The Workplace of the Australian Info Commissioner’s newest Notifiable Information Breaches Report revealed a speedy rise nationwide in notifiable information breaches within the first six months of 2024 — a 9% improve compared with the ultimate six months of 2023 and the best variety of notifications since 2020.
The report, launched in September, confirmed that latest information breaches, together with the seashore of medical prescription service MediSecure affecting 12.9 million Australians, have prompted a robust response from the OAIC. The company warned that it’s adopting a harder stance on information privateness and breaches, emphasising that organisations should prioritise privateness of their information practices.
Which industries skilled essentially the most information breaches?
The OAIC has revealed statistical info on information breach notifications because the launch of the Notifiable Information Breaches scheme in Australia in 2018. The most recent report revealed:
- A complete of 527 notifications occurred from January to June 2024, marking a 9% improve compared with the 485 notifications acquired from July to December 2023.
- The newest six-month interval noticed the best variety of notifications acquired since July to December 2020, throughout the depths of the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic.
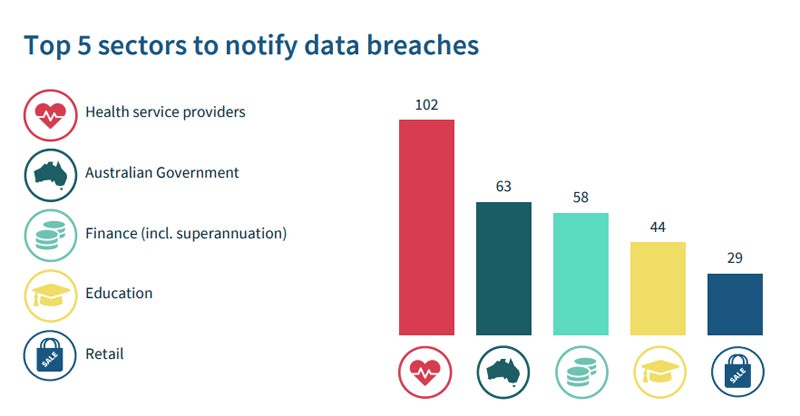
- The highest 5 sectors struggling information breaches have been well being service suppliers (102 breaches), the Australian Authorities (63), finance (58), training (44), and retail (29).
- Malicious or legal assaults, each exterior and inside, have been the supply of 67% of all information breaches, adopted by human error (30%) and glitches (3%).
- Malicious or legal assaults included cyber incidents (57%), social engineering/impersonation (27%), theft of paperwork or information storage (8%), and rogue worker/insider threats (8%).
- Most breaches reported (63%) concerned 100 folks or fewer, however there have been eight large-scale breaches impacting over 100,000 folks, together with Australia’s “largest ever” MediSecure breach.
SEE: Australian organisations experiencing highest fee of knowledge breaches
Cyber incidents dominate malicious and legal assaults in Australia
Cyber incidents proceed to be a prevalent trigger of knowledge breaches, representing 38% of whole breaches. Cyber incidents have been outlined as these together with phishing, ransomware, compromised or stolen credentials (methodology unknown), brute-force assaults, hacking, and malware — however not social engineering-style assaults.
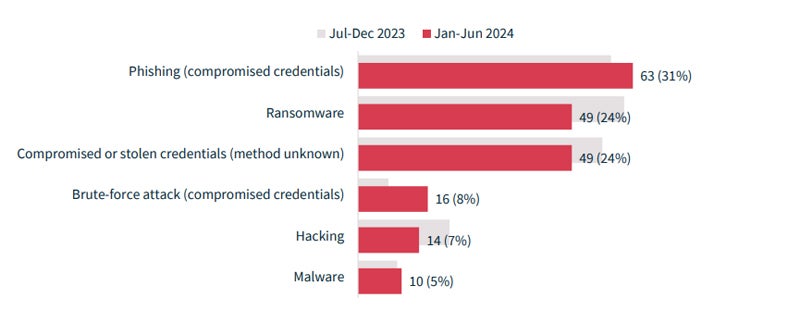
Among the many varied malicious or legal assaults, cyber incidents had the best influence on people. The typical of 107,123 people have been affected by the 201 cyber incidents, whereas a mean of 4,709 people have been impacted by incidents brought on by rogue staff or insider threats.
Within the report, Australian Privateness Commissioner Carly Type mentioned that the continued prevalence of cyber incidents within the information breach totals reported to the OAIC got here “as our increasing reliance on digital tools and online services exposes our details more frequently to malicious cyber actors.”
