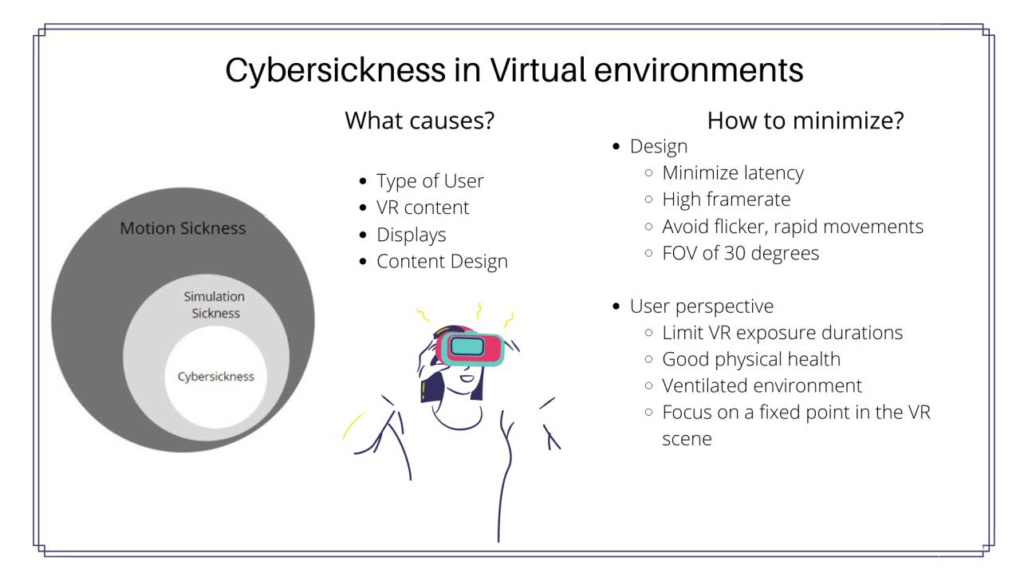
Among the many stranger impacts of VR, a examine by Yee and Bailenson (2007) explored the idea of the “Proteus Effect,” which refers back to the phenomenon the place a person’s habits in a digital atmosphere is influenced by their avatar’s look.
The examine discovered that individuals assigned taller avatars exhibited extra assured and assertive habits in subsequent digital interactions, demonstrating the potential for VR to change habits and self-perception.
The optimistic case for VR
Whereas it’s essential to acknowledge and deal with the dangers related to VR, it’s equally essential to acknowledge this expertise’s quite a few advantages and alternatives.
Some of the promising purposes of VR is within the discipline of training. Immersive digital environments can present college students with partaking and interactive studying experiences, permitting them to discover advanced ideas and phenomena in ways in which conventional instructing strategies can’t replicate.
For instance, a examine by Parong and Mayer (2018) discovered that college students who discovered by way of a VR simulation exhibited higher retention and data switch than those that discovered by way of a desktop simulation or slideshow.
VR additionally holds large potential within the realm of healthcare, notably within the areas of remedy and rehabilitation.
For instance, a meta-analysis by Fodor et al. (2018) examined the effectiveness of VR interventions for varied psychological well being circumstances, together with anxiousness problems, phobias, and post-traumatic stress dysfunction (PTSD). The findings indicated that VR-based therapies successfully lowered signs and improved affected person outcomes, highlighting this expertise’s therapeutic potential.
Furthermore, VR can function a strong instrument for fostering empathy and social connection. VR can promote understanding, compassion, and inclusivity by permitting people to expertise the world from completely different views and stroll in others’ footwear.
An intriguing examine by Herrera et al. (2018) investigated the influence of a VR expertise designed to advertise empathy towards homeless people.
The paradox of connectivity
At first look, the prospect of residing in a world of hyper-personalized realities might look like the final word achievement of a solipsistic dream – an opportunity to lastly inhabit a universe that’s completely tailor-made to our personal particular person wants and needs.
It may additionally be a world we will reside in endlessly, saving and loading checkpoints as we roam digital environments perpetually.
However left unmitigated, there’s one other facet to this final type of autonomy.
The notion of “reality” as a steady and goal floor of expertise depends upon a typical perceptual and conceptual framework—a set of shared assumptions, classes, and norms that enable us to speak and coordinate our actions with others.
If we change into enveloped in our individualized digital worlds the place every particular person inhabits their very own bespoke actuality, this widespread floor would possibly change into more and more fragmented.
When your digital world radically differs from mine, not simply in its floor particulars however in its deepest ontological and epistemological foundations, mutual understanding and collaboration danger fraying on the edges.
On this sense, the hyper-personalized realities of the AI age signify a paradox: at the same time as they promise to attach us in ever-more intimate and immersive methods, they threaten to drive us additional aside.
Steering a hyper-personalized future
The arrival of AI-powered, hyper-personalized digital realities oddly mirrors our distant ancestors’ remoted, individualized worlds.
As humanity spends extra time in these hyper-personalized realities, the extra our ideas, feelings, and behaviors might change into attuned to their very own distinctive logic and construction.
So, how can we undertake the benefits of next-gen VR with out dropping sight of our shared humanity?
Vigilance, consciousness, and respect are essential. The long run will see some who embrace residing in VR worlds, augmenting themselves with mind implants and cybernetics, and so forth. It would additionally see those that reject that favor a extra conventional life-style.
We should respect each views.
This implies being aware of the algorithms and interfaces that mediate our expertise of the world and actively looking for experiences that problem our assumptions and biases. Hopefully, it is going to change into intuitive to maintain one foot exterior of the digital world.
So, as we collect across the flickering screens of our digital campfires, allow us to not overlook the teachings of our ancestors, the significance of intersubjectivity, and the perils of retreating into isolation.
Beneath the floor of our variations and idiosyncrasies, we share a elementary cognitive structure formed by tens of millions of years of evolutionary historical past.