Think about enjoying the traditional first-person shooter DOOM, however with a twist: the sport isn’t working on code written by programmers.
As a substitute, it’s being generated in real-time by an AI system. This successfully describes GameNGen, a breakthrough AI mannequin not too long ago unveiled by Google and Tel Aviv College researchers.
GameNGen can simulate DOOM at over 20 frames per second utilizing a single Tensor Processing Unit (TPU).
Inside this TPU, we’re witnessing the delivery of video games that may primarily suppose and create themselves.
In different phrases, as an alternative of human programmers defining each side of a recreation’s conduct, an AI system learns to generate your complete recreation expertise on the fly.
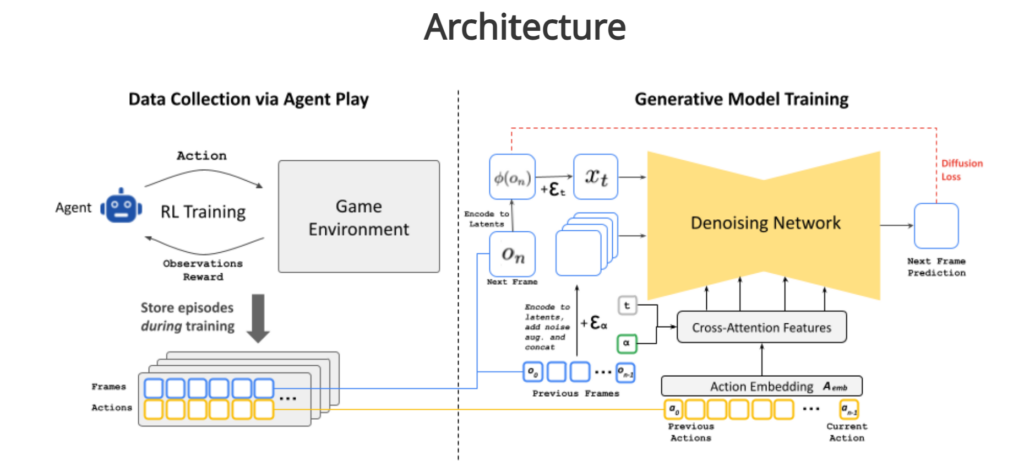
At its core, GameNGen makes use of a kind of AI referred to as a diffusion mannequin, just like these utilized in picture era instruments like DALL-E or Steady Diffusion. Nonetheless, the researchers have tailored this expertise for real-time recreation simulation.
The system is skilled in two phases. First, a reinforcement studying (RL) agent – one other kind of AI – is taught to play DOOM. As this AI agent performs, its gameplay classes are recorded, creating a big dataset of recreation states, actions, and outcomes.
Within the second section, this dataset is used to coach GameNGen itself. The mannequin learns to foretell the sport’s subsequent body based mostly on the earlier frames and the participant’s actions.
Consider it like educating the AI to think about how the sport world would reply to every participant’s transfer.
One of many greatest challenges is sustaining consistency over time. Because the AI generates body after body, small errors can accumulate, probably resulting in weird or unimaginable recreation states.
To fight this, the researchers carried out a intelligent “noise augmentation” method throughout coaching. They deliberately added various ranges of random noise to the coaching information, educating the mannequin methods to appropriate and eradicate this noise.
This helps GameNGen keep visible high quality and logical consistency even over lengthy play classes.
Whereas GameNGen is at present centered on simulating an current recreation, its underlying structure hints at much more thrilling prospects.
In concept, comparable programs may generate fully new recreation environments and mechanics on the fly, resulting in video games that adapt and evolve in response to participant actions in ways in which go far past present procedural era methods.
The trail to AI-driven recreation engines
GameNGen isn’t rising in isolation. It’s the newest in a sequence of developments bringing us nearer to a world the place AI doesn’t simply help in recreation growth – it turns into the event course of itself. For instance:
- World Fashions, launched in 2018, demonstrated how an AI may be taught to play video video games by constructing an inner mannequin of the sport world.
- AlphaStar, from 2019. is an AI developed by DeepMind particularly for taking part in the real-time technique recreation StarCraft II. AlphaStar makes use of reinforcement studying and complicated neural networks to grasp the sport, attaining glorious proficiency and competing towards high human gamers.
- GameGAN, developed by Nvidia in 2020, confirmed how generative adversarial networks may recreate easy video games like Pac-Man with out entry to the underlying engine.
- DeepMind’s Genie, unveiled earlier this 12 months, takes issues a step additional by producing playable recreation environments from video clips.
- DeepMind’s SIMA, additionally launched this 12 months, is a sophisticated AI agent designed to know and act on human directions throughout numerous 3D environments. Utilizing pre-trained imaginative and prescient and video prediction fashions, SIMA can navigate, work together, and carry out duties in numerous video games with out entry to their supply codes.
There are additionally quite a few initiatives that use AI to create or increase in-game options, from producing extremely real looking dialogue to personalizing NPC interactions to character arcs, in-game environments, and different variables.
All of it factors in direction of a tantalizing future wherein worlds can develop and reply to participant actions with realism and depth.
Some view that recreation builders could possibly be free of the drudgery of guide asset creation and in a position to give attention to high-level design and storytelling inside these new frameworks.
