The U.S. Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Safety Company (CISA) has added two vulnerabilities in its Recognized Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, together with a Linux kernel privilege elevation flaw.
The high-severity flaw tracked as CVE-2024-1086 was first disclosed on January 31, 2024, as a use-after-free downside within the netfilter: nf_tables element, however was first launched by a commit in February 2014.
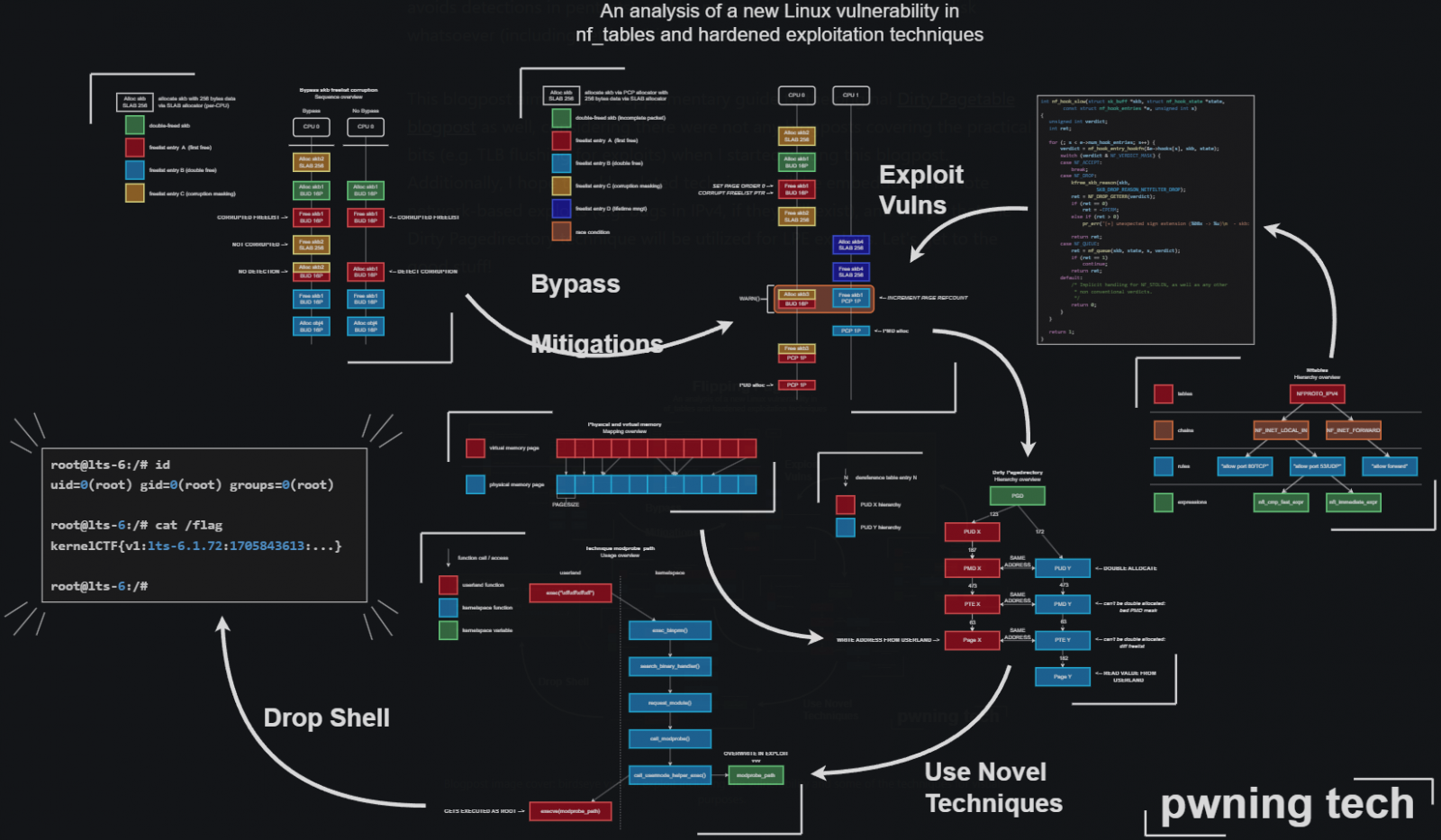
Netfilter is a framework offered by the Linux kernel that enables numerous networking-related operations, equivalent to packet filtering, community tackle translation (NAT), and packet mangling.
The vulnerability is triggered as a result of the ‘nft_verdict_init()’ operate permits constructive values for use as a drop error inside the hook verdict, inflicting the ‘nf_hook_slow()’ operate to execute a double free when NF_DROP is issued with a drop error that resembles NF_ACCEPT.
Exploitation of CVE-2024-1086 permits an attacker with native entry to attain privilege escalation on the goal system, probably gaining root-level entry.
The difficulty was fastened by way of a commit submitted in January 2024, which rejects QUEUE/DROP verdict parameters, thus stopping exploitation.
The repair has been backported to a number of steady kernel variations as listed beneath:
- v5.4.269 and later
- v5.10.210 and later
- v6.6.15 and later
- v4.19.307 and later
- v6.1.76 and later
- v5.15.149 and later
- v6.7.3 and later
In late March 2024, a safety researcher utilizing the alias ‘Notselwyn’ printed a detailed write-up and proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit on GitHub, showcasing the best way to obtain native privilege escalation by exploiting the flaw on Linux kernel variations between 5.14 and 6.6.
Whereas most Linux distrobutions pushed out fixes pretty shortly, Purple Hat had not pushed out a repair till March, making it doable that risk actors used the general public exploit on compromised techniques.
CISA didn’t share particular particulars about how the vulnerability is exploited, however BleepingComputer has seen posts on hacking boards concerning the public exploits.
The cybersecurity company has now given federal businesses till June 20, 2024, to use the out there patches.
If updating shouldn’t be doable, admins are really useful to use the next mitigations:
- Blocklist ‘nf_tables’ if it isn’t wanted/actively used.
- Limit entry to consumer namespaces to restrict the assault floor.
- Load the Linux Kernel Runtime Guard (LKRG) module (could cause instability)
The second flaw CISA added on the KEV catalog this time, additionally setting the due date to June 20, is CVE-2024-24919, an info disclosure vulnerability impacting VPN gadgets from Verify Level.
Following the seller’s disclosure and safety replace launch for this flaw, researchers from Watchtowr Labs printed their evaluation, underlining that the vulnerability is much worse than what Verify Level’s bulletin mirrored.
