During the last decade, the Chinese language authorities has established an environment friendly pipeline of capture-the-flag (CTF) tournaments each as a approach to entice cyber-savvy residents to cybersecurity, and as a part of its cybersecurity curriculum and coaching routine.
The efforts have paid off.
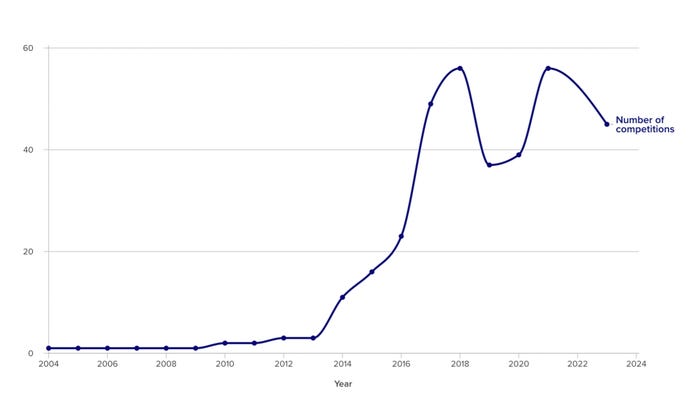
At present, the nation has greater than 50 annual competitions used as a part of the coaching of tens of 1000’s — and presumably, lots of of 1000’s — of cybersecurity specialists, whereas creating stronger connections to authorities and business, in line with a analysis report printed by the Atlantic Council on Oct. 18. Furthermore, sector-specific contests — concentrating on cellular, autonomous automobiles, and sensible cities, for instance — assist deepen the technical experience of members and tackle the precise wants of every business.
General, the Chinese language authorities has efficiently marshaled the nation towards fixing its cybersecurity shortages and the aim of turning into a cyber superpower, says Eugenio Benincasa, senior cyber protection researcher on the Middle of Safety Research at ETH Zurich and a co-author of the report.
“China, like the West, has a scarcity of talents, and addressing that scarcity through a system that can help you to evaluate talent is definitely a better way of addressing the problem,” he says. “If you look at the entire ecosystem, there are many ways in which hacking contests can bring better allocation of resources, both in the short and also in the long term.”
In 2014, Chinese language President Xi Jinping referred to as for the nation to turn into a “cyber great power,” aiming to strengthen its know-how business, whereas on the identical time, embarking on a home effort to limit its reliance on international know-how. Cybersecurity has turn into a key ingredient of that effort: The Chinese language authorities has efficiently created a pipeline for coaching future cybersecurity specialists, restricted the dissemination of vulnerability data, and established its personal cybersecurity suppliers. These embody hacking companies and cyber-range operators — comparable to Beijing Integrity Tech and Cyber Peace — which act each as hosts for reputable infrastructure and for some nation-state actors, comparable to Flax Storm.
Essential Curriculum for Cybersecurity Research
Hacking contests are a key element of the nation’s efforts. Not less than 129 distinctive cybersecurity occasions, together with 54 annual contests, had been recognized by the report’s authors, Benincasa and Dakota Cary, a strategic advisory advisor at Sentinel One.
China’s Ministry of Training accounts for probably the most competitions — a complete of twenty-two — recognized by the researchers, in contrast with 14 related to the Our on-line world Administration of China, and 13 sponsored by the Ministry of Public Safety, in line with the report. About two-thirds of universities thought of hacking contests to be an essential a part of the curriculum for cybersecurity specialists, with greater than three-quarters of scholars (77%) taking part in a minimum of one occasion by the top of their sophomore yr.
For the reason that early 2010s, China’s CTF competitions have taken off. Supply: “Capture the (red) flag” report, Atlantic Council
Amongst different advantages, the competitions permit the Chinese language authorities to achieve essential data on new methods and strategies, in addition to gathering exploit strategies utilized by members, which the federal government mandated since 2018. Hacking contests may entice youthful members, comparable to excessive schoolers, into the sector of cybersecurity, and assist professionals sustain their abilities.
In comparison with China’s complete method, Western nations proceed to fall brief, Benincasa says.
“There are contests that are organized by the private companies or universities, but they do not go into the detail or scale that we see in China, nor they are part of university degrees,” he says. “They do not count as part of the evaluation to your grades, and so that practical-skill, direct-confrontation component is absent compared to the Chinese ecosystem.”
China’s Reversal of Cyber Fortunes
The trouble is a reversal of the state of affairs earlier than 2015, when Chinese language CTF groups struggled in worldwide contests and met with social condemnation domestically for benefiting from vulnerability awards. China’s CTF ecosystems — particularly the intercollegiate competitions, which deliver collectively lots of of groups — are actually the very best on the earth, in line with the researchers. Main contests embody the Data Safety Ironman Triathlon, Qiang Wang Cup, Wangding Cup, and Nationwide College Cyber Security League.
The occasions all have authorities help, with the Ministry of Public Safety, the Individuals’s Liberation Military, the Ministry of State Safety, and the Ministry of Training all sponsoring a minimum of one of many university-based occasions every.
Western governments may be taught from the method, Benincasa says. Presently, the US and Europe face a shortage of cyber expertise due to a scarcity of a pipeline for funneling technically minded college students into cybersecurity roles.
“We are behind when it comes to, specifically, the hacking-contest ecosystem,” he says. “We need to integrate CTF contests into academic curricula, so we can have a better, more direct correlation between hacking classes and the graduation of talent.”
China was in a position to turnaround its cybersecurity image, and the lesson is, specializing in sensible expertise by hacking contests and CTF tournaments — in addition to creating deeper pipelines between universities, the federal government, and business — may go a great distance towards fixing the issues.
“This was very much a bottom-up, organically driven process that at some point the state recognized and encouraged,” he says. “They started seeing these successes abroad and recognizing — because of geopolitical occasions like Stuxnet and [Edward] Snowden — recognizing how important [cybersecurity] is and that contributed to the breaking of taboos and … a big change in the culture.”