As Africa experiences quick financial progress, cybercrime seems to be retaining tempo.
In 2023, for instance, the typical variety of weekly cyberattacks impacting African companies grew 23% in comparison with the prior years, the quickest improve worldwide, in keeping with Interpol’s 2024 African Cyberthreat Evaluation, with ransomware and enterprise electronic mail compromise (BEC) topping the checklist of great threats. Digital illiteracy, ageing infrastructure, and a scarcity of safety professionals all current challenges to stopping financial loss attributable to cybercrime, in keeping with a report printed final month by Entry Partnership and the Centre for Human Rights on the College of Pretoria.
Because the continent’s gross home product (GDP) grows to an estimated $4 trillion by 2027, cyberattacks and cybercrime represent a big drag on financial growth, and African nations have to speed up their coaching of cybersecurity expertise, says Nicole Isaac, vice chairman of worldwide public coverage for expertise big Cisco.
“Africa faces the most significant impact from cyber threats compared to any other continent,” she says, including “nearly [all] financial leaders in Africa consider cybercrime a significant threat along with macroeconomic conditions and political and social instability.”
At present, Africa accounts for eleven of the world’s top-20 quickest rising economies, with Niger, Senegal, and Libya main the area’s robust economies with progress charges of no less than 7.9%, in keeping with the African Improvement Financial institution Group. South Africa, Nigeria, and Egypt are the three largest economies within the area, however none have signed the Malabo Conference, the cybercrime protocols put ahead by the African Union.
South Africa, for one, has seen cybercrime value the financial system round 2.2 billion Rand per yr (US $123 million), a lot of it made attainable by the overall lack of cyber-safety information, says Heinrich Bohlmann, affiliate professor within the Division of Economics on the College of Pretoria in South Africa.
Cybercrime is commonly the results of customers at house and at work being unaware of cyber dangers and scams, he says. “They too easily click or reply to things they shouldn’t, and in the workplace, this can, of course, have massive repercussions for businesses.”
A Instructing Second
The rising value of cybercrime ought to be thought of a possibility, particularly as Africa embarks on its digital transformation. Whereas many western and Asian populations are ageing quickly, Africa is seen as a supply of younger, tech-savvy staff sooner or later, who will likely be properly located to make use of new applied sciences, similar to AI for enterprise and to enhance cybersecurity.
African nations must advance rapidly and develop collaborative relationships simply as quick, says Caroline Parker, managing director in FTI Consulting’s South Africa monetary communications observe.
“It is essential that governments put the requisite guardrails in place by developing robust regulatory frameworks to enhance cybersecurity best practice,” she says. “This cannot be an isolated response from individual governments given how portable the problem is across borders, therefore, harmonization of standards and regulations is required on a regional basis.”
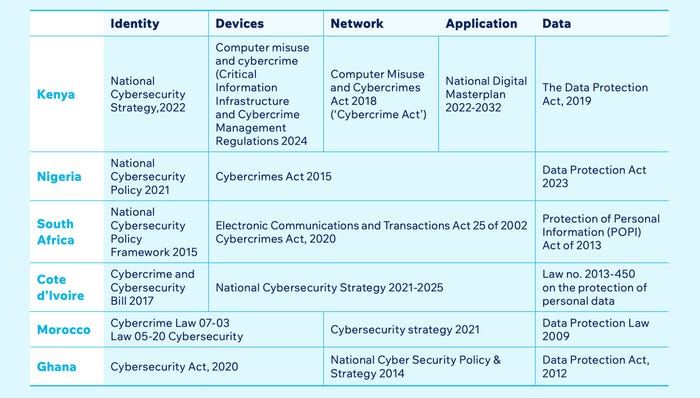
Cybersecurity coverage protections by a number of African nations. Supply: Elevating Africa’s Cyber Resilience report
AI may assist convey a number of adjustments to Africa, with the financial worth of AI in sub-Saharan Africa anticipated to create greater than US $130 billion in progress, in keeping with Entry Partnership and the College of Pretoria’s “Elevating Africa’s Cyber Resilience” report. AI has the potential to empower under-represented teams, offering them with the abilities and alternatives wanted to securely take part within the digital financial system, Cisco’s Isaac says.
“AI systems can significantly enhance human capabilities in threat detection and incident response through machine learning and deep learning techniques,” she says. “They can also simplify cybersecurity operations by automating routine tasks such as malware detection and vulnerability assessment.”
Want for Higher Cybercrime Information
The stories and estimates additionally underscore the necessity for higher information on the issue of cybercrime, as present estimates usually should not have supporting proof and look like overinflated. For instance, one information level within the “Elevating Africa’s Cyber Resilience” report posits that cybercrime will value African economies 10% of GDP. The UN Financial Fee of Africa cites the ten% determine as properly. Neither report has supporting information.
In actuality the price is probably going 30 occasions much less. Estimates of the price of cybercrime in Africa usually fluctuate between $4 billion and $10 billion per yr. With the present GDP of Africa estimated at $2.81 trillion by the Worldwide Financial Fund, the biggest value of cybercrime finally ends up round 0.3% of GDP.
The information actually has not been well-explored, says the College of Pretoria’s Bohlmann.
“For Africa as a whole, [the cost] could be anything,” he says. “However, the 10% of GDP equating to US $4.12 billion is clearly a typo or mistake.”