A brand new model of the Banshee info-stealing malware for macOS has been evading detection over the previous two months by adopting string encryption from Apple’s XProtect.
Banshee is an info stealer centered on macOS techniques. It emerged in mid-2024 as a stealer-as-a-service accessible to cybercriminals for $3,000.
Its supply code was leaked on the XSS boards in November 2024, resulting in the undertaking shutting down for the general public and creating a chance for different malware builders to enhance on it.
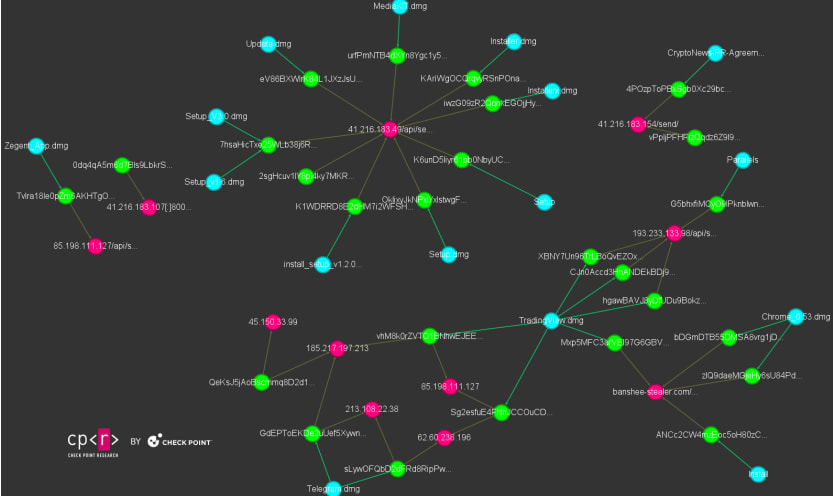
Based on Examine Level Analysis, which found one of many new variants, the encryption methodology current in Banshee permits it to mix in with regular operations and to look authentic whereas accumulating delicate info from contaminated hosts.
One other change is that it now not keep away from techniques belonging to Russian customers.
Supply: Examine Level
XProtect encryption
Apple’s XProtect is the malware detection know-how constructed into macOS. It makes use of a algorithm, much like antivirus signatures, to determine and block identified malware.
The newest model of Banshee Stealer adopted a string encryption algorithm that XProtect itself makes use of to guard its knowledge.
By scrambling its strings and solely decrypting them throughout execution, Banshee can evade normal static detection strategies.
It is usually potential that macOS and third-party anti-malware instruments deal with the actual encryption approach with much less suspicion, permitting Banshee to function undetected for longer intervals.
Stealing delicate knowledge
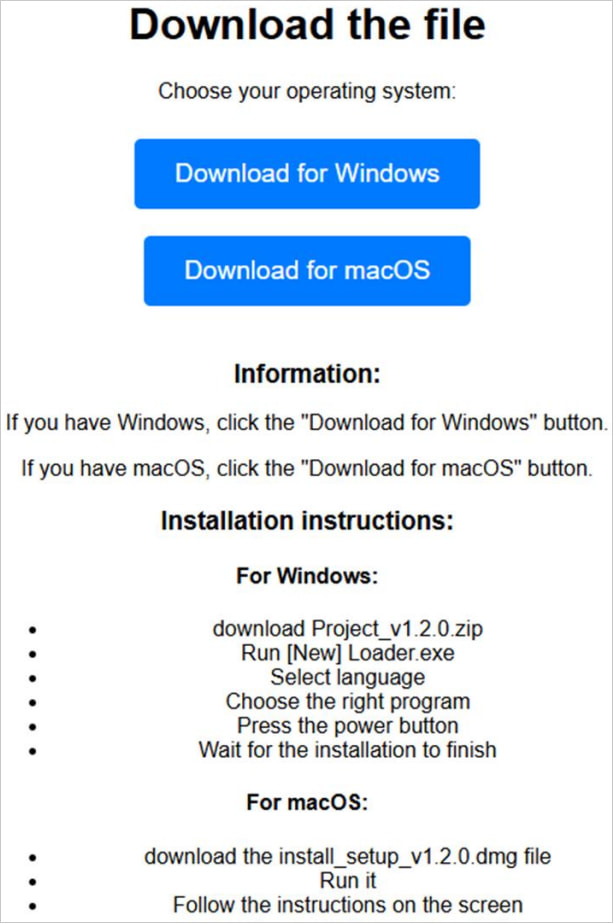
The newest Banshee stealer variant is primarily distributed by way of misleading GitHub repositories concentrating on macOS customers by software program impersonation. The identical operators additionally goal Home windows customers, however with Lumma Stealer.
Supply: Examine Level
Examine Level studies that whereas the Banshee malware-as-a-service operation has remained down since November, a number of phishing campaigns continued to distribute the malware since the supply code leaked.
The infostealer targets knowledge saved in standard browsers (e.g. Chrome, Courageous, Edge, and Vivaldi), together with passwords, two-factor authentication extensions, and cryptocurrency pockets extensions.
It additionally collects fundamental system and networking details about the host and serves victims misleading login prompts to steal their macOS passwords.
