Over 1,000 misconfigured ServiceNow enterprise situations have been discovered exposing Data Base (KB) articles that contained delicate company info to exterior customers and potential risk actors.
The uncovered info contains personally identifiable info (PII), inner system particulars, consumer credentials, entry tokens for reside manufacturing programs, and different important info relying on the Data Base subject.
Aaron Costello, chief of SaaS safety analysis at AppOmni, discovered over a thousand ServiceNow on-line situations which are unintentionally exposing firm info as a result of configuration points.
That is nonetheless a big downside regardless of ServiceNow’s updates in 2023 explicitly aimed toward enhancing Entry Management Lists (ACLs), however which did not apply to KBs.
Uncovered KB articles
ServiceNow is a cloud-based software program platform organizations use to handle digital workflows throughout varied departments and processes.
It’s a full resolution that comes with IT service and IT operations administration, HR duties, customer support administration, safety instruments integration, and a information base.
The information base characteristic acts as a repository of articles the place organizations can share how-to guides, FAQs, and different inner procedures for customers approved to view them. Nonetheless, as many of those articles will not be meant to be seen publicly, they will comprise delicate details about a company.
After a 2023 report by Costello on ServiceNow information publicity, the corporate rolled out a safety replace that launched new ACLs to forestall unauthenticated entry to buyer information. Nonetheless, AppOmni says that almost all ServiceNow KBs make the most of the Person Standards permission system moderately than ACLs, making the replace much less helpful.
Moreover, some public-facing widgets that expose buyer info didn’t obtain the 2023 ACL replace and proceed to permit unauthenticated entry.
Resulting from this, Costello says that misconfigured entry controls on public-facing ServiceNow widgets can nonetheless be used to question information in KBs with out requiring any authentication.
“These instances were considered by the affected organizations to be sensitive in nature, such as PII, internal system details, and active credentials / tokens to live production systems,” AppOmni says in a new report revealed as we speak.
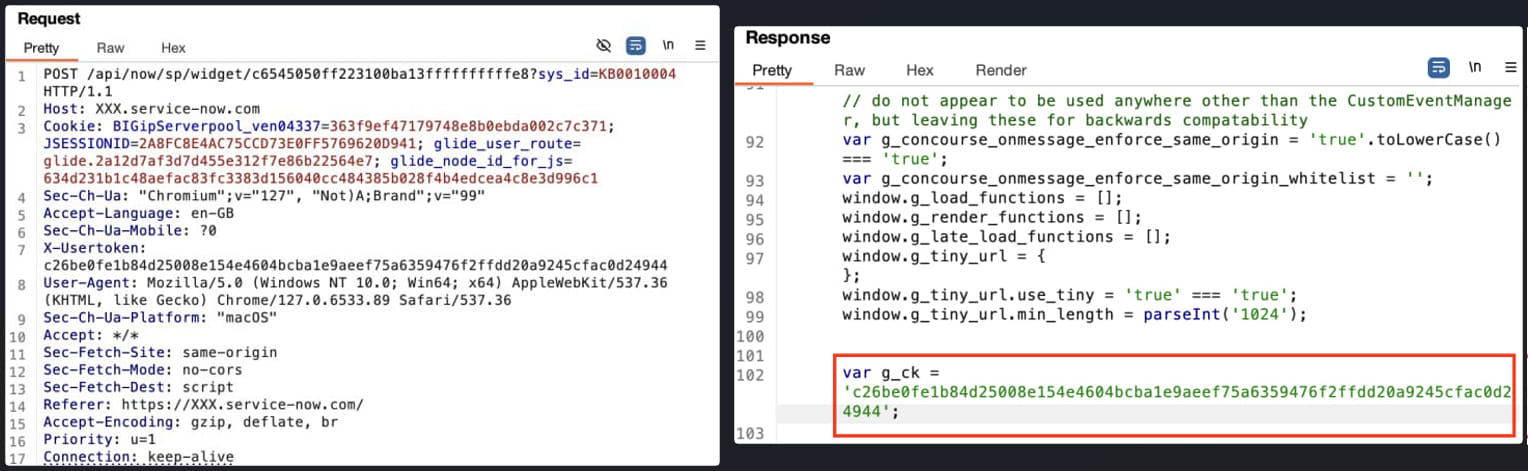
Utilizing instruments like Burp Suite, a malicious actor can ship numerous HTTP requests to a weak endpoint to brute-force the KB article quantity.
The researchers clarify that Data Base article IDs are incremental within the format KBXXXXXXX, so a risk actor can brute drive a ServiceNow occasion by incrementing the KB quantity beginning at KB0000001 till they discover one that’s unintentionally uncovered.
AppOmni developed a proof-of-concept assault as an instance how an exterior actor can entry a ServiceNow occasion with out authentication, seize a token to be used in HTTP requests, question the general public widget to retrieve KB articles, and brute-force the IDs of all hosted articles.
Supply: AppOmni
Blocking unauthorized entry
AppOmni means that SecureNow admins defend KB articles by setting the suitable ‘Person Standards’ (Can Learn/Can not Learn), blocking all unauthorized customers.
Standards like “Any User” or “Guest User” result in configurations that do not defend the articles from arbitrary exterior entry.
If public entry to Data Bases is not explicitly wanted, directors ought to flip it off to forestall articles from being accessible on the web.
The researchers additionally spotlight particular safety properties that may guard information from unauthorized entry, even within the case of misconfigurations. These are:
- glide.knowman.block_access_with_no_user_criteria (True): Ensures that entry is robotically denied to authenticated and unauthenticated customers if no Person Standards are set for a KB article.
- glide.knowman.apply_article_read_criteria (True): Requires customers to have express “Can Read” entry to particular person articles, even when they’ve “Can Contribute” entry to the whole KB.
- glide.knowman.show_unpublished (False): Prevents customers from seeing draft or unpublished articles, which can comprise delicate, unreviewed info.
- glide.knowman.part.view_roles.draft (Admin): Defines a listing of roles that may view KB articles in a draft state.
- glide.knowman.part.view_roles.overview (Admin): Defines a listing of roles that may view KB articles in a overview state.
- glide.knowman.part.view_roles.stagesAndRoles (Admin): Defines a listing of roles that may view KB articles which are in a customized state.
Lastly, it is suggested to activate ServiceNow’s pre-built out-of-the-box (OOB) guidelines that robotically add Visitor Customers to the “Cannot Read” record for newly created KBs, requiring admins to particularly give them entry when wanted.
