Risk actors behind the Akira ransomware group have extorted roughly $42 million in illicit proceeds after breaching the networks of greater than 250 victims as of January 1, 2024.
“Since March 2023, Akira ransomware has impacted a wide range of businesses and critical infrastructure entities in North America, Europe, and Australia,” cybersecurity businesses from the Netherlands and the U.S., together with Europol’s European Cybercrime Centre (EC3), mentioned in a joint alert.
“In April 2023, following an initial focus on Windows systems, Akira threat actors deployed a Linux variant targeting VMware ESXi virtual machines.”
The double-extortion group has been noticed utilizing a C++ variant of the locker within the early levels, earlier than shifting to a Rust-based code as of August 2023. It is price noting that the e-crime actor is fully totally different from the Akira ransomware household that was lively in 2017.
Preliminary entry to focus on networks is facilitated by way of exploiting identified flaws in Cisco home equipment (e.g., CVE-2020-3259 and CVE-2023-20269).
Alternate vectors contain the usage of Distant Desktop Protocol (RDP), spear-phishing, legitimate credentials, and digital non-public community (VPN) companies missing in multi-factor authentication (MFA) protections.
Akira actors are additionally identified to leverage numerous methods to arrange persistence by creating a brand new area account on the compromised system, in addition to evade detection by abusing the Zemana AntiMalware driver to terminate antivirus-related processes by way of what’s known as a Carry Your Personal Susceptible Driver (BYOVD) assault.
To assist in privilege escalation, the adversary depends on credential scraping instruments like Mimikatz and LaZagne, whereas Home windows RDP is utilized to maneuver laterally throughout the sufferer’s community. Information exfiltration is achieved by way of FileZilla, WinRAR, WinSCP, and RClone.
“Akira ransomware encrypts targeted systems using a hybrid encryption algorithm that combines Chacha20 and RSA,” Pattern Micro mentioned in an evaluation of the ransomware revealed in October 2023.
“Additionally, the Akira ransomware binary, like most modern ransomware binaries, has a feature that allows it to inhibit system recovery by deleting shadow copies from the affected system.”
Blockchain and supply code knowledge suggests that Akira ransomware group is probably going affiliated with the now-defunct Conti ransomware gang. A decryptor for Akira was launched by Avast final July, nevertheless it’s extremely possible the shortcomings have since been plugged.
Akira’s mutation to focus on Linux enterprise environments additionally follows related strikes by different established ransomware households akin to LockBit, Cl0p, Royal, Monti, and RTM Locker.
LockBit’s Struggles to Come Again
The disclosure comes as Pattern Micro revealed that the sweeping legislation enforcement takedown of the prolific LockBit gang earlier this February has had a big operational and reputational affect on the group’s skill to bounce again, prompting it to submit previous and pretend victims on its new knowledge leak web site.
“LockBit was one of the most prolific and widely used RaaS strains in operation, with potentially hundreds of affiliates, including many associated with other prominent strains,” Chainalysis famous in February.
The blockchain analytics agency mentioned it uncovered cryptocurrency trails connecting a LockBit administrator to a journalist primarily based in Sevastopol generally known as Colonel Cassad, who has a historical past of soliciting donations for Russian militia group operations within the sanctioned jurisdictions of Donetsk and Luhansk following the onset of the Russo-Ukrainian battle in 2022.
It is price mentioning that Cisco Talos, in January 2022, linked Colonel Cassad (aka Boris Rozhin) to an anti-Ukraine disinformation marketing campaign orchestrated by the Russian state-sponsored group generally known as APT28.
“Following the operation, LockBitSupp [the alleged leader of LockBit] appears to be attempting to inflate the apparent victim count while also focusing on posting victims from countries whose law enforcement agencies participated in the disruption,” Pattern Micro mentioned in a latest deep dive.
“This is possibly an attempt to reinforce the narrative that it would come back stronger and target those responsible for its disruption.”
In an interview with Recorded Future Information final month, LockBitSupp acknowledged the short-term decline in earnings, however promised to enhance their safety measures and “work as long as my heart beats.”
“Reputation and trust are key to attracting affiliates, and when these are lost, it’s harder to get people to return. Operation Cronos succeeded in striking against one element of its business that was most important: its brand,” Pattern Micro said.
Agenda Returns with an Up to date Rust Model
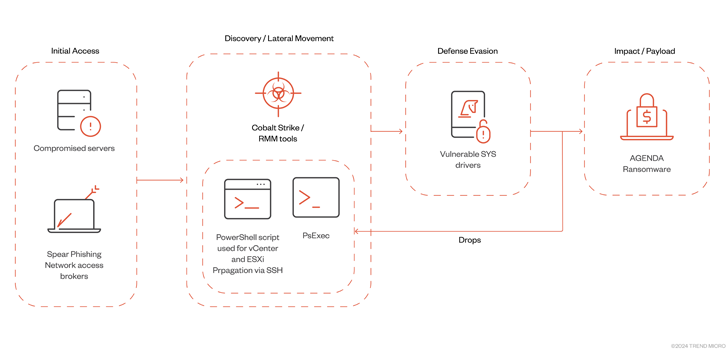
The event additionally follows the Agenda ransomware group’s (aka Qilin and Water Galura) use of an up to date Rust variant to contaminate VMWare vCenter and ESXi servers by way of Distant Monitoring and Administration (RMM) instruments and Cobalt Strike.
“The Agenda ransomware’s ability to spread to virtual machine infrastructure shows that its operators are also expanding to new targets and systems,” the cybersecurity firm mentioned.
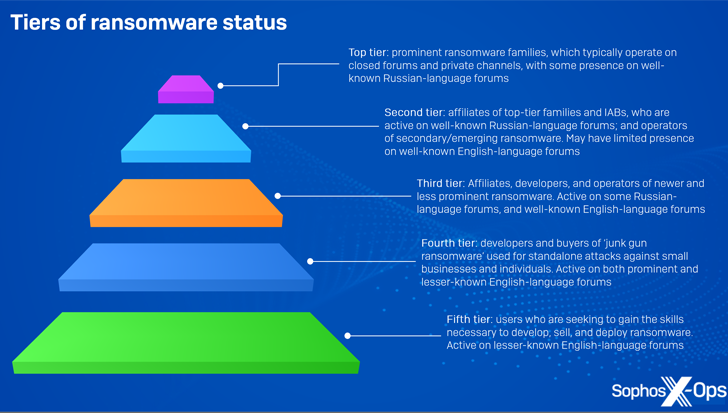
At the same time as a recent crop of ransomware actors continues to energise the risk panorama, it is also changing into clearer that “crude, cheap ransomware” offered on the cybercrime underground is being put to make use of in real-world assaults, permitting lower-tier particular person risk actors to generate important revenue with out having to be part of a well-organized group.
Apparently, a majority of those varieties can be found for a single, one-off value ranging from as little as $20 for a single construct, whereas a couple of others akin to HardShield and RansomTuga are supplied at no further value.
“Away from the complex infrastructure of modern ransomware, junk-gun ransomware allows criminals to get in on the action cheaply, easily, and independently,” Sophos mentioned, describing it as a “relatively new phenomenon” that additional lowers the price of entry.
“They can target small companies and individuals, who are unlikely to have the resources to defend themselves or respond effectively to incidents, without giving anyone else a cut.”