The variety of Microsoft vulnerabilities has largely flattened in 2023, with elevation of privilege and identification assaults being significantly frequent, in response to BeyondTrust’s annual Microsoft Vulnerabilities report.
Identification and entry administration options firm BeyondTrust studied probably the most important CVEs of 2023 and Microsoft vulnerability information from Microsoft’s month-to-month Patch Tuesday bulletins. The report consists of vulnerability traits and tips on the right way to scale back identification assaults.
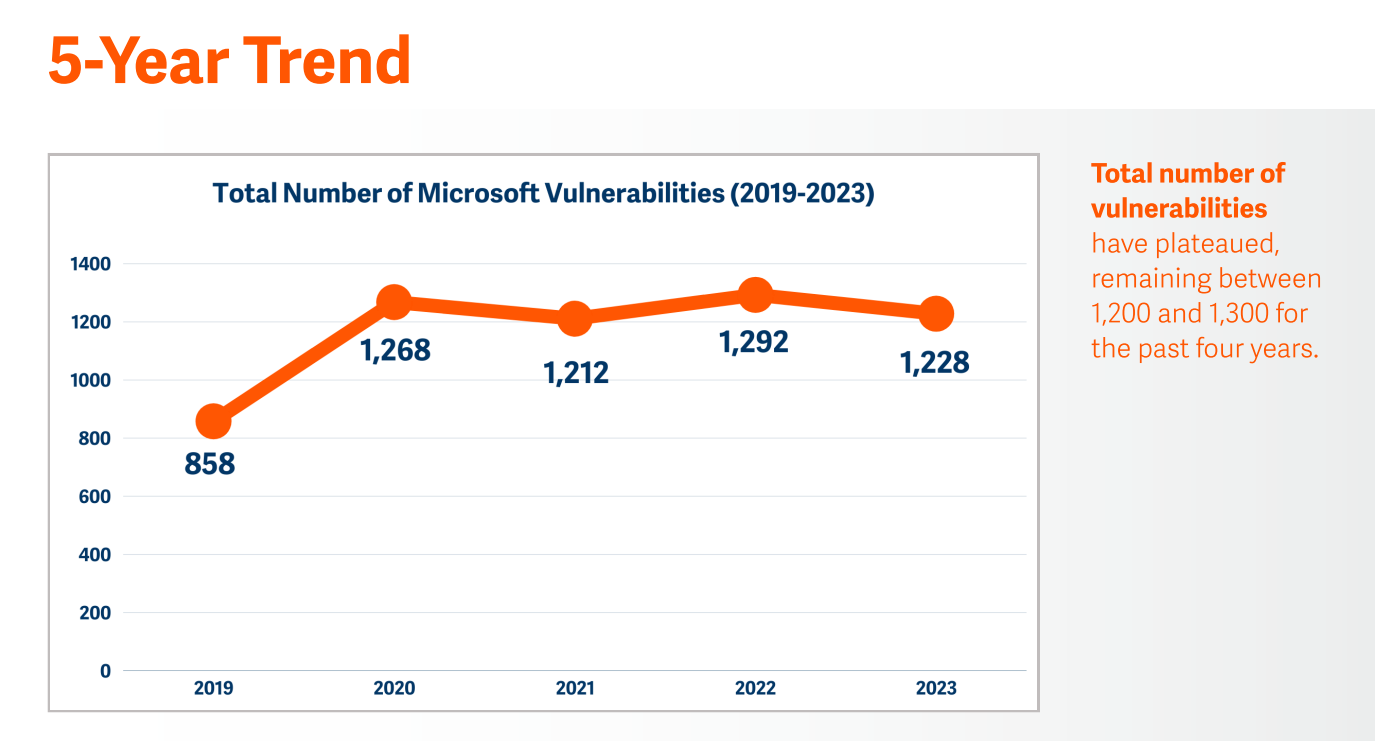
Microsoft reported 1,228 vulnerabilities in 2023
The full variety of Microsoft vulnerabilities has remained largely regular for the previous 4 years, with a slight (5%) dip in 2023 from 1,292 to 1,228 reported vulnerabilities.
“Microsoft’s efforts to promptly patch known vulnerabilities may be offsetting the discovery of new ones by reducing the window of opportunity for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities,” David Morimanno, director of identification and entry administration applied sciences, Integral Companions, instructed BeyondTrust. “Also, as the MS codebase matures, new vulnerabilities might be getting introduced at a slower rate.”
The speed of essential Microsoft vulnerabilities (i.e., these with a rating of 9.0 or increased on NIST’s Frequent Vulnerability Scoring System) has slowed. There have been 84 Microsoft essential vulnerabilities in 2023, in comparison with 89 in 2022 and a five-year excessive of 196 in 2020.