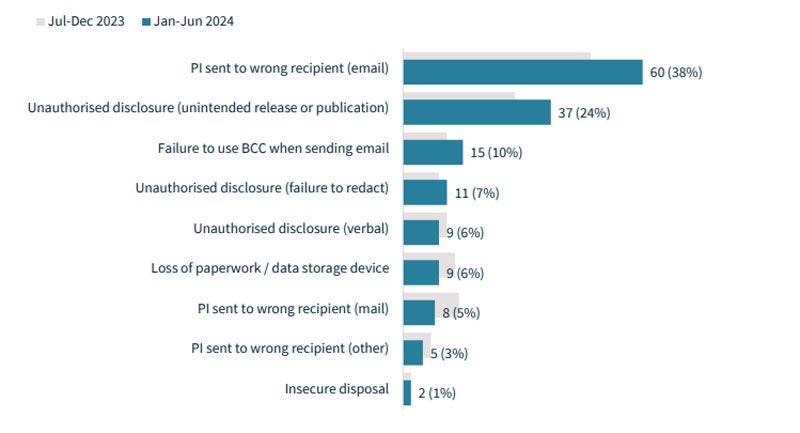
Nevertheless, human error nonetheless accounts for 30% of notifiable information breaches. The highest classes of human error have been:
- Personally identifiable info despatched to the flawed e mail recipient (38%).
- Unauthorised disclosure of knowledge, or unintended launch or publication (24%).
- Failure to make use of the Bcc (Blind copy) choice when sending e mail (10%).
Spike in information breaches places Australian Authorities companies in highlight
The OAIC famous that the Australian Authorities reported the second highest variety of information breaches of all sectors, its highest place ever, although it has beforehand featured within the prime 5 breached sectors. In line with the report:
- Authorities companies reported 63 information breaches from January to June 2024, accounting for 12% of all information breach notifications in Australia.
- The Authorities accounted for the best variety of social engineering or impersonation-style information breaches, making up 42% of such incidents. In line with the OAIC, these breaches usually concerned a menace actor impersonating a buyer to achieve entry to an account utilizing respectable credentials.
- The Authorities can be slower to behave: it had the most important proportion (87%) of notifications the place the company recognized the incident over 30 days after it occurred, whereas 78% of Authorities notifications have been made greater than 30 days after the company grew to become conscious of the incident.
SEE: Is Australia’s public sector prepared for a serious cyber safety incident?
How can organisations cease information breaches?
Safety specialists frequently remind organisations that many information breaches or cyber assaults might be prevented by implementing primary cyber safety measures. The OAIC offered a number of suggestions based mostly on developments in information breach information.
Mitigating cyber threats
The OAIC really helpful implementing multi-factor authentication as a primary precedence to cease cyber threats, or robust password administration insurance policies and practices if MFA is unavailable. The company additionally really helpful:
- Implementing layer safety controls to keep away from a single level of failure.
- Implementing ranges of entry to info based mostly on roles and obligations.
- Leveraging safety monitoring to detect, reply to, and report incidents or uncommon exercise.
The OAIC pointed to frameworks together with Australia’s Important Eight, the Australian Alerts Directorate’s Info Safety Guide, the U.S.-based Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Know-how’s Cyber Security Framework, in addition to the Worldwide Organisation for Standardisation’s ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 info safety administration requirements as measures to information enchancment in practices.
Prolonged provide chain dangers
In line with the OAIC, some large-scale information breaches are being brought on by provide chain compromises, such because the breach impacting MediSecure and one other incident involving Outabox. The company added that outsourcing the dealing with of private info to 3rd events stays a prevalent danger.
The company mentioned firms ought to take into account the dangers of outsourcing the dealing with of private info on the earliest stage of procurement, together with to cloud suppliers. It additionally really helpful that organisations put in place a strong provider risk-management framework, alongside extra strong safety measures.
Addressing the human issue
The OAIC emaphsised that people stay a major menace to the energy of privateness practices. These threats embody breaches as a consequence of human error or staff being tricked by phishing.
The company urged organisations to implement technical measures to cut back errors and emphasised that educating workers is crucial to make sure they perceive their privateness and safety obligations. It additionally really helpful prioritising coaching workers in safe info dealing with practices.
Misconfiguration of cloud-based information holdings
Some organisations are “overlooking” cloud safety as they digitally rework, the OAIC mentioned. Numerous information breaches throughout the quarter occurred when an Australian entity misconfigured safety settings as a consequence of human error, leaving private info weak to unauthorised entry or public disclosure.
The OAIC mentioned organisations shouldn’t assume cloud safety accountability lies with the supplier. The company identified that cloud safety and administration must be a precedence, highlighting the significance of measures corresponding to safe entry controls via MFA, IP entry controls, and encryption.