A brand new ‘FakeUpdate’ marketing campaign focusing on customers in France leverages compromised web sites to indicate faux browser and utility updates that unfold a brand new model of the WarmCookie backdoor.
FakeUpdate is a cyberattack technique utilized by a risk group referred to as ‘SocGolish’ who compromises or creates faux web sites to indicate guests faux replace prompts for quite a lot of functions, equivalent to internet browsers, Java, VMware Workstation, WebEx, and Proton VPN.
When customers click on on replace prompts designed to look reliable, a faux replace is downloaded that drops a malicious payload, like info-stealers, cryptocurrency drainers, RATs, and even ransomware.
The most recent marketing campaign was found by researchers at Gen Menace Labs, who noticed the WarmCookie backdoor being distributed as faux Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, and Java updates.
WarmCookie, first found by eSentire in mid-2023, is a Home windows backdoor not too long ago seen distributed in phishing campaigns utilizing faux job gives as lures.
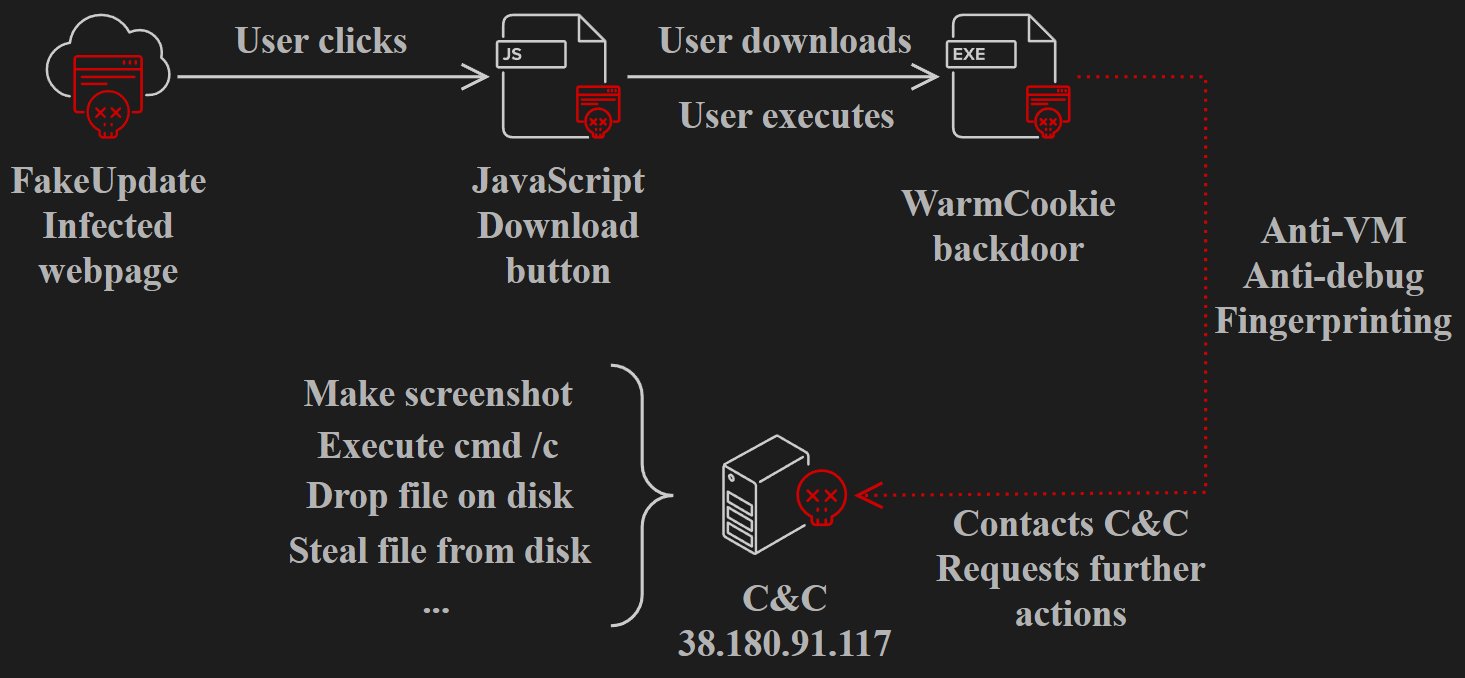
Its broad capabilities embrace information and file theft, system profiling, program enumeration (through the Home windows Registry), arbitrary command execution (through CMD), screenshot capturing, and the flexibility to introduce further payloads on the contaminated system.
Within the newest marketing campaign noticed by Gen Menace Labs, the WarmCookie backdoor has been up to date with new options, together with operating DLLs from the temp folder and sending again the output, in addition to the flexibility to switch and execute EXE and PowerShell recordsdata.
The lure used to set off the an infection is a faux browser replace, which is frequent for FakeUpdate assaults. Nonetheless, Gen Digital additionally discovered a web site the place a faux Java replace was promoted on this marketing campaign.

Supply: BleepingComputer
The an infection chain begins with the consumer clicking on a faux browser replace discover, which triggers JavaScript that fetches the WarmCookie installer and prompts the consumer to avoid wasting the file.
Supply: Gen Menace Labs
When the faux software program replace is executed, the malware performs some anti-VM checks to make sure it isn’t operating on an analyst’s surroundings and sends the newly contaminated system’s fingerprint to the command and management (C2) server, awaiting directions.
Though Gen Menace Labs says the attackers use compromised web sites on this marketing campaign, a number of the domains shared within the IoC part, like “edgeupdate[.]com” and “mozilaupgrade[.]com,” appear particularly chosen to match the ‘FakeUpdate’ theme.
Bear in mind, Chrome, Courageous, Edge, Firefox, and all trendy browsers are mechanically up to date when new updates turn out to be obtainable.
A program restart could also be wanted for an replace to be utilized to the browser, however manually downloading and executing updater packages is rarely part of an precise replace course of and needs to be seen as an indication of hazard.
In lots of circumstances, FakeUpdates compromise reliable and in any other case reliable web sites, so these pop-ups needs to be handled with warning even whenever you’re on a well-recognized platform.
