Citrix notified clients this week to manually mitigate a PuTTY SSH shopper vulnerability that would permit attackers to steal a XenCenter admin’s non-public SSH key.
XenCenter helps handle Citrix Hypervisor environments from a Home windows desktop, together with deploying and monitoring digital machines.
The safety flaw (tracked as CVE-2024-31497) impacts a number of variations of XenCenter for Citrix Hypervisor 8.2 CU1 LTSR, which bundle and use PuTTY to make SSH connections from XenCenter to visitor VMs when clicking the “Open SSH Console” button.
Citrix says that the PuTTY third-party element has been eliminated beginning with XenCenter 8.2.6, and any variations after 8.2.7 will not embody it.
“An issue has been reported in versions of PuTTY prior to version 0.81; when used in conjunction with XenCenter, this issue may, in some scenarios, allow an attacker who controls a guest VM to determine the SSH private key of a XenCenter administrator who uses that key to authenticate to that guest VM while using an SSH connection,” Citrix explains in a Wednesday safety advisory.
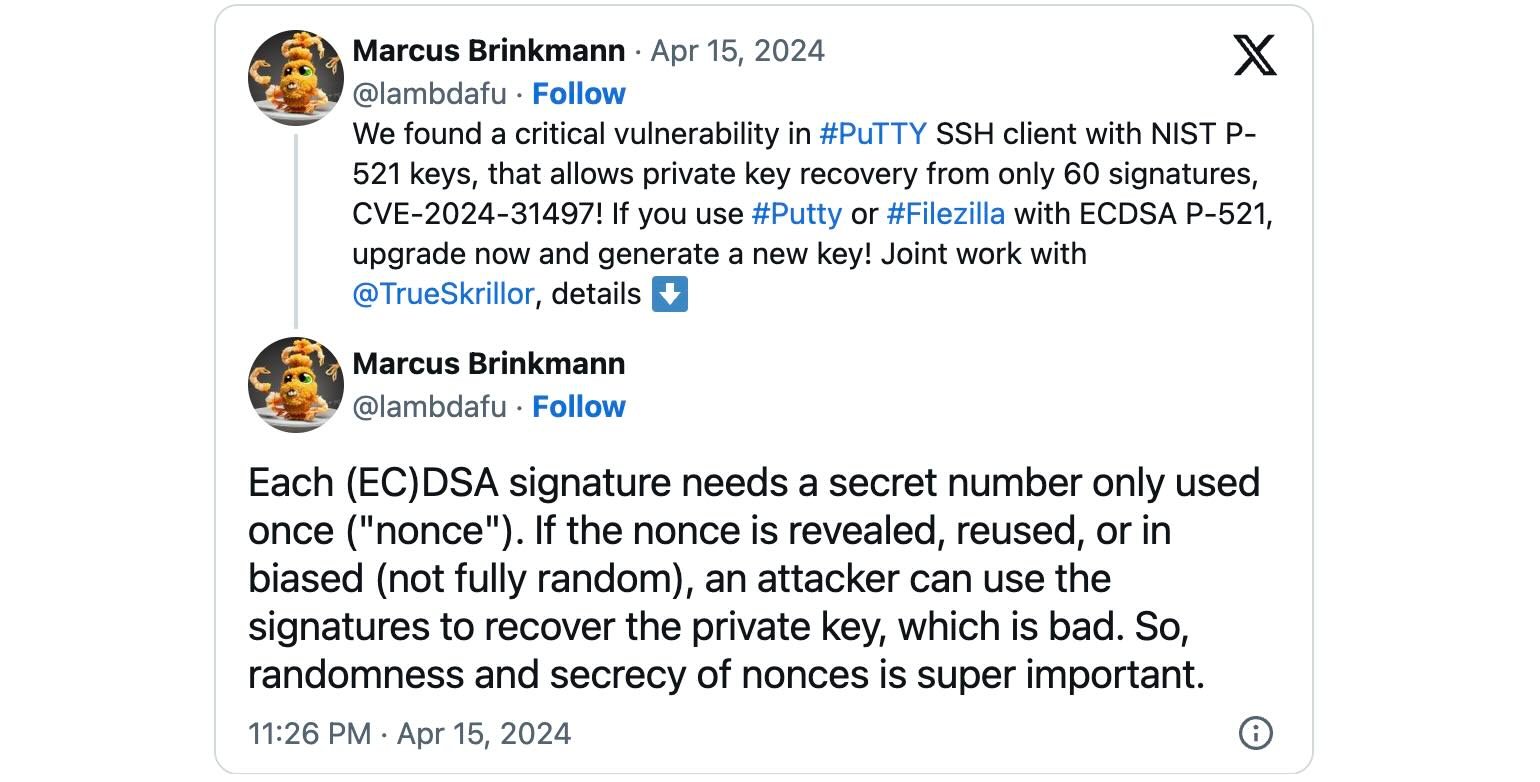
Discovered and reported by Fabian Bäumer and Marcus Brinkmann of Ruhr College Bochum, CVE-2024-31497 is attributable to how older variations of the Home windows-based PuTTY SSH shopper generate ECDSA nonces (short-term distinctive cryptographic numbers) for the NIST P-521 curve used for authentication.
The corporate informed admins who wish to mitigate the vulnerability to obtain the newest model of PuTTY and set up it rather than the model bundled with older XenCenter releases.
“Customers who do not wish to use the “Open SSH Console” functionality may remove the PuTTY component completely,” Citrix added.
“Customers who wish to maintain the existing usage of PuTTY should replace the version installed on their XenCenter system with an updated version (with a version number of at least 0.81).”
In January, CISA ordered U.S. federal businesses to patch the CVE-2023-6548 code injection and the CVE-2023-6549 buffer overflow Citrix Netscaler vulnerabilities someday after Citrix warned they have been actively exploited as zero-days.
One other vital Netscaler flaw (tracked as CVE-2023-4966 and dubbed Citrix Bleed) was exploited as a zero-day by a number of hacking teams to breach authorities organizations and high-profile tech firms, reminiscent of Boeing, earlier than being patched in October.
The Well being Sector Cybersecurity Coordination Middle (HHS’ cybersecurity workforce) additionally warned well being organizations in a sector-wide alert to safe NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway situations in opposition to surging ransomware assaults.