One other international chip scarcity could possibly be looming, with a brand new report predicting skyrocketing demand for AI-related services and products that suppliers might battle to satisfy.
AI workloads may develop by between 25% and 35% yearly as much as 2027, based on consultancy Bain and Firm. Nevertheless, a requirement enhance of simply 20% has a excessive chance of upsetting the equilibrium and plunging the world into one other chip scarcity.
“The AI explosion across the confluence of the large end markets could easily surpass that threshold, creating vulnerable chokepoints throughout the supply chain,” the authors of the World Know-how Report 2024 wrote.
Our starvation for AI may even necessitate the constructing of bigger information centres with over a gigawatt of capability. Present information centres are typically between 50 and 200 megawatts.
Combining the demand for AI infrastructure and AI-enabled merchandise, the marketplace for AI software program and {hardware} is predicted to develop between 40% and 55% yearly over the following three years.
If giant information centres at the moment value between $1 billion and $4 billion, in 5 years they may attain between $10 billion and $25 billion, the report states. This leads to a complete AI market prediction of between $780 billion and $990 billion (£584 billion and £741 billion) for 2027.
SEE: Gartner Predicts Worldwide AI Chip Income Will Achieve 33% in 2024
The provision spider’s internet, and the strain it’s beneath
To maintain this rising demand, the availability chain for AI parts should be capable to scale up on the similar tempo. However, in actuality, the chain is extra like a posh spider’s internet, with the chip uncooked supplies on the centre.
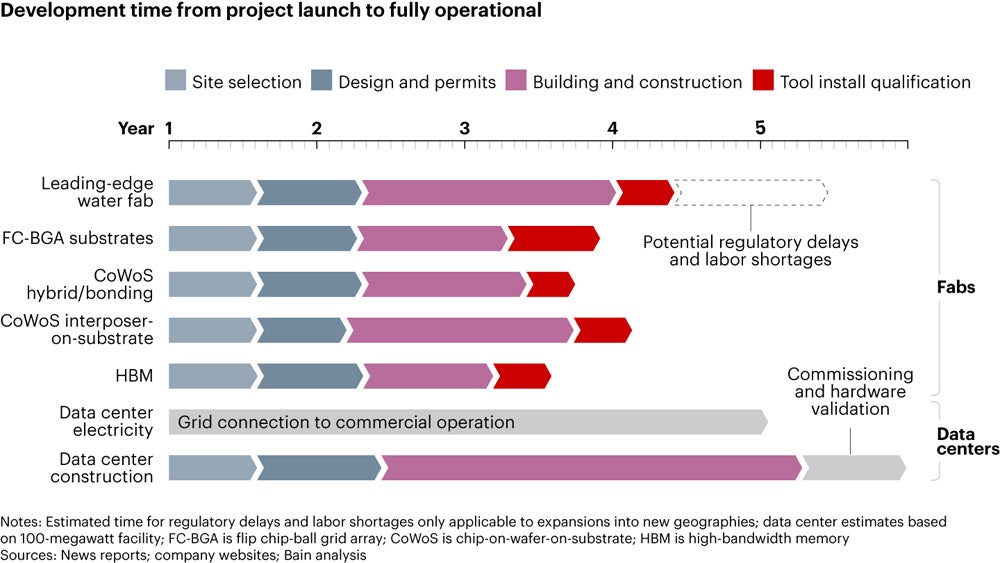
In a single path are the fabs and infrastructure required to scale up chip manufacturing, and one other is the information centres wanted for the AI merchandise to perform. Every has a lead time of between three-and-a-half years to over 5 years, based on Bain, posing a big blocker for maintaining with demand.
Bleeding-edge fabs that manufacture probably the most superior chips are probably the most weak hyperlink, based on the report. They might want to elevate their output by between 25% and 35% between 2023 and 2026 to maintain up with the expected 31% and 15% gross sales progress in PCs and smartphones respectively.
As much as 5 extra bleeding-edge fabs would should be constructed to maintain up, costing an estimated $40 billion to $75 billion.
There’s additionally the availability chain concerned in turning chips into smartphones and PCs with on-device AI performance, comparable to Apple Intelligence gadgets, that are rising in reputation as customers have a better need for information safety.
SEE: Gartner: AI-enabled PCs to Dominate Laptop computer Choices for Companies
Certainly, the silicon floor space within the common pocket book core processing unit and smartphone processor have already elevated by 5% and 16%, respectively, to accommodate for the on-device neural processing engines. Bain predicts these merchandise may enhance the demand for upstream parts by 30% or extra by 2026.
Packaging is one other arm of the net, and if GPU demand doubles by 2026, suppliers would wish to triple their manufacturing capability. Plus, numerous energy and cooling necessities hyperlink each a part of the method to utility corporations, which may even have to scale to demand.
The final international chip scarcity
Because the inception of the present generative AI growth, chipmakers have thrived. Main graphics processing unit vendor NVIDIA introduced report revenues of $30 billion (£24.7 billion) within the second quarter of 2024, and has a inventory market worth of over $3 trillion (£2.2 trillion). Swap producer Broadcom and reminiscence chip maker SK Hynix have seen related success.