How Microsoft vulnerabilities are labeled
Microsoft has its personal severity score system distinct from NIST, which is able to produce barely totally different numbers. For instance, 33 Microsoft vulnerabilities from 2023 had been labeled as essential in NIST’s scoring system, however Microsoft itself labeled 84 vulnerabilities in 2023 as essential. Microsoft’s classification system nonetheless displays the general pattern of a slight lower in vulnerabilities year-over-year, displaying a lower in extreme vulnerabilities by 6%.
BeyondTrust famous that not all recorded Microsoft vulnerabilities pose important threat; some are largely theoretical or would have minimal influence even when they had been exploited. Nonetheless, some could be severely damaging to a corporation if exploited, and these are those Microsoft tends to categorise as essential — whether or not or not a risk actor has actively exploited the vulnerability.
The commonest sorts of Microsoft vulnerabilities
The commonest sorts of vulnerabilities in 2023 had been:
- Elevation of privilege (490).
- Distant code execution (356).
- Data disclosure (124).
- Denial of service (109).
- Spoofing (90).
- Safety failure bypass (56).
- Tampering (3).
Among the many vulnerabilities listed as essential, most had been discovered within the Home windows Desktop and Server classes. These two classes have the identical codebase, so it’s not shocking their numbers are comparable.
Though elevation of privilege was the commonest vulnerability, with 490 cases in 2023, that was a big lower from 715 cases in 2022. Azure and Home windows Server specifically noticed a lot fewer elevation of privilege vulnerabilities.
SEE: Microsoft just lately opened basic entry to Safety Copilot, the generative AI add-on to its suite of safety merchandise. (TechRepublic)
Distant code execution vulnerabilities decreased in Azure, Workplace and Home windows however elevated in Home windows Server.
Particulars on which sorts of vulnerabilities cropped up during which Microsoft merchandise and when could be present in the whole report.
Risk actors concentrate on identity-based infiltration strategies
“As the overall number of Microsoft vulnerabilities stabilizes and the number of critical vulnerabilities decreases, we see that attackers, much like water, will flow to the path of least resistance and focus much more of their attention on identities,” the report acknowledged.
Microsoft suffered the Midnight Blizzard assault, a state-sponsored breach that might have impacted U.S. federal companies due to identity-based infiltration enabled by password spraying.
“Midnight Blizzard was another case of the popular adage, ‘Attackers don’t break in – they log in,’” Jay Beale, CEO and CTO of IT consulting firm InGuardians, Inc., instructed BeyondTrust within the report.
Identification-based infiltration is so simple as an attacker buying respectable login data one way or the other. Identification dangers could be tough to establish forward of time and might crop up in any of the next methods:
- The joiner, mover and leaver course of.
- Consumer permissions, rights, privileges and roles.
- Entitlements authentication, similar to multi-factor authentication or single sign-on.
- Authorization for identities and accounts at relaxation and working throughout runtime.
Defenders ought to begin to suppose extra holistically about privileges, identification hygiene and identification risk detection with the intention to detect extra identity-based infiltration assaults, the report suggested.
“Fostering a culture of awareness and education among all users is crucial,” Paula Januszkiewicz, CEO of CQURE, instructed BeyondTrust. “Unlike hacking, which is often a solitary job, cybersecurity is inherently a collaborative effort. This perspective, echoed in the report, highlights the importance of a people-centric approach to cybersecurity.”
Why Microsoft vulnerabilities are lowering
BeyondTrust listed some doable explanation why dangers to Microsoft merchandise are steadily lowering. Refresh cycles proceed, lastly phasing out long-forgotten code that might be unsupported and as much as 20 years outdated. Particularly, merchandise made earlier than Microsoft instituted the Safety Growth Lifecycle in 2004 are being totally phased out. Microsoft’s long-term safety efforts could also be paying off. Cloud applied sciences have matured and might now be secured extra successfully.
BeyondTrust attributed a few of the success in lowering vulnerabilities to Microsoft’s elevated collaboration with its safety analysis neighborhood. Particularly, the safety analysis neighborhood detected lots of the distant code execution vulnerabilities present in Home windows Server in 2023.
Utilizing a Chromium code base for Edge as a substitute of a customized Microsoft codebase and eradicating assist for Web Explorer might have each diminished cases of essential vulnerabilities in Edge.
Microsoft has locked down some ways attackers can exploit phishing and malware payloads utilizing Workplace purposes. Nonetheless, the addition of assist for SketchUp Software program’s proprietary SKP recordsdata in June 2022 allowed for some vulnerabilities to be exploited by way of 3D fashions.