For instance, Marcus Holmström, CEO of recreation growth studio The Gang, defined to MIT, “Instead of sitting and doing it by hand, now you can test different approaches,” highlighting the expertise’s capability for speedy prototyping and iteration.
Holmström continued, “For example, if you’re going to build a mountain, you can do different types of mountains, and on the fly, you can change it. Then we would tweak it and fix it manually so it fits. It’s going to save a lot of time.”
Some within the business echo this optimism, seeing AI as a software to reinforce human creativity somewhat than exchange it.
Borislav Slavov, a BAFTA-winning composer identified for his work on Baldur’s Gate 3, believes AI may push composers out of their consolation zones and permit them to “focus way more on the essence – getting inspired and composing deeply emotional and strong themes.”
However for each voice heralding the advantages of AI-driven recreation design, there’s one other sounding a notice of warning.
Jess Hyland, a veteran recreation artist and member of the Impartial Employees Union of Nice Britain’s recreation staff department, instructed the BBC, “I’m very aware that I could wake up tomorrow and my job could be gone.”
The US SAG-AFTRA union, which launched the landmark Hollywood strike towards manufacturing studios final 12 months, not too long ago initiated one other strike over online game rights. Whereas it doesn’t strictly have an effect on builders, the strike contains the proper to knowledgeable consent for the AI use of online game actors’ faces, voices, and our bodies and truthful compensation for any such makes use of.
For a lot of within the business, it’s not simply the concern of job displacement. It’s in regards to the elementary nature of creativity in recreation growth.
“It’s not why I got into making games,” Hyland provides, expressing concern that artists could possibly be decreased to mere editors of AI-generated content material. “The stuff that AI generates, you become the person whose job is fixing it.”
The clone wars vs user-generated gaming
Whereas AAA studios would possibly see AI as a software for pushing the boundaries of what’s attainable, the image may look very totally different for indie builders.
Whereas AI recreation growth may decrease boundaries to entry, permitting extra individuals to carry their concepts to life, it additionally dangers flooding the market with AI-generated content material, making it more durable for actually unique works to face out.
As an example, Chris Knowles, a former senior engine developer at UK gaming agency Jagex, warns that AI has the potential to exacerbate points with recreation cloning, significantly within the cell market.
“Anything that makes the clone studios’ business model even cheaper and quicker makes the difficult task of running a financially sustainable indie studio even harder,” Knowles cautions.
The query is, how do you actually steadiness AI’s dangers to the business with the potential upsides for avid gamers, and gaming as a complete ecosystem?
Can we actually cease AI from revolutionizing an business that prides itself on pushing technological boundaries? In spite of everything, gaming is an business that has actually relied on expertise to progress.
Earlier within the 12 months, we spoke to Chris Benjaminsen, co-founder at AI recreation startup FRVR, who defined to us:
“I don’t think the world has had truly user-generated games yet. We’ve had user-generated games platforms where people were generating UGC, but it’s always been limited with some of the capabilities that whatever platform supported, right? If you have a platform with a bunch of templates for puzzle games, you get a bunch of puzzle games, but you can’t create unique games on any platform that just supports templates. I think that AI can change everything.”
He argued that this enables individuals to drive recreation creation from the bottom up. It acts as an antidote to large-scale builders who choose initiatives based mostly on their monetary returns.
“Rather than having very few people decide what games people should be allowed to play, we want to allow anyone to create whatever they want and then let the users figure out what is fun. I don’t believe most of the games industry knows what people want. They just care about what they can make the most money on.”
It’s a pertinent level. Amidst all of the business disruption, we will’t lose sight of an important stakeholder: the gamers.
Think about RPGs the place each playthrough is actually distinctive, or technique video games with AI opponents who adapt in methods no human designer may predict.
This, mixed with granting individuals the ability of alternative over their gaming experiences, may usher in a brand new period ruled by gamers themselves.
Sure, builders will get squeezed like many others throughout the artistic industries, however adaption in fast-moving technical disciplines has all the time been crucial. It’s by no means superb for individuals to lose their jobs, nevertheless it’s a lot worse in the event that they lose their jobs to the detriment of the business they dedicated their time to.
AI’s position in gaming appears extra more likely to result in healthful outcomes than in visible arts or movie & TV. Recreation builders could discover it simpler to adapt to and work alongside AI instruments somewhat than being changed by them. This contrasts with fields like music, the place AI can generate merchandise straight competing with human artists.
The technical complexity of recreation growth may allow a extra complementary relationship between AI and human creativity than a purely aggressive one. Maybe that’s a naive or overly optimistic stance to take.
Ultimately, AI’s impacts on recreation growth will probably be debated for years to return. Like several highly effective software, its affect will depend upon a wide range of stakeholders, from the gamers to the studios.
Will these stakeholders collectively leverage AI to push the boundaries of interactive leisure?
Or will we enable it to homogenize recreation growth, sacrificing the distinctive visions of human creators on the altar of effectivity?
The reply, like the way forward for gaming itself, and certainly that of many different artistic industries, is but to be written. However one factor is for certain: the controller is in our arms proper now.
How we play this subsequent stage will decide the course of the sport business for generations to return.