These report earnings have been realised by solely a handful of core corporations that management giant parts of the availability chain. NVIDIA, an American firm, designs nearly all of GPUs which can be used to coach AI fashions. Nevertheless, they’re manufactured by Taiwan’s TSMC. TSMC and Samsung Electronics are additionally the one two corporations that may take advantage of cutting-edge chips on a big scale.
Nevertheless it has not all the time been plain crusing inside the {industry}. A world chip scarcity was sparked in early 2020 as a result of COVID-19 pandemic. Provide points amongst this comparatively small variety of corporations continued for over three years, impacting industries comparable to shopper electronics and AI.
Even previous to the pandemic, the semiconductor provide chain was on shaky floor because of a sequence of occasions, together with commerce wars between the U.S. and China, and Japan and Korea, impacting commodity pricing and distribution. As well as, pure disasters, comparable to a drought in Taiwan and three plant fires in Japan between 2019 and 2021, contributed to uncooked materials shortages.
“Extreme weather, natural disasters, geopolitical strife, a pandemic, and other major disruptions over the past decade have made abundantly clear how supply shocks can severely limit the industry’s ability to meet demand,” the Bain and Firm report states.
Want for AI sovereignty may exacerbate chip scarcity
It’s not only a lack of producing capability that would result in a second international chip scarcity.
“Geopolitical tensions, trade restrictions, and multinational tech companies’ decoupling of their supply chains from China continue to pose serious risks to semiconductor supply. Delays in factory construction, materials shortages, and other unpredictable factors could also create pinch points,” the report states.
The U.S., for instance, has utilized chip-related export controls on the sale of semiconductors to China, in addition to the Netherlands and Japan. The U.Ok. additionally blocked nearly all of license functions for corporations searching for to export semiconductor expertise to China in 2023.
China’s Ministry of Commerce additionally introduced it could implement export controls on gallium and germanium-related objects “to safeguard national security and interests.” These uncommon metals are important in chip manufacturing, and China produces 98% and 54% of the world’s provide of gallium and of germanium respectively.
Governments worldwide are additionally spending billions of {dollars} to spice up their very own capability for semiconductor manufacturing, with a main purpose being to scale back their reliance on different international locations. Nevertheless, information safety additionally performs an element; by protecting the availability chain inside their borders, authorities can higher shield in opposition to espionage and cyber assaults.
In 2022, the U.S. handed the CHIPS Act, to supply wanted semiconductor analysis investments and manufacturing incentives in addition to reinforce America’s financial system, nationwide safety, and provide chains. The White Home has additionally launched a blueprint for an AI Invoice of Rights to assist regulate AI domestically and invested within the proof-of-concept for shared nationwide AI analysis infrastructure.
Intel, TSMC, Texas Devices, and Samsung — the world’s largest reminiscence chipmaker — have all introduced plans to construct fabs within the U.S.
In August 2023, it was introduced that the U.Ok. authorities will commit £100 million ($126 million) to fostering AI {hardware} growth and shoring up potential pc chip shortages. Simply this month, Amazon Internet Companies introduced plans to take a position £8 billion on information centres within the nation over the following 5 years.
SEE: UK Authorities Declares £32m for AI Tasks After Scrapping Funding for Supercomputers
The European Union supplied €43 billion ($46 billion) in subsidies to spice up its semiconductor sector with its European Chips Act, which was adopted in July 2023. The bloc additionally has the lofty purpose of manufacturing 20% of the world’s semiconductors by 2030,
However Anne Hoecker, head of Bain’s World Know-how apply, mentioned that the quests for information sovereignty shall be “time-consuming and incredibly expensive.”
She mentioned in a press launch: “While less complex in some ways than building semiconductor fabs, these projects require more than securing local subsidies. Hyperscalers and other big tech firms may continue to invest in localized AI operations that will ensure significant competitive advantages.”
The Bain report provides that small language fashions with algorithms that use RAG, or retrieval-augmented technology, and vector embeddings, may stand to profit from information sovereignty, as they deal with loads of the computing, networking, and storage duties near the place AI information is saved.
Steering for executives within the AI provide chain for withstanding a chip scarcity
The Bain report outlines some suggestions for corporations that utilise semiconductors on surviving one other international chip scarcity:
- Forge a deep understanding of and monitor all the AI provide chain, together with information centre parts, PCs and smartphones, and peripheral gadgets like routers and community tools.
- Signal long-term buy agreements to safe entry to chips by potential disruption.
- Design merchandise to make use of industry-standard semiconductors as a substitute of application-specific chips to maximise compatibility with totally different suppliers and adaptability in sourcing.
- Strengthen the availability chain in opposition to geopolitical uncertainties comparable to tariffs or laws by diversifying suppliers and sourcing parts from a number of areas.
The report’s authors wrote: “Executives should really feel weary from the semiconductor provide disruptions spurred by the pandemic, however there’s no time to relaxation as a result of the following huge provide shock looms. This time, nevertheless, the indicators are clear, and the {industry} has an opportunity to arrange.
“The path forward demands vigilance, strategic foresight, and swift action to reinforce supply chains. With proactive measures, business leaders can ensure their resilience and success in an increasingly AI-enabled world.”