A malware botnet is exploiting a zero-day vulnerability in end-of-life GeoVision units to compromise and recruit them for possible DDoS or cryptomining assaults.
The flaw is tracked as CVE-2024-11120 and was found by Piort Kijewski of The Shadowserver Basis. It’s a essential severity (CVSS v3.1 rating: 9.8) OS command injection downside, permitting unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary system instructions on the gadget.
“Unauthenticated remote attackers can exploit this vulnerability to inject and execute arbitrary system commands on the device,” warns Taiwan’s CERT.
“Moreover, this vulnerability has already been exploited by attackers, and we have received related reports.”
In response to TWCERT, the vulnerability impacts the next gadget fashions:
- GV-VS12: A 2-channel H.264 video server that converts analog video indicators into digital streams for community transmission.
- GV-VS11: A single-channel video server designed to digitize analog video for community streaming.
- GV-DSP LPR V3: A Linux-based system devoted to license plate recognition (LPR).
- GV-LX4C V2 / GV-LX4C V3: Compact digital video recorders (DVRs) designed for cell surveillance purposes.
All of those fashions have reached the tip of life and are now not supported by the seller, so no safety updates are anticipated.
Risk monitoring platform The Shadowserver Basis reviews that roughly 17,000 GeoVision units are uncovered on-line and are weak to the CVE-2024-11120 flaw.
Kijewski instructed BleepingComputer that the botnet seems to be a Mirai variant, which is normally used as a part of DDoS platforms or to carry out cryptomining.
Many of the uncovered units (9,100) are primarily based in america, adopted by Germany (1,600), Canada (800), Taiwan (800), Japan (350), Spain (300), and France (250).
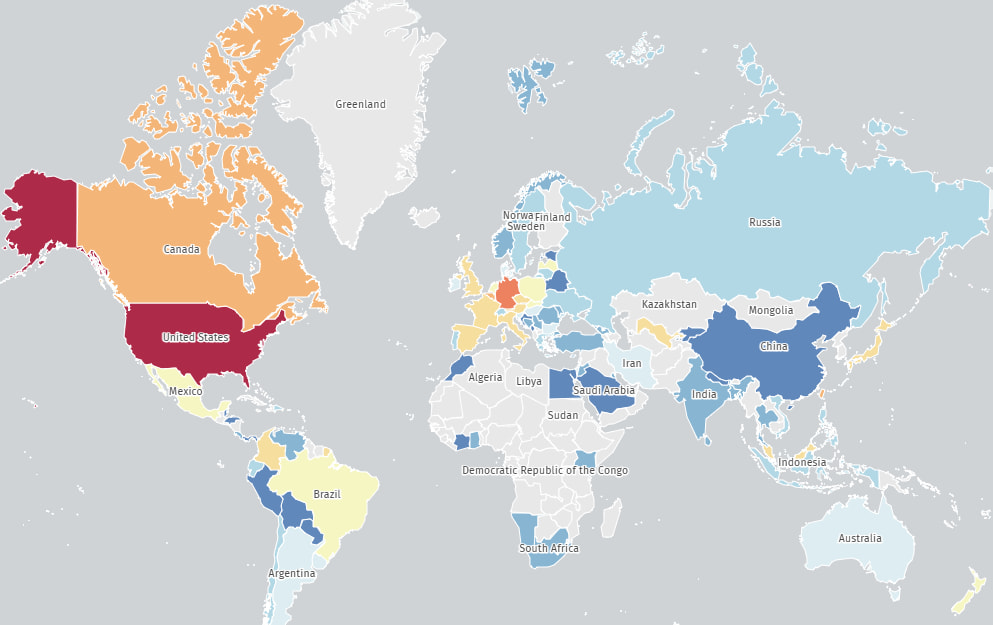
Supply: The Shadowserver Basis
Generally, indicators of botnet compromise embrace units heating excessively, changing into sluggish or unresponsive, and having their configuration arbitrarily modified.
If you happen to discover any of those signs, carry out a tool reset, change the default admin password to one thing robust, flip off distant entry panels, and place the gadget behind a firewall.
Ideally, these units needs to be changed with actively supported fashions, but when that is not possible, they need to be remoted on a devoted LAN or subnet and intently monitored.

.